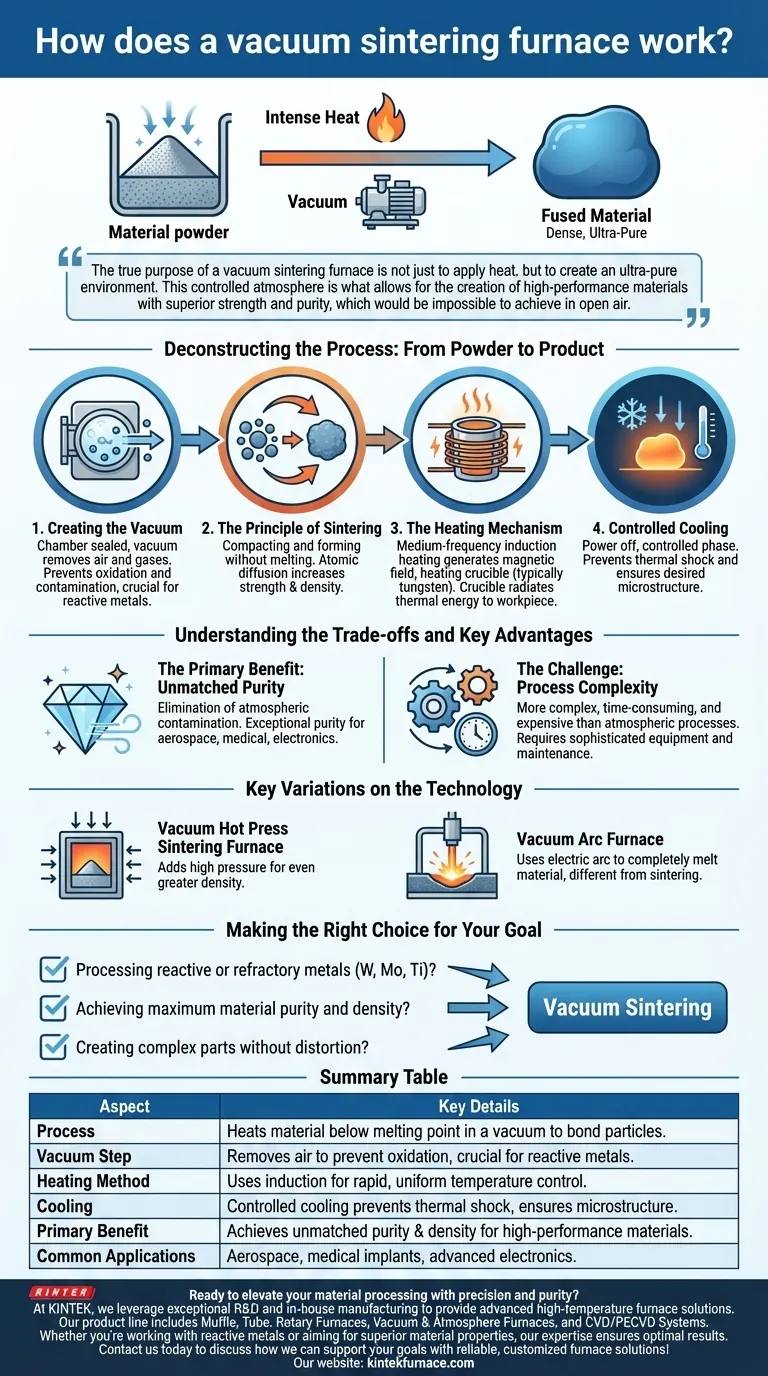
At its core, a vacuum sintering furnace works by using a combination of intense heat and a vacuum to fuse material powders into a solid, dense object. The process heats the material to just below its melting point, causing the individual particles to bond together, while the vacuum prevents air from reacting with the material and creating impurities.
The true purpose of a vacuum sintering furnace is not just to apply heat, but to create an ultra-pure environment. This controlled atmosphere is what allows for the creation of high-performance materials with superior strength and purity, which would be impossible to achieve in open air.
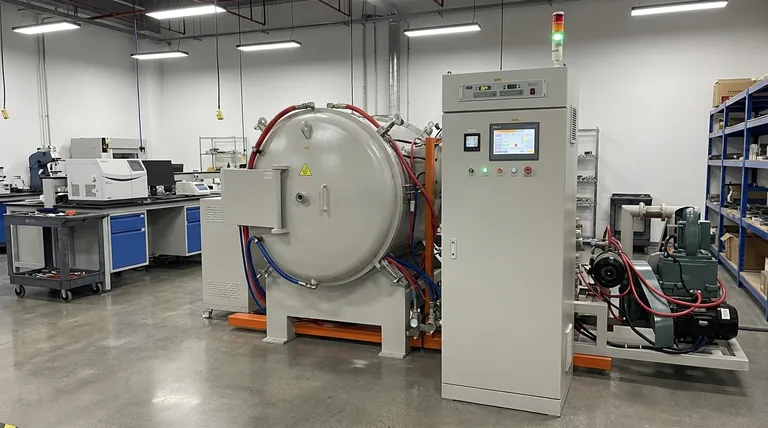

Deconstructing the Process: From Powder to Product
The operation of a vacuum sintering furnace can be broken down into a precise sequence of steps, each serving a critical function in developing the final material's properties.
The Critical First Step: Creating the Vacuum
Before any heating occurs, the furnace chamber is sealed and a powerful vacuum system removes nearly all the air and other atmospheric gases. This step is paramount because it prevents oxidation and contamination, especially when working with highly reactive or refractory metals like tungsten, molybdenum, and titanium.
The Principle of Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. As the temperature rises, atomic diffusion occurs across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them into a single, densified piece. This dramatically increases the material's strength and density.
The Heating Mechanism: Induction and Radiation
Most modern vacuum sintering furnaces use medium-frequency induction heating. An electrical coil generates a powerful magnetic field around a crucible, typically made of tungsten. This field induces electrical currents within the crucible, causing it to heat up rapidly to extremely high temperatures.
The heated crucible then radiates this thermal energy to the workpiece placed inside it, ensuring uniform and controlled heating without direct contact.
Controlled Cooling
Once the material has been held at the target sintering temperature for the required duration, the power is shut off. The furnace then undergoes a controlled cooling phase, which is just as important as the heating cycle for preventing thermal shock and ensuring the desired final microstructure of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Advantages
While incredibly effective, vacuum sintering is a specialized process with a distinct set of benefits and considerations.
The Primary Benefit: Unmatched Purity
The defining advantage of this process is the elimination of atmospheric contamination. This results in a final product with exceptional purity, ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, medical implants, and advanced electronics where material integrity is non-negotiable.
The Challenge: Process Complexity
Vacuum sintering is generally more complex, time-consuming, and expensive than traditional atmospheric furnace processes. The equipment is sophisticated, and the requirement for creating and maintaining a high-quality vacuum adds to the operational overhead.
Key Variations on the Technology
It's important to distinguish vacuum sintering from related technologies. A vacuum hot press sintering furnace, for example, adds high pressure to the heat and vacuum, which can help achieve even greater density. A vacuum arc furnace, by contrast, uses an electric arc to completely melt the material, which is a fundamentally different process from sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or refractory metals: Vacuum sintering is essential to prevent the oxidation that would ruin materials like tungsten, molybdenum, or titanium alloys.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material purity and density: The controlled, contaminant-free environment of a vacuum furnace is the only way to guarantee superior mechanical and physical properties.
- If your primary focus is creating complex parts without distortion: Sintering allows for the formation of intricate net-shape or near-net-shape parts directly from powder, minimizing the need for post-process machining.
Ultimately, mastering materials engineering comes down to controlling the processing environment to achieve a specific outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Heats material below melting point in a vacuum to bond particles without liquefaction. |
| Vacuum Step | Removes air to prevent oxidation and contamination, crucial for reactive metals. |
| Heating Method | Uses medium-frequency induction heating for rapid, uniform temperature control. |
| Cooling | Controlled cooling phase prevents thermal shock and ensures desired microstructure. |
| Primary Benefit | Achieves unmatched purity and density, ideal for high-performance materials. |
| Common Applications | Aerospace components, medical implants, advanced electronics. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're working with reactive metals or aiming for superior material properties, our expertise ensures optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals with reliable, customized furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments



















