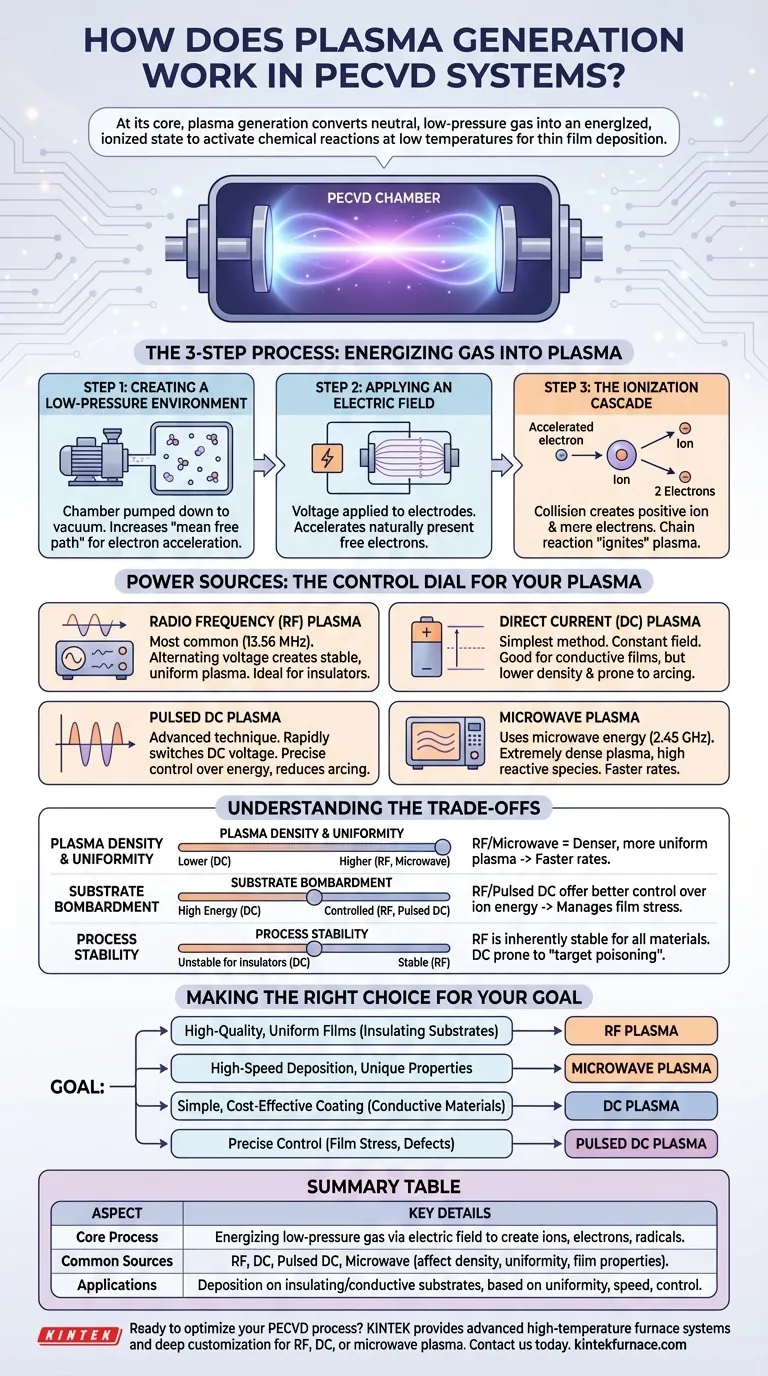
At its core, plasma generation in a Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) system is the process of converting a neutral, low-pressure gas into an energized, ionized state. This is achieved by applying a strong electric field between two electrodes within the reaction chamber, which strips electrons from the gas molecules and creates a highly reactive mixture of ions, electrons, and neutral radicals.
The goal of generating plasma is not simply to create light and energy, but to activate chemical reactions at low temperatures. The specific method used to supply this energy—be it Radio Frequency, DC, or something else—directly controls the plasma's characteristics and, ultimately, the final properties of the deposited thin film.

The Fundamental Principle: Energizing Gas into Plasma
To understand PECVD, you must first understand the three-step process of creating a stable, useful plasma for deposition.
Step 1: Creating a Low-Pressure Environment
Before any energy is applied, the reaction chamber is pumped down to a low pressure. This vacuum environment is critical because it reduces the density of gas molecules.
This increases the "mean free path"—the average distance a particle can travel before colliding with another—allowing electrons to accelerate and gain significant energy from the electric field.
Step 2: Applying an Electric Field
Once the desired low pressure is reached, a voltage is applied to electrodes within the chamber. This creates a powerful electric field that permeates the precursor gas.
A small number of naturally present free electrons are immediately accelerated by this field, gaining kinetic energy as they travel through the gas.
Step 3: The Ionization Cascade
This is where the plasma "ignites." An accelerated electron collides with a neutral gas atom or molecule, knocking another electron loose.
This collision creates a positive ion and two free electrons. These two electrons are then accelerated by the field, leading to more collisions and creating four electrons, then eight, and so on. This chain reaction, known as an ionization cascade, rapidly transforms the neutral gas into a partially ionized plasma.
Power Sources: The Control Dial for Your Plasma
The "flavor" of the plasma—its density, energy, and stability—is determined by the type of power supply used to create the electric field.
Radio Frequency (RF) Plasma
This is the most common method in PECVD. An alternating voltage at a high frequency, typically the industry-standard 13.56 MHz, is applied to the electrodes.
Because the voltage polarity switches millions of times per second, the electrons oscillate rapidly in the chamber, sustaining a very stable and uniform plasma. RF is highly effective for depositing insulating films where a DC current cannot be sustained.
Direct Current (DC) and Pulsed DC Plasma
A Direct Current (DC) supply is the simplest method, creating a constant electric field. It is often used for depositing conductive films but produces a lower-density plasma and is prone to arcing.
Pulsed DC is a more advanced technique. By turning the DC voltage on and off rapidly, it allows for more precise control over the plasma's energy and reduces arcing, which is critical for controlling film stress and quality.
Microwave Plasma
In this method, microwave energy (typically at 2.45 GHz) is used to energize the electrons. This approach can create an extremely dense plasma with a high concentration of reactive species.
This high density often leads to faster deposition rates and can enable the formation of unique material properties, though the equipment is generally more complex.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why the Power Source Matters
The choice of power source is a critical engineering decision with direct consequences for your process and results.
Plasma Density and Uniformity
RF and microwave sources generate much denser and more spatially uniform plasmas compared to simple DC systems. Higher density means more reactive species are available, which typically translates to a faster deposition rate.
Substrate Bombardment
The energy of the ions striking your substrate surface has a profound impact on the film's properties. A continuous DC plasma can lead to high-energy bombardment, while RF and Pulsed DC offer better control over ion energy, which helps manage film stress, density, and adhesion.
Process Stability
RF plasma is inherently stable and reliable for a wide range of materials, including dielectrics (insulators). DC plasma can be unstable when depositing insulating materials, as charge builds up on the surface and disrupts the electric field, a phenomenon known as "target poisoning."
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of plasma generation method should be dictated by the specific requirements of the film you are creating.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, uniform films on insulating substrates: RF plasma is the conventional and most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-speed deposition or achieving unique material properties: Microwave plasma offers the highest density, enabling faster rates and novel chemistries.
- If your primary focus is simple, cost-effective coating on conductive materials: A standard DC system may be sufficient for your needs.
- If your primary focus is precise control over film stress and preventing defects: Pulsed DC provides a powerful tool to finely manage ion energy and process stability.
Understanding how plasma is generated transforms it from a "black box" into a tunable instrument for engineering materials at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Plasma Generation Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Energizing low-pressure gas via electric field to create ions, electrons, and radicals for chemical reactions at low temperatures. |
| Common Power Sources | Radio Frequency (RF), Direct Current (DC), Pulsed DC, and Microwave, each affecting plasma density, uniformity, and film properties. |
| Primary Applications | Deposition of thin films on insulating or conductive substrates, with choices based on uniformity, speed, and control needs. |
Ready to optimize your PECVD process with tailored plasma solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with RF, DC, or microwave plasma for superior thin film deposition. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















