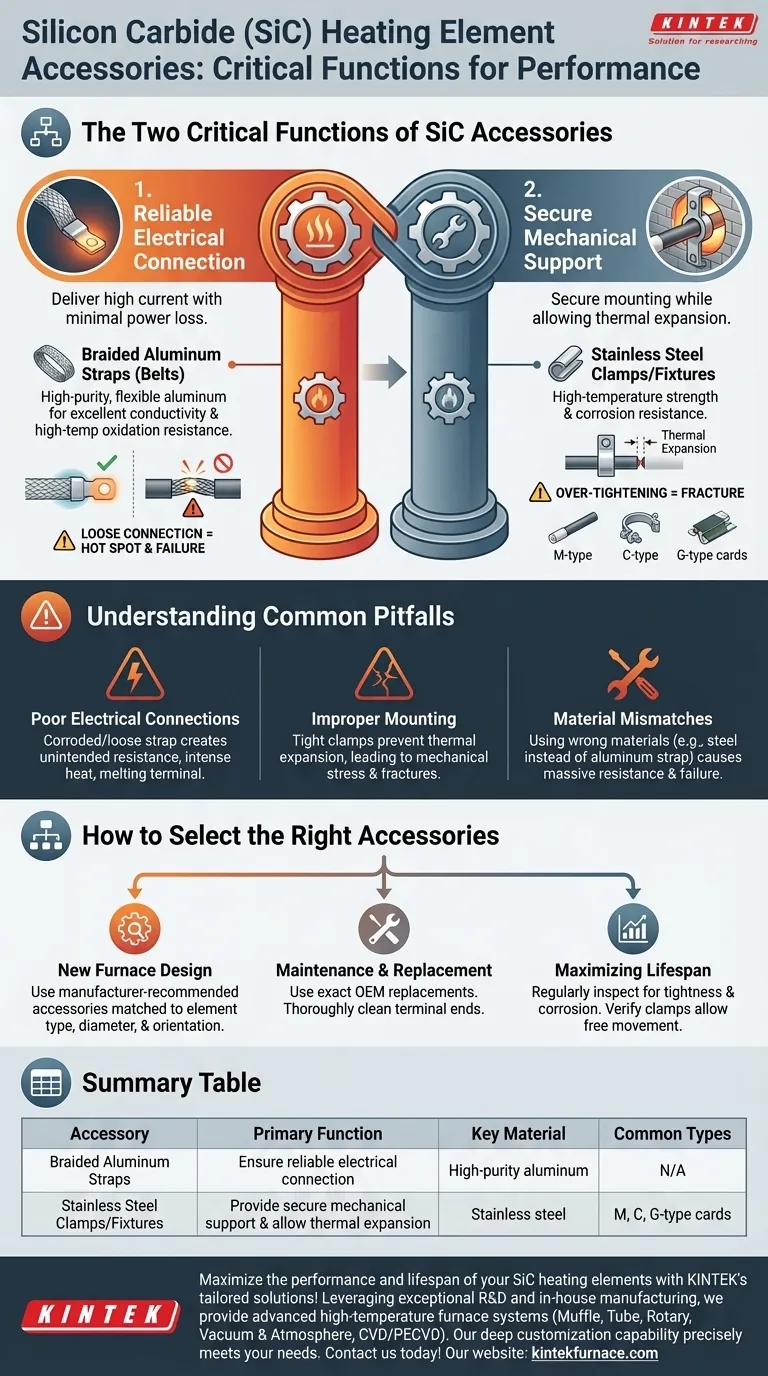
At their core, the accessories for silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements serve two critical functions: establishing a reliable electrical connection and providing secure mechanical mounting. The most common accessories are high-purity aluminum connecting straps for conductivity and stainless steel clamps or fixtures to hold the elements in place within a high-temperature furnace.
The performance and lifespan of expensive SiC heating elements depend directly on the quality and proper installation of their accessories. Viewing these components as secondary parts, rather than as an integral part of the heating system, is a frequent and costly mistake.
The Two Critical Functions of SiC Accessories
Silicon carbide elements operate under extreme electrical load and intense heat. Their accessories are engineered specifically to manage these conditions safely and efficiently. The roles are distinct but interconnected.
Function 1: Ensuring Reliable Electrical Connection
The primary goal here is to deliver high current to the element with minimal power loss or localized heating at the connection point.
This is achieved using braided aluminum connecting straps (also called belts). High-purity, flexible aluminum is the material of choice because it offers excellent electrical conductivity and resists high-temperature oxidation.
A secure, tight connection between the strap and the element's cold end is non-negotiable. A loose connection increases electrical resistance, creating a "hot spot" that can lead to arcing, damage the element terminal, and cause premature failure.
Function 2: Providing Secure Mechanical Support
SiC elements are ceramic and therefore brittle; they cannot be subjected to significant mechanical stress, especially at operating temperature.
Stainless steel clamps and fixtures are used to mount the elements securely within the furnace wall or structure. Stainless steel is used for its high-temperature strength and resistance to corrosion.
These fixtures must hold the element firmly but not rigidly. They must allow for slight thermal expansion and contraction as the element heats and cools. Over-tightening a clamp can easily cause the element to crack and fail.
Common fixture types include M, C, and G-type cards, each designed for different element shapes (e.g., rod, U-type, W-type) and installation requirements, such as vertical or horizontal mounting.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Mistakes in accessory selection or installation are a primary cause of SiC element failure. Understanding these risks is key to ensuring a long service life for your heating system.
The Risk of Poor Electrical Connections
A corroded or loose aluminum strap acts like a resistor in the circuit. This unintended resistance generates intense heat precisely where you don't want it—at the connection terminal. This can melt the strap, destroy the element's cold end, and halt production.
The Danger of Improper Mounting
SiC elements grow in length as they heat up. If mounting clamps are too tight or do not allow for this thermal expansion, the resulting mechanical stress will fracture the element. The mounting system must support the element's weight without constraining its natural movement.
The Problem with Material Mismatches
Using accessories not specifically designed for SiC elements is a critical error. Substituting a steel strap for an aluminum one, for example, would introduce massive electrical resistance. Using a clamp made from a low-grade metal could cause it to fail at high temperatures, allowing the element to fall and break.
How to Select the Right Accessories
Your selection criteria should be driven by whether you are designing a new system or maintaining an existing one.
- If your primary focus is new furnace design: Always select accessories recommended by the element manufacturer that are specifically matched to the element's type (e.g., Rod, U, DB), diameter, and mounting orientation.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and replacement: Use exact OEM replacement parts for straps and clamps. During replacement, thoroughly clean the element's terminal ends to ensure a pristine electrical contact surface.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Regularly inspect all connecting straps for tightness and signs of corrosion or overheating, and verify that mounting clamps are secure but still allow the element to move freely.
Properly selecting and installing these critical accessories is the most effective way to protect your investment and ensure a reliable high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Accessory | Primary Function | Key Material | Common Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Braided Aluminum Straps | Ensure reliable electrical connection with minimal resistance | High-purity aluminum | N/A |
| Stainless Steel Clamps/Fixtures | Provide secure mechanical support and allow for thermal expansion | Stainless steel | M, C, G-type cards |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your SiC heating elements with KINTEK's tailored solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















