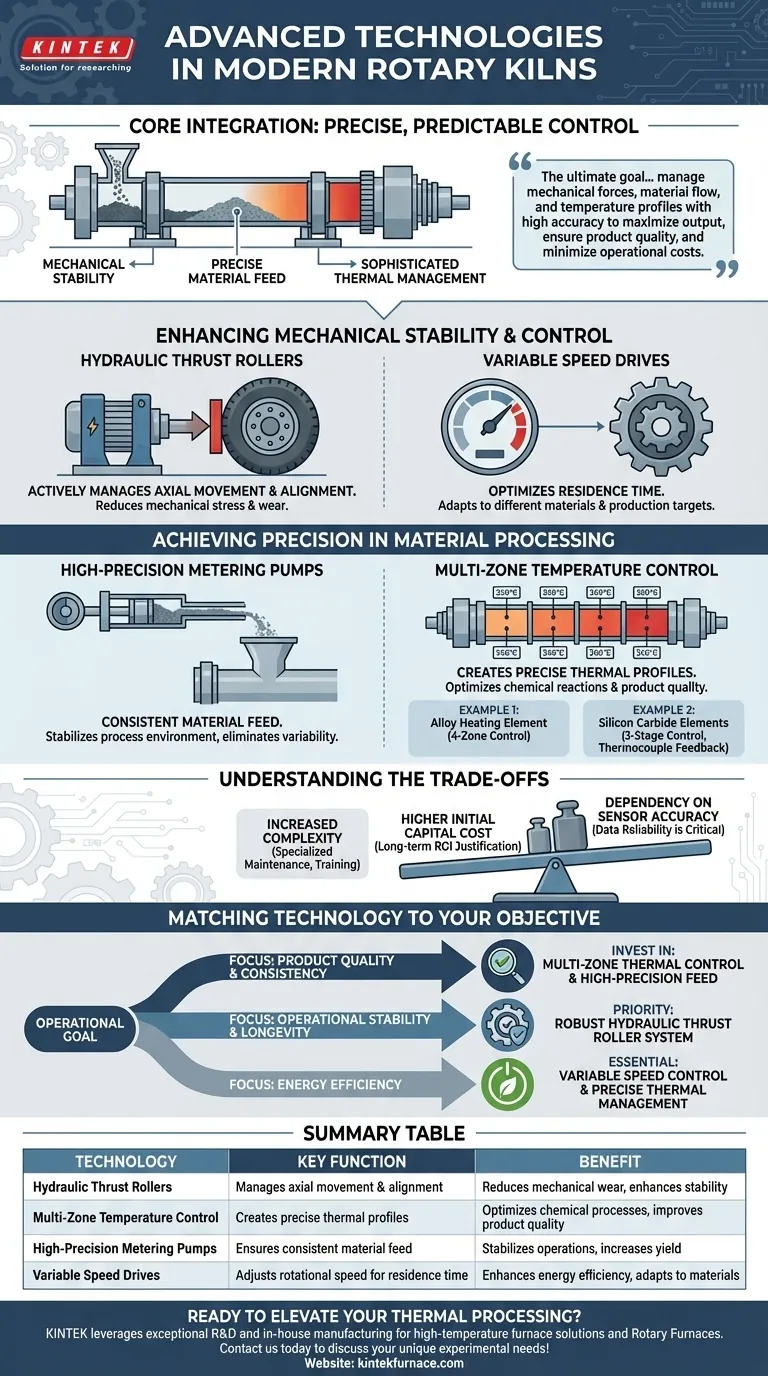
At their core, modern rotary kilns integrate advanced technologies focused on mechanical stability, precise material feed, and sophisticated thermal management. Key systems include hydraulic thrust rollers for alignment, high-precision metering pumps for consistent feed rates, and multi-zone temperature control systems to optimize the chemical process. These advancements work together to improve stability, increase yield, and lower energy consumption.
The ultimate goal of advanced kiln technology is to achieve a state of precise, predictable control. By managing mechanical forces, material flow, and temperature profiles with high accuracy, operators can maximize output, ensure product quality, and minimize the operational costs of these energy-intensive assets.

Enhancing Mechanical Stability and Control
A rotary kiln is a massive, dynamic piece of equipment. Maintaining its stability during operation is fundamental to its performance and longevity. Advanced technologies directly address the immense physical forces at play.
The Role of Hydraulic Thrust Rollers
Older kilns often suffer from uncontrolled axial movement, causing excessive wear on the main gear and support components.
Modern kilns use hydraulic block wheel devices, also known as hydraulic thrust rollers. These systems actively manage the kiln's slight downhill creep, preventing the tires from making hard contact with their retaining blocks. This ensures smooth rotation and dramatically reduces mechanical stress and wear.
Optimizing Rotational Speed
The time a material spends inside the kiln, known as residence time, is a critical process variable.
Advanced kilns incorporate variable speed drives governed by high-precision speed control valves. This allows operators to finely tune the kiln's rotational speed, adapting the residence time to different raw materials or production targets for optimal processing.
Achieving Precision in Material Processing
The quality of the final product, whether cement clinker or calcined minerals, depends entirely on consistency. This requires precise control over both what goes into the kiln and the thermal environment inside it.
High-Precision Material Feed
Inconsistent material feed is a primary cause of temperature fluctuations and poor product quality.
To solve this, modern systems utilize high-precision metering piston pumps. These devices deliver a steady, predictable volume of slurry or granular solids into the kiln, creating a stable process environment and eliminating a major source of operational variability.
Sophisticated Thermal Management
A rotary kiln isn't just one hot tube; it's a carefully engineered thermal reactor with distinct temperature zones required for different chemical reactions.
The most significant advancement is multi-zone temperature control. By dividing the kiln into separately controlled heating zones, operators can create a precise temperature profile along the length of the kiln.
Examples of Multi-Zone Control
Different kiln designs achieve this in different ways. For instance, an electrically heated kiln with an alloy heating element may have four separately controllable temperature zones.
A kiln using silicon carbide heating elements might employ a three-stage temperature control system. This is managed by multiple thermocouples that provide feedback to a controller, which then adjusts the temperature by varying the number of energized heating rods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While these technologies offer significant benefits, they are not without their complexities. A clear-eyed view of the trade-offs is essential for making informed decisions.
Increased Complexity and Maintenance
Advanced hydraulic and electronic control systems are inherently more complex than their purely mechanical predecessors. They require specialized knowledge for maintenance, troubleshooting, and calibration, which can impact training and staffing requirements.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
A kiln outfitted with precision hydraulic, feed, and thermal control systems carries a higher initial purchase price. This investment must be justified by the long-term return on investment from improved energy efficiency, higher yield, and reduced mechanical wear.
Dependency on Sensor Accuracy
The entire control strategy relies on a constant stream of accurate data from sensors, especially thermocouples. A single faulty or improperly calibrated sensor can feed incorrect information to the control system, leading to poor process decisions and suboptimal performance.
Matching Technology to Your Objective
The right combination of technologies depends entirely on your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: Multi-zone thermal control and high-precision material feed systems are the most critical technologies to invest in.
- If your primary focus is operational stability and longevity: The priority should be a robust hydraulic thrust roller system to minimize long-term mechanical wear and prevent costly downtime.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: A combination of variable speed control and precise, multi-zone thermal management is essential to ensure no energy is wasted by overheating or running the kiln inefficiently.
By understanding how these integrated systems function, you can move from simply operating a kiln to truly mastering the entire thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Technology | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Thrust Rollers | Manages axial movement and alignment | Reduces mechanical wear, enhances stability |
| Multi-Zone Temperature Control | Creates precise thermal profiles | Optimizes chemical processes, improves product quality |
| High-Precision Metering Pumps | Ensures consistent material feed | Stabilizes operations, increases yield |
| Variable Speed Drives | Adjusts rotational speed for residence time | Enhances energy efficiency, adapts to materials |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with advanced rotary kiln solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for improved efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















