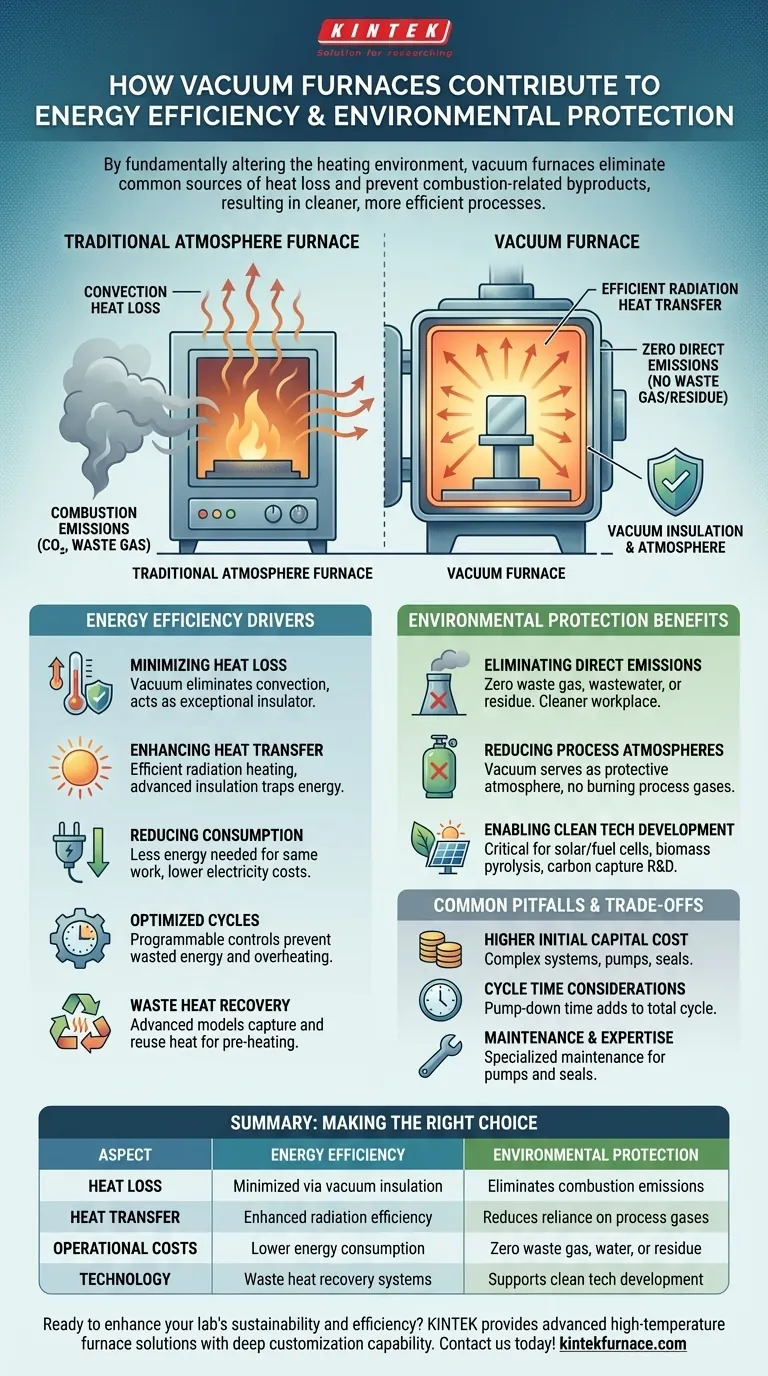
At their core, vacuum furnaces contribute to energy efficiency and environmental protection by fundamentally altering the environment in which heating occurs. By removing air and other gases, these systems eliminate common sources of heat loss and completely prevent the creation of combustion-related byproducts, resulting in a cleaner and more efficient process.
The primary advantage of a vacuum furnace lies in its controlled environment. This vacuum virtually eliminates heat loss from convection and eliminates the need for combustible process atmospheres, simultaneously driving down energy consumption and cutting direct operational emissions to zero.

The Principle: How a Vacuum Transforms Heat Treatment
To understand the benefits of a vacuum furnace, you must first understand why removing air is so impactful. The vacuum itself is not just an empty space; it is an active component of the system's efficiency.
Minimizing Heat Loss
In a traditional furnace, a significant amount of energy is lost as heated gas molecules (air) move around and transfer thermal energy away from the workpiece and heating elements. This process is called convection.
Because a vacuum has minimal gas molecules, heat loss through convection is drastically reduced. This makes the vacuum an exceptional insulator, ensuring the vast majority of energy is used for its intended purpose: heating the part.
Enhancing Heat Transfer Efficiency
With convection largely eliminated, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation. This is a more direct and efficient method of heating the workpiece, reducing the energy needed to reach and maintain the target temperature.
Modern vacuum furnaces compound this effect by using advanced, high-quality insulation materials. These materials work in tandem with the vacuum to contain thermal energy, preventing it from escaping the hot zone.
Driving Energy Efficiency
The physical principles of a vacuum directly translate into measurable gains in energy efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Reducing Overall Consumption
By minimizing heat loss, vacuum furnaces simply require less energy to perform the same amount of work compared to conventional atmosphere furnaces. This directly lowers electricity consumption and reduces production costs.
Optimizing Cycles with Modern Controls
Modern systems are equipped with programmable controllers that precisely manage heating and cooling cycles. This optimization ensures no energy is wasted by overshooting temperatures or holding them for longer than necessary, further improving efficiency.
The Advantage of Waste Heat Recovery
Some advanced vacuum furnace models incorporate waste heat recovery technology. These systems capture and reuse heat that would otherwise be lost during the cooling phase, pre-heating subsequent loads or performing other useful work, further maximizing energy utilization.
Understanding the Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of vacuum furnaces extend beyond simple energy savings. They represent a fundamental shift toward cleaner manufacturing processes.
Eliminating Direct Process Emissions
The most significant environmental benefit is the complete elimination of direct emissions. Because there is no combustion, a vacuum furnace produces no waste gas (like CO₂), wastewater, or waste residue during operation.
This not only protects the external environment but also improves workplace safety by creating a cleaner, healthier atmosphere for employees.
Reducing Reliance on Process Atmospheres
Many heat treatment processes, such as annealing and hardening, require a specific atmosphere to protect the part's surface. In a vacuum furnace, the vacuum itself serves as this protective atmosphere.
This eliminates the need to purchase, store, and burn process gases (like natural gas or endothermic gas), which are a primary source of emissions in conventional furnaces.
Enabling Clean Technology Development
Beyond their direct operational benefits, vacuum furnaces are a critical enabling technology for the green economy. They are used in the research and production of:
- Materials for solar cells and fuel cells.
- Biomass pyrolysis for renewable energy.
- Research into carbon capture and storage solutions.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, vacuum furnaces are a specialized technology with specific considerations that must be weighed.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems that involve high-performance pumps, seals, and control systems. This sophistication typically results in a higher upfront investment compared to simpler atmosphere furnaces.
Cycle Time Considerations
The process of pulling a vacuum—known as pump-down time—adds to the total cycle time. For certain high-volume, low-margin applications, this can be a key consideration in production throughput.
Maintenance and Expertise
The vacuum system, including pumps and seals, requires specialized maintenance and a higher level of operator expertise to ensure peak performance and reliability. Leaks or pump failures can compromise part quality and lead to downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment technology depends entirely on your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: The energy savings and elimination of consumable process gases make a vacuum furnace a compelling choice despite a higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is meeting stringent environmental regulations: The zero-emission nature of vacuum processing provides an unmatched advantage for compliance and corporate sustainability goals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing or clean tech R&D: The clean, controlled, and highly repeatable environment of a vacuum furnace is an absolute requirement.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic investment in process control, operational efficiency, and environmental stewardship.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Energy Efficiency | Environmental Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Loss | Minimized via vacuum insulation | Eliminates combustion emissions |
| Heat Transfer | Enhanced radiation efficiency | Reduces reliance on process gases |
| Operational Costs | Lower energy consumption | Zero waste gas, water, or residue |
| Technology | Waste heat recovery systems | Supports clean tech development |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability and efficiency? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can reduce your energy costs and environmental impact!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















