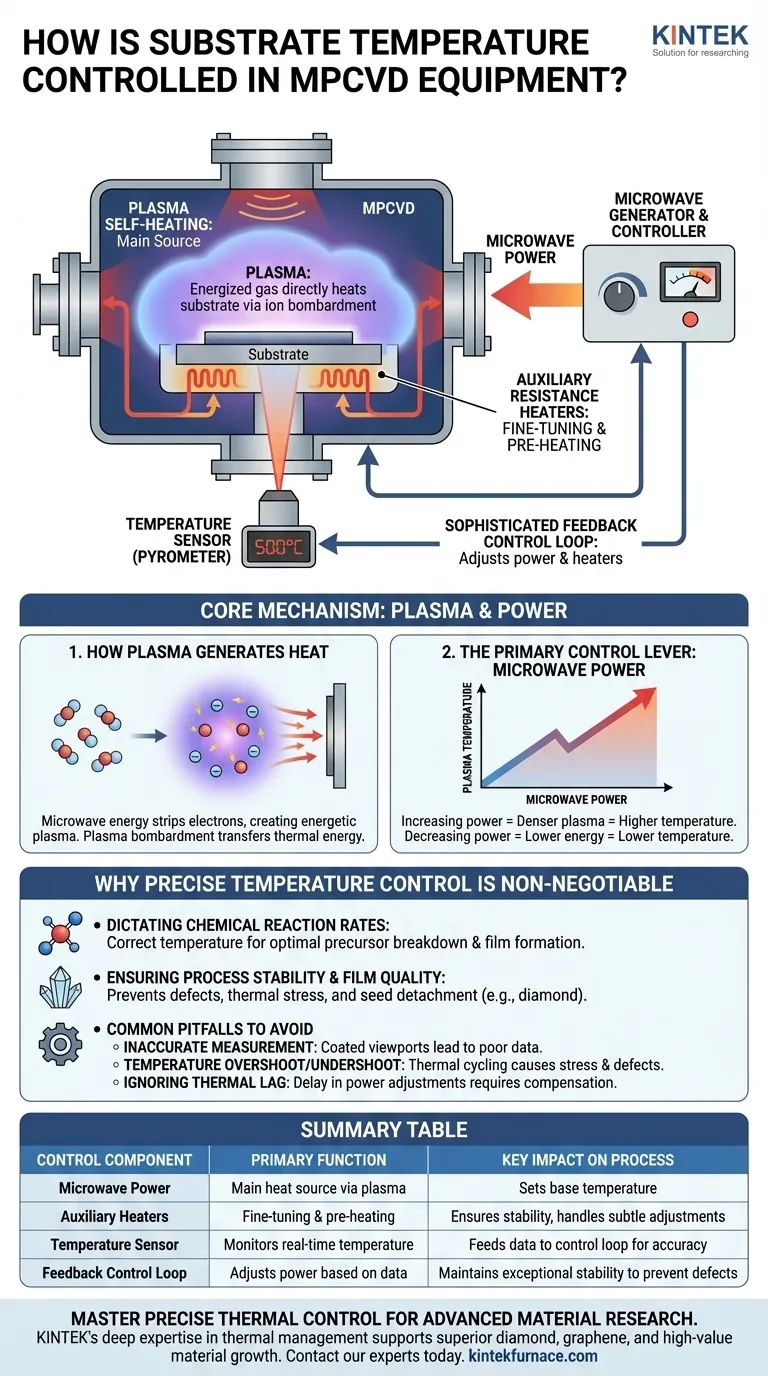
In Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) systems, substrate temperature is primarily achieved through microwave plasma self-heating. The system energizes a gas into a plasma, which directly heats the substrate it contacts. This primary heating mechanism is then precisely managed by a control system that adjusts microwave power and often uses auxiliary heaters and temperature sensors to ensure stable and accurate thermal conditions for deposition.
The core challenge in MPCVD is not merely heating the substrate, but maintaining an exceptionally stable temperature. This stability is achieved by treating the microwave plasma as the primary heat source and using a sophisticated feedback loop of sensors and power controllers to dictate the precise rate of chemical reactions, which ultimately determines the quality of the final material.

The Core Mechanism: Plasma and Power
How Plasma Generates Heat
The process begins by introducing a gas into a vacuum chamber. Microwave energy is then applied, which energizes the gas molecules and strips away their electrons, creating a highly reactive and energetic state of matter known as plasma.
This hot plasma is in direct contact with the substrate holder and the substrate itself. The constant bombardment of energetic ions and radicals from the plasma transfers a significant amount of thermal energy, causing the substrate's temperature to rise.
The Primary Control Lever: Microwave Power
The temperature of the plasma is directly proportional to the amount of microwave power applied to it. Therefore, the most fundamental way to control the substrate temperature is by adjusting the microwave power output.
Increasing the power makes the plasma denser and more energetic, leading to a higher substrate temperature. Conversely, decreasing the power reduces the plasma's energy and lowers the temperature.
The Role of Auxiliary Control Systems
While plasma self-heating is the main driver, most advanced MPCVD systems incorporate additional components for fine-tuning and stability. This includes auxiliary resistance heaters built into the substrate stage.
These heaters can be used to pre-heat the substrate to a baseline temperature before the plasma is ignited or to make minor, precise adjustments during deposition that are too subtle for coarse microwave power changes. A temperature sensor, typically a non-contact pyrometer, constantly monitors the substrate and feeds data back to a controller, which then adjusts both microwave power and auxiliary heating to maintain the desired setpoint.
Why Precise Temperature Control is Non-Negotiable
Dictating Chemical Reaction Rates
Chemical vapor deposition is fundamentally a process governed by chemical reactions on a hot surface. These reactions are extremely temperature-dependent.
The correct temperature ensures that precursor gases break down and react at the optimal rate to form the desired film. An incorrect temperature can lead to incomplete reactions, the formation of unwanted chemical compounds, or a poor crystalline structure.
Ensuring Process Stability and Film Quality
For demanding applications like single-crystal diamond growth, temperature stability is paramount. Fluctuations in temperature can cause immense thermal stress.
This instability can lead to process failures such as arcing, the plasma flame extinguishing, or, critically, the detachment of delicate crystal seeds from the substrate surface, ruining the entire growth run.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Inaccurate Temperature Measurement
The control system is only as good as the data it receives. If the viewport for the temperature sensor (pyrometer) becomes coated with deposition material, the reading will be inaccurate, leading to poor control. The system might apply incorrect power levels, compromising the material quality.
Temperature Overshoot and Undershoot
A poorly tuned control loop can cause the temperature to swing above and below the target setpoint. This thermal cycling can introduce stress into the growing film, leading to defects or even delamination from the substrate. Smooth, continuous power adjustments are essential.
Ignoring Thermal Lag
There is a delay between adjusting the microwave power and seeing the corresponding change in substrate temperature. A control system must be programmed to account for this thermal lag to prevent over-correcting and causing the temperature instability mentioned above.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving your desired outcome in an MPCVD process requires a clear understanding of how temperature influences your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Your priority is a perfectly calibrated and clean temperature sensor providing accurate data to a well-tuned feedback control loop.
- If your primary focus is high-quality crystal growth (e.g., diamond): Emphasize smooth, stable power delivery and minimal thermal fluctuation to prevent stress-induced defects and seed detachment.
- If your primary focus is exploring new materials: Concentrate on systematic experiments to identify the precise temperature window where the desired chemical reactions occur efficiently and unwanted byproducts are minimized.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is the key to unlocking the full potential of the MPCVD process.
Summary Table:
| Control Component | Primary Function | Key Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Power | Main heat source via plasma energy | Directly sets base substrate temperature |
| Auxiliary Heaters | Provides fine-tuning and pre-heating | Ensures stability and handles subtle adjustments |
| Temperature Sensor (Pyrometer) | Monitors substrate temperature in real-time | Feeds data to the control loop for accuracy |
| Feedback Control Loop | Adjusts power based on sensor data | Maintains exceptional stability to prevent defects |
Master precise thermal control for your advanced material research. Unstable substrate temperature can lead to process failure, poor film quality, and wasted resources. KINTEK's deep expertise in high-temperature systems, including advanced furnace and CVD/PECVD solutions, translates into a profound understanding of the precise thermal management required for successful MPCVD processes. Let our engineers help you achieve the stable, repeatable conditions necessary for superior diamond, graphene, or other high-value material growth.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific R&D goals with tailored solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















