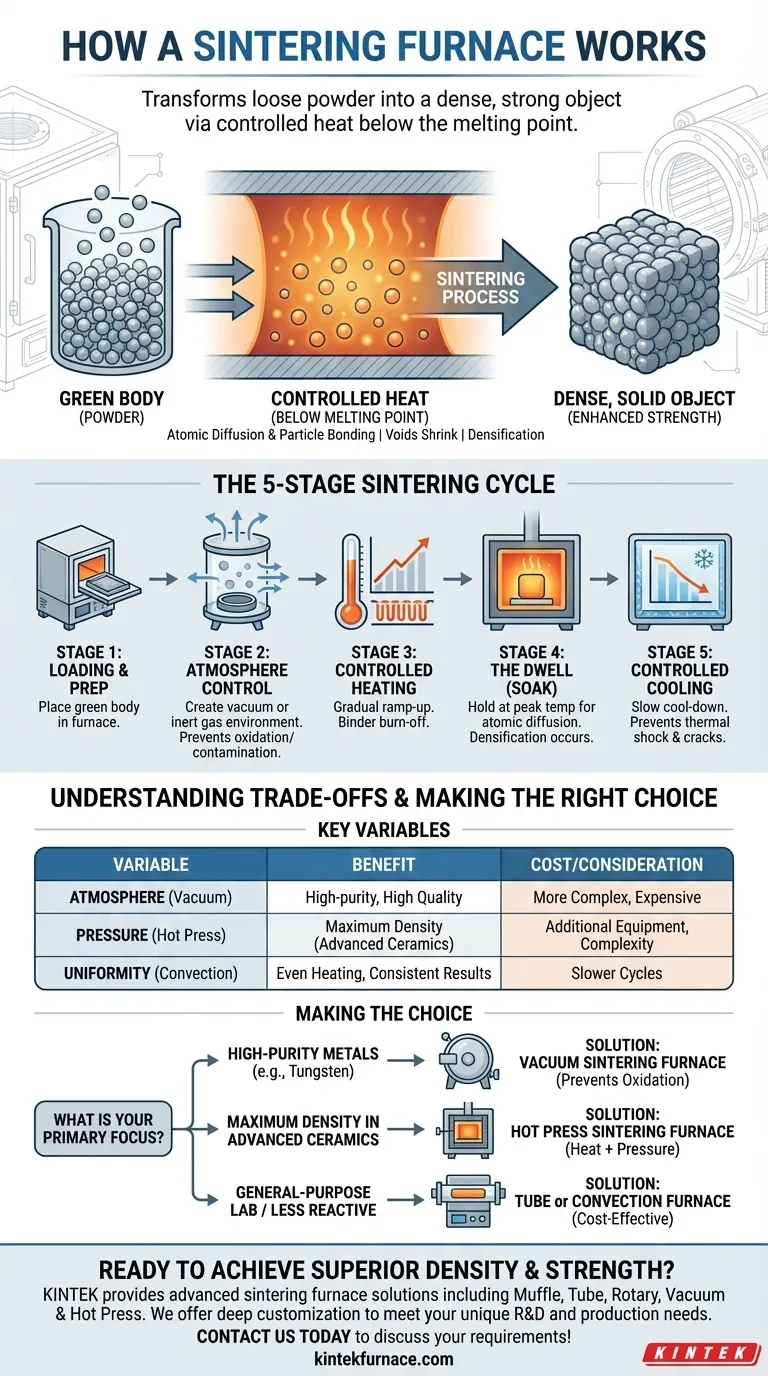
At its core, a sintering furnace works by heating a compacted powder material to a high temperature, just below its melting point. This intense heat causes the individual particles to bond and fuse together, transforming the loose powder into a dense, solid object with significantly increased strength and integrity. The key is applying this heat in a highly controlled environment to achieve specific material properties without liquefying the substance.
The fundamental purpose of a sintering furnace is not simply to heat a material, but to precisely manage temperature, time, and atmosphere to induce atomic diffusion between particles, fundamentally enhancing the material's density and mechanical strength.

The Core Principle: Sintering Explained
To understand how the furnace works, you must first understand the goal of sintering itself. It is a thermal treatment process for consolidating powdered materials.
From Powder to Solid Mass
The starting point is a "green body," which is a loosely compacted powder, often held together by a binder. The goal of the furnace is to turn this fragile object into a durable, solid part.
The Role of Temperature (Without Melting)
The furnace applies heat to energize the atoms within the powder particles. As the temperature rises, atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, creating strong chemical bonds or "necks" where they touch. Crucially, this happens below the material's melting point, preserving the object's shape.
The Goal: Enhanced Density and Strength
As particles fuse, the voids and pores between them shrink, causing the entire part to densify and become stronger. The final product is a solid mass with mechanical properties far superior to the initial powder compact.
Inside the Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
A typical sintering cycle is a carefully orchestrated sequence of stages, each critical to the final outcome.
Stage 1: Loading and Preparation
The green body, often made of ceramic or metal powder, is carefully placed inside the furnace chamber.
Stage 2: Atmosphere Control
For many materials, especially reactive metals, this is the most critical step. The furnace creates a vacuum by pumping out atmospheric gases. This prevents oxidation and contamination, which would compromise the material's purity and final properties.
Stage 3: Controlled Heating Ramp-Up
The furnace's heating elements (or induction coils in some designs) begin to raise the temperature. This ramp-up must be gradual and precisely controlled to ensure the part heats uniformly and to allow any binders to burn off cleanly.
Stage 4: The Dwell or "Soak" Phase
The furnace holds the material at its peak sintering temperature—often between 1300°C and 1600°C for materials like zirconia. During this "soak" time, the critical atomic diffusion and particle bonding occur, leading to densification.
Stage 5: Controlled Cooling
Finally, the furnace begins a slow, controlled cooling phase. Cooling too quickly can create internal stresses, leading to thermal shock and cracks in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of sintering process involves balancing quality, cost, and material requirements.
Atmosphere vs. Cost
Operating in a vacuum or controlled gas environment produces exceptionally high-purity, high-quality parts. However, the equipment is significantly more complex and expensive than furnaces that operate in open air.
Pressure as a Critical Variable
Some materials, particularly advanced ceramics, are difficult to densify with heat alone. A hot press sintering furnace applies high pressure simultaneously with high temperature. This physically forces the particles together, achieving densities that are otherwise impossible.
Uniformity vs. Speed
Ensuring uniform heat distribution is paramount. Methods like mechanical convection, which uses fans and baffles, provide more even heating than simple gravity convection. However, achieving perfect uniformity often requires slower heating and cooling cycles, extending the overall process time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
The type of furnace and process you need depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-purity refractory metals (e.g., tungsten): You must use a vacuum sintering furnace to prevent oxidation and ensure the material's integrity.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in advanced ceramics: A hot press sintering furnace that combines heat and pressure is often the only effective solution.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or less reactive materials: A simpler, more cost-effective tube or convection furnace may be perfectly sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process comes from understanding that the furnace is a tool for precisely manipulating a material's atomic structure.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Critical Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation/contamination | Vacuum or specific gas environment |
| Heating Ramp-Up | Ensures uniform heating & binder removal | Controlled heating rate |
| Dwell (Soak) Phase | Enables atomic diffusion & particle bonding | Peak temperature & time |
| Controlled Cooling | Prevents thermal shock & internal stresses | Controlled cooling rate |
Ready to achieve superior material density and strength?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced sintering furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique sintering requirements—whether you need high-purity vacuum environments for refractory metals or high-pressure hot pressing for advanced ceramics.
Contact us today to discuss how our sintering expertise can enhance your R&D and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















