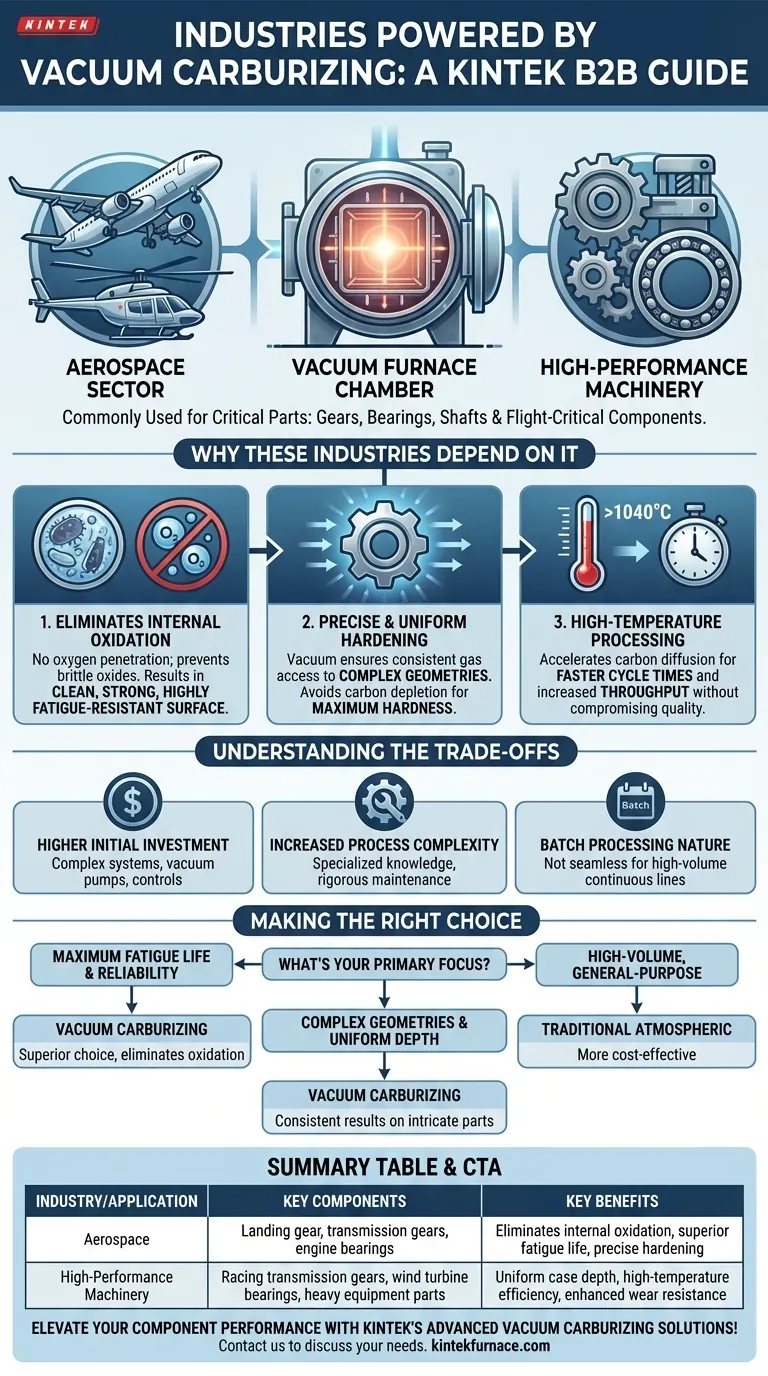
Vacuum carburizing is essential in high-stakes industries where component integrity and performance are non-negotiable. It is most commonly found in the aerospace sector and in the manufacturing of high-performance machinery, particularly for critical parts like gears, bearings, and shafts that demand exceptional wear resistance and fatigue strength.
While traditional carburizing is widespread, vacuum carburizing is the go-to process for industries requiring flawless, high-endurance components. Its key advantage is the elimination of internal oxidation, leading to superior fatigue life and predictable material performance, which is critical in aerospace and precision engineering.
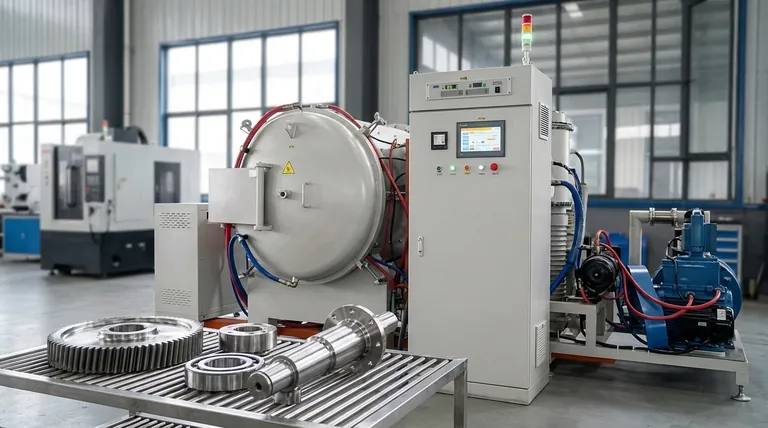

Why These Industries Depend on Vacuum Carburizing
The choice to use vacuum carburizing over traditional atmospheric methods is driven by the need for superior material properties that cannot be reliably achieved otherwise. Industries like aerospace operate with zero tolerance for material failure.
The Critical Advantage: Eliminating Internal Oxidation
Internal oxidation occurs in traditional carburizing when oxygen penetrates the steel's surface, forming brittle, non-metallic oxides in the grain boundaries. These oxides act as microscopic stress points, drastically reducing the component's fatigue life.
Vacuum carburizing completely prevents this. By performing the process in a vacuum, there is no oxygen to cause this damaging oxidation, resulting in a clean, strong, and highly fatigue-resistant surface layer.
Achieving Precise and Uniform Hardening
The vacuum environment ensures that the carburizing gas has uniform access to all surfaces of a part, even those with complex geometries like gear teeth.
This results in a highly consistent and precisely controlled carbon concentration from the surface inward. The process avoids the carbon depletion sometimes seen at the very surface in other methods, ensuring maximum hardness where it's needed most.
High-Temperature Processing for Faster Results
Vacuum furnaces can operate at very high temperatures, often exceeding 1040°C. This accelerates the carbon diffusion process significantly.
The primary benefit is a shorter overall cycle time compared to conventional methods. This increases throughput and operational efficiency without compromising the quality of the hardened case.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its benefits are significant, vacuum carburizing is not the default choice for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnace systems are technologically complex and represent a significantly higher capital investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. The cost of vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems adds to the initial expense.
Increased Process Complexity
Operating and maintaining a vacuum furnace requires specialized knowledge. The process is less forgiving than atmospheric heat treating, demanding well-trained operators and a rigorous maintenance schedule for the vacuum system.
Batch Processing Nature
Vacuum carburizing is fundamentally a batch process. While individual cycles may be faster, it may not integrate as seamlessly into a high-volume, continuous production line as some atmospheric furnace designs.
Key Applications and Components
The unique benefits of vacuum carburizing make it the required choice for specific, high-stress components.
Aerospace Components
In the aerospace industry, safety and reliability are paramount. The process is used for flight-critical parts such as:
- Landing gear components
- Helicopter transmission gears and shafts
- Actuator components
- Engine bearings
High-Performance Machinery
In the machinery and automotive sectors, vacuum carburizing is reserved for the most demanding applications where standard components would fail prematurely.
Examples include gears for high-performance racing transmissions, components for high-pressure injection molding systems, and critical bearings for wind turbines and heavy earth-moving equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct carburizing method depends entirely on your final component's performance requirements and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum fatigue life and reliability: Vacuum carburizing is the superior choice because it eliminates the internal oxidation that compromises component strength.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of general-purpose parts: Traditional atmospheric carburizing is often more cost-effective due to lower equipment and operational costs.
- If you need to process complex geometries with uniform case depth: The vacuum environment ensures consistent results on intricate parts, making it ideal for precision gears and tools.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum carburizing is a strategic decision to prioritize material perfection and long-term performance over initial cost.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Key Components | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Landing gear, transmission gears, engine bearings | Eliminates internal oxidation, superior fatigue life, precise hardening |
| High-Performance Machinery | Racing transmission gears, wind turbine bearings, heavy equipment parts | Uniform case depth, high-temperature efficiency, enhanced wear resistance |
Elevate your component performance with KINTEK's advanced vacuum carburizing solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering



















