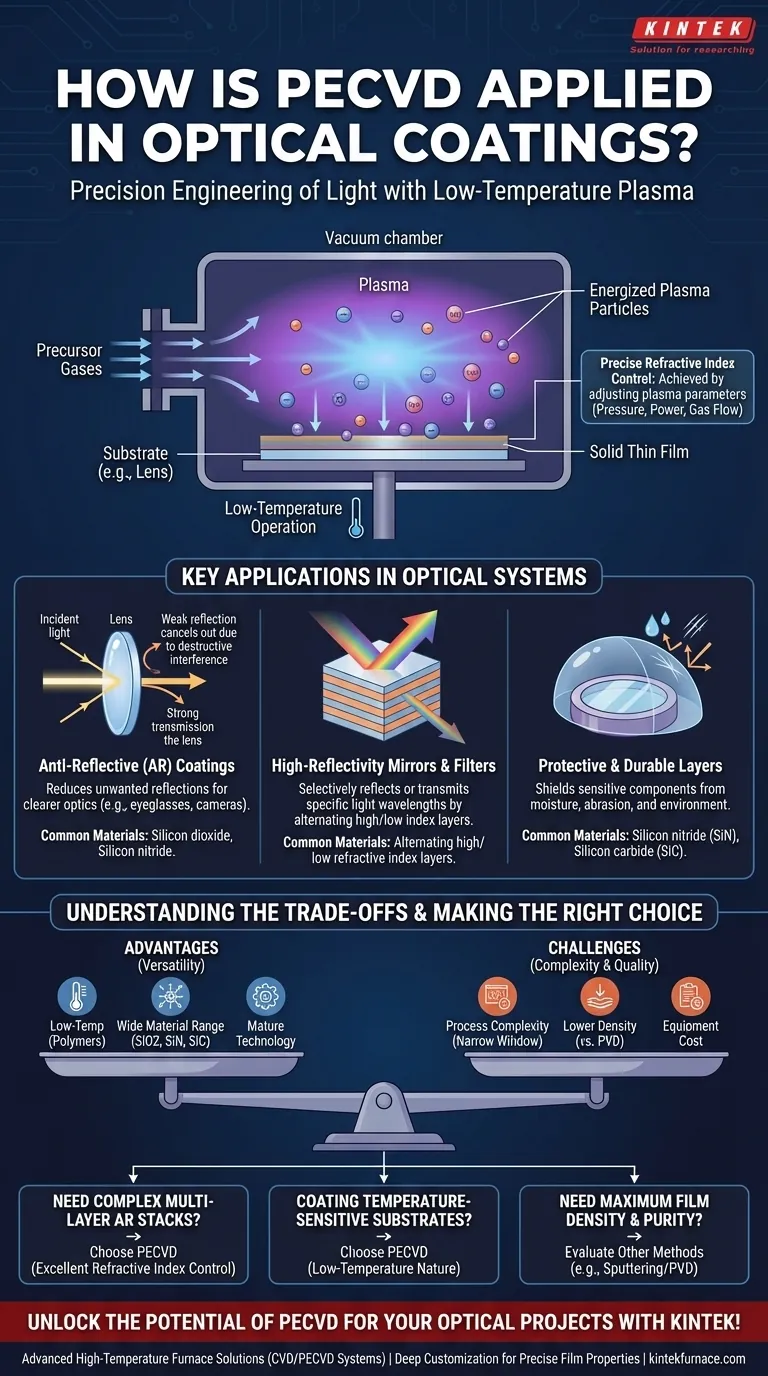
In optical applications, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a foundational process used to deposit thin, highly-engineered films onto surfaces like lenses, mirrors, and semiconductors. These films are designed with specific thicknesses and compositions to precisely control how light is reflected, transmitted, or absorbed, thereby enhancing the performance and durability of the optical component.
The true value of PECVD in optics lies not just in its ability to deposit a coating, but in its low-temperature operation and precise control over plasma parameters. This allows for the meticulous tuning of a film's refractive index, which is the fundamental property required to create sophisticated optical effects.

The Core Principle: Engineering Light with Plasma
PECVD manipulates gases at a molecular level to build a solid film with specific optical properties. The use of plasma is what makes this process uniquely suited for a wide range of optical components.
From Gas to Solid Film
In a PECVD process, precursor gases are introduced into a vacuum chamber. An electric field is then applied to ignite the gas into a plasma, a state of matter containing reactive ions and radicals. These energized particles react and condense on the substrate surface, building a thin, solid film one layer at a time.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Unlike traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which requires very high heat, PECVD uses the energy of the plasma—not high temperature—to drive the chemical reactions. This makes it ideal for coating temperature-sensitive substrates, such as polymers or previously fabricated electronic devices, without causing damage.
Tailoring the Refractive Index
The primary goal in optical coating is to control the refractive index. By precisely adjusting the plasma parameters—such as pressure, gas flow rates, and power—engineers can change the chemical composition and density of the depositing film. This directly tunes its refractive index, allowing for the design of complex optical structures.
Key Applications in Optical Systems
PECVD's precise control enables the creation of a variety of functional coatings that are essential in modern optics and photonics.
Anti-Reflective (AR) Coatings
Perhaps the most common application, AR coatings reduce unwanted reflections from surfaces like eyeglass lenses and camera optics. This is achieved by depositing one or more layers with carefully chosen refractive indices and thicknesses that cause reflected light waves to destructively interfere.
High-Reflectivity Mirrors and Filters
By alternating layers of high and low refractive index materials, PECVD can create highly reflective mirrors for specific wavelengths of light. This same principle is used to produce optical filters that selectively transmit certain colors while reflecting others, used in devices from sunglasses to advanced photometers.
Protective and Durable Layers
PECVD is used to deposit hard, transparent films like silicon nitride (SiN) and silicon carbide (SiC). These coatings serve as passivation or protective layers that shield sensitive optical components from moisture, abrasion, and environmental damage, significantly increasing their lifespan.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is a choice with specific trade-offs that must be considered against other deposition techniques.
Film Quality vs. Other Methods
PECVD films, due to the lower process temperature and plasma chemistry, can sometimes have lower density or higher hydrogen content compared to films deposited by higher-temperature methods or physical vapor deposition (PVD). For applications demanding the absolute highest film purity or density, other methods may be more suitable.
The Advantage of Versatility
The wide range of materials that can be deposited—including silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, and amorphous silicon—makes PECVD incredibly versatile. Its use extends far beyond optics into semiconductors, solar cells, and LEDs, meaning the technology is mature and well-understood.
Process Complexity
Achieving a specific refractive index and film uniformity requires meticulous control over numerous variables. The process window can be narrow, demanding sophisticated equipment and process expertise to maintain consistency and repeatability, especially in high-volume manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting PECVD depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and its intended function.
- If your primary focus is creating multi-layer anti-reflective coatings: PECVD offers the excellent refractive index control necessary to build complex optical stacks.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers: PECVD's low-temperature nature makes it one of the best and sometimes only viable options.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum film density and purity for extreme performance: You should evaluate whether sputtering or other PVD methods might better serve your specific requirements, despite their own trade-offs.
Ultimately, PECVD is a versatile and indispensable tool for engineering the interaction between light and matter.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflective Coatings | Reduces reflections via destructive interference | Silicon dioxide, silicon nitride |
| High-Reflectivity Mirrors/Filters | Selectively reflects/transmits specific wavelengths | Alternating high/low refractive index layers |
| Protective Layers | Shields from moisture, abrasion, and damage | Silicon nitride (SiN), silicon carbide (SiC) |
Unlock the potential of PECVD for your optical projects with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Whether you're developing anti-reflective coatings, durable mirrors, or protective layers for temperature-sensitive substrates, our deep customization capabilities ensure precise control over film properties. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your optical coating performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















