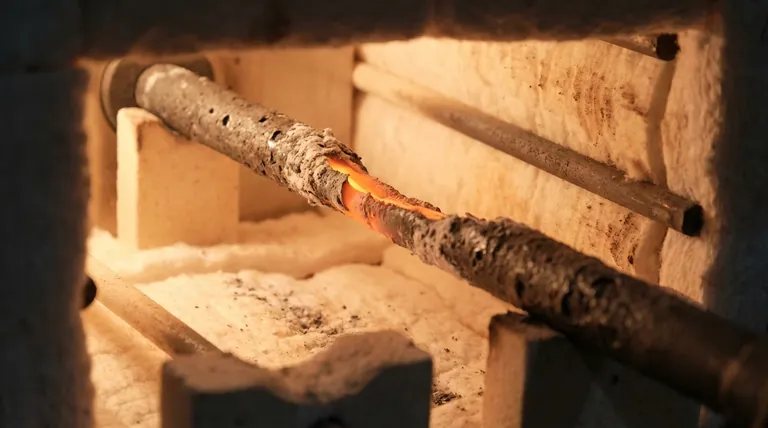
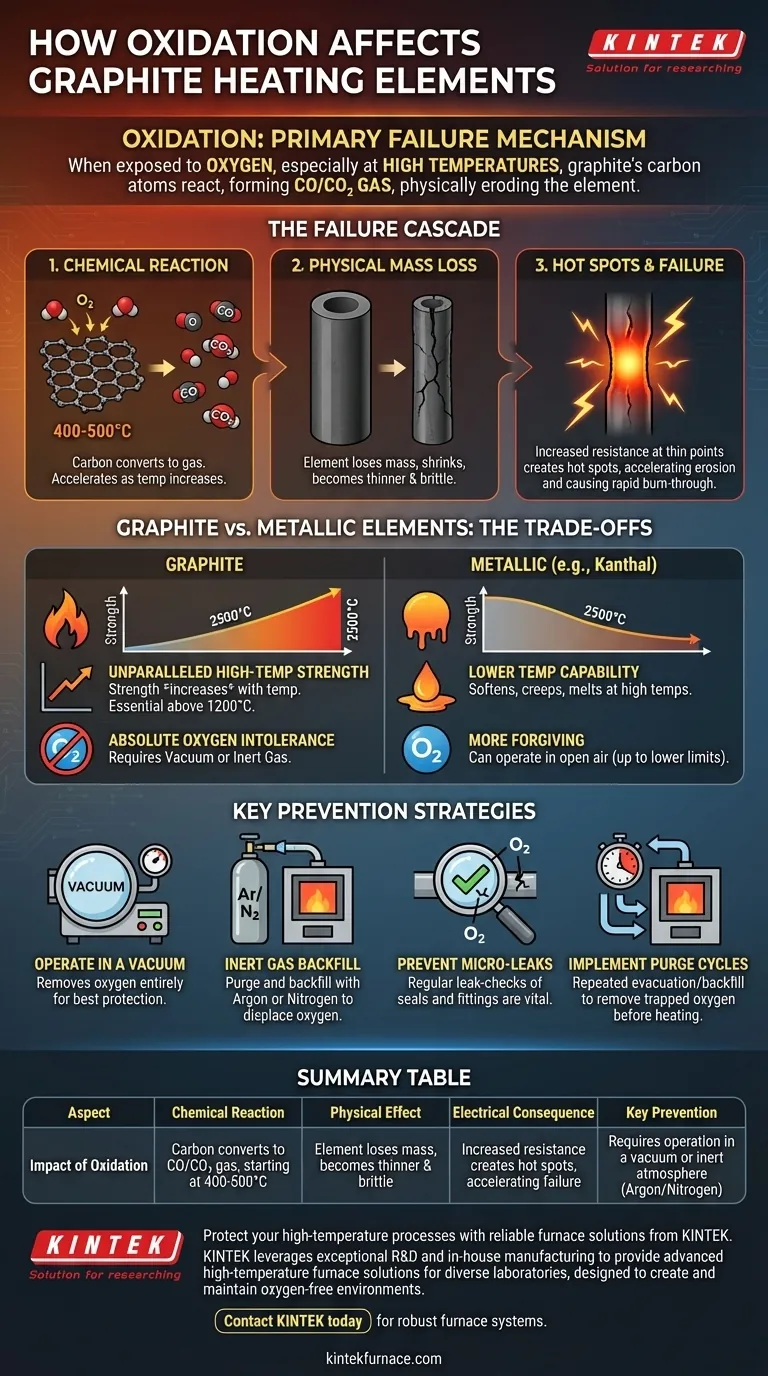
In short, oxidation is the primary failure mechanism for graphite heating elements. When exposed to oxygen, especially at high temperatures, the carbon atoms that form the graphite react and are converted into carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide gas. This process physically erodes the element, causing it to become thinner, weaker, and eventually fail.
While graphite offers unparalleled performance at extreme temperatures where metals fail, this advantage is entirely conditional. Managing its environment to prevent oxidation is not an optional maintenance task; it is the fundamental requirement for successful and reliable operation.

The Failure Cascade: How Oxidation Destroys Graphite
To effectively manage graphite heating elements, you must understand the chain reaction that oxidation triggers. It is a process of accelerating decay that impacts the element both chemically and physically.
The Chemical Reaction
At its core, oxidation is a simple chemical reaction where solid carbon is converted into a gas. This reaction begins slowly at temperatures around 400-500°C (752-932°F) and accelerates exponentially as temperature increases.
The solid carbon of your heating element literally vanishes into the atmosphere of your furnace.
The Consequence: Physical Mass Loss
As the graphite oxidizes, the element loses mass and its cross-sectional area shrinks. It becomes physically thinner and more brittle over time.
This gradual erosion is the most visible symptom of an oxidation problem, often starting in one specific area.
The Final Straw: Electrical Resistance and Hot Spots
This is the critical step that leads to rapid failure. As a section of the heating element thins, its electrical resistance at that point increases.
According to Ohm's law, higher resistance at a constant current leads to more heat being generated. This creates a localized "hot spot."
This hot spot accelerates the rate of oxidation in that specific area, which makes it even thinner, which in turn increases its resistance and makes it even hotter. This feedback loop causes the element to burn through and break very quickly.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Metallic Elements
If graphite is so vulnerable to oxidation, why use it at all? The decision hinges on a critical trade-off between temperature capability and environmental requirements.
The High-Temperature Advantage of Graphite
Unlike metallic elements that soften, creep, and melt at high temperatures, graphite's mechanical strength actually increases with temperature, peaking around 2500°C (4532°F).
This makes graphite the superior and often only choice for vacuum and controlled-atmosphere furnaces operating above 1200°C (2192°F).
The Environmental Dependency
The trade-off for this high-temperature performance is graphite's absolute intolerance for oxygen. It must be operated in a vacuum or an oxygen-free inert atmosphere.
Metallic elements (like Kanthal or Nichrome) are often more forgiving and can operate in open air, but only up to their much lower maximum operating temperatures.
Key Strategies for Preventing Oxidation
Preventing oxidation is about controlling the furnace atmosphere. There is no other way to ensure the longevity and reliability of your graphite elements.
Operating in a Vacuum
The most effective method is to remove the oxygen entirely by pulling a vacuum. A high vacuum provides the best possible protection for the graphite.
Even a rough vacuum is significantly better than operating in open air, as it dramatically reduces the amount of available oxygen.
Using an Inert Gas Backfill
A common industrial practice is to purge the furnace chamber of air and then backfill it with an inert gas like Argon or Nitrogen.
This creates a positive pressure environment where the inert gas physically displaces any oxygen, protecting the elements. Argon is heavier than air and often preferred for its effectiveness in purging.
The Danger of Micro-Leaks
Premature element failure is almost always traced back to an oxygen source. A tiny, unnoticed leak in a door seal, a fitting, or a viewport can introduce enough oxygen to destroy an element over time.
Regular leak-checking of your furnace vessel is the most important preventative maintenance you can perform.
Implementing Purge Cycles
Before heating the furnace, you must run a purge cycle. This involves repeatedly evacuating the chamber and backfilling it with inert gas to remove any residual atmospheric oxygen trapped inside.
Skipping or shortening this step is a frequent cause of reduced element lifespan.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum element lifespan: Invest in a high-integrity vacuum system or a meticulously controlled inert gas environment with strict, documented purging protocols.
- If your primary focus is operating at the highest possible temperatures: Graphite is your only viable choice, which means creating and maintaining an oxygen-free environment is a non-negotiable part of your process.
- If you are experiencing premature element failure: Immediately begin a systematic search for air leaks in your furnace chamber and critically review your gas purging procedures.
By mastering the operational environment, you unlock the full potential and exceptional reliability of graphite heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Oxidation |
|---|---|
| Chemical Reaction | Carbon converts to CO/CO₂ gas, starting at 400-500°C |
| Physical Effect | Element loses mass, becomes thinner and brittle |
| Electrical Consequence | Increased resistance creates hot spots, accelerating failure |
| Key Prevention | Requires operation in a vacuum or inert atmosphere (Argon/Nitrogen) |
Protect your high-temperature processes with reliable furnace solutions from KINTEK.
Oxidation is the primary enemy of graphite heating elements, but you can prevent it with the right equipment and protocols. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is designed to create and maintain the oxygen-free environments essential for graphite element longevity.
Our strong deep customization capability allows us to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring maximum performance and element lifespan.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our robust furnace systems can safeguard your graphite heating elements and enhance your high-temperature applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity



















