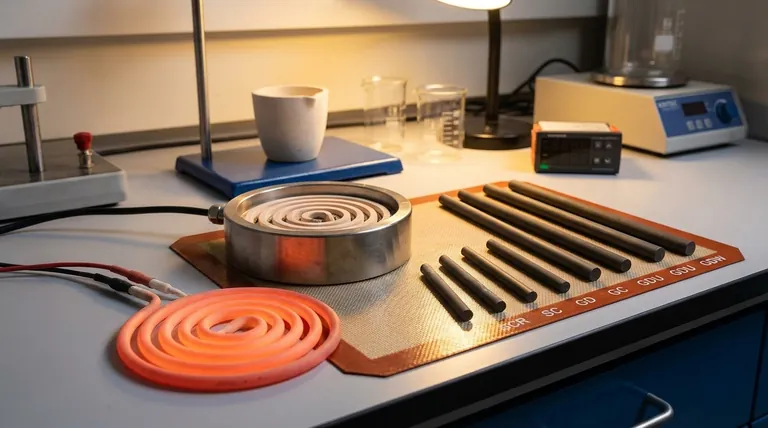
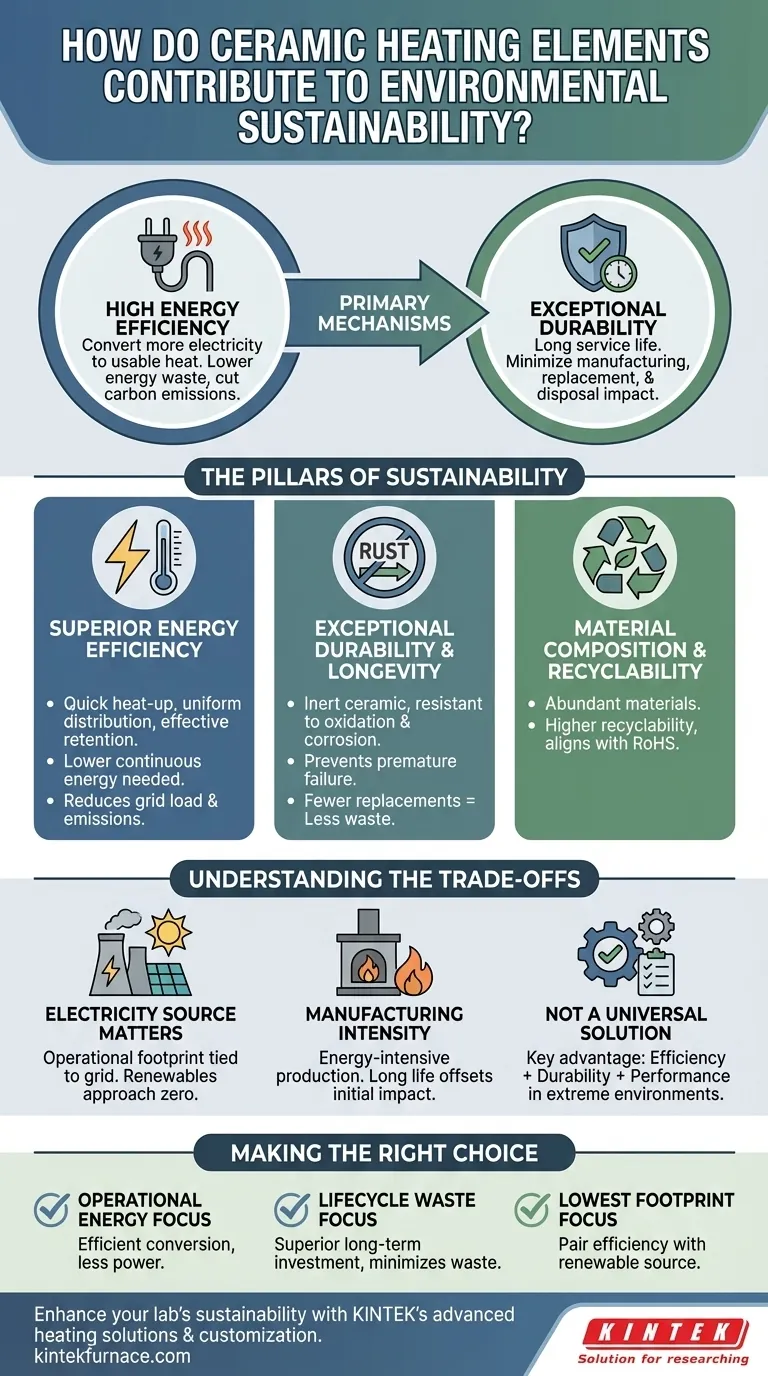
At their core, ceramic heating elements contribute to environmental sustainability through two primary mechanisms: high energy efficiency and exceptional durability. They convert a greater percentage of electricity into usable heat, reducing energy waste, and their long service life minimizes the environmental impact associated with manufacturing, replacement, and disposal.
The true measure of a heating technology's sustainability goes beyond its fuel source. It hinges on operational efficiency and lifecycle longevity. Ceramic heaters excel in both, offering a compelling path to reduced energy consumption and less material waste over time.

The Pillars of Sustainability in Ceramic Heating
To understand the environmental benefits, we must look at how these components function throughout their lifecycle, from energy use to eventual disposal. The advantages are rooted in their fundamental material properties.
Pillar 1: Superior Energy Efficiency
Ceramic heaters work by passing electricity through a robust ceramic material, which acts as a resistor to generate heat. Their design inherently promotes efficiency.
These elements possess high thermal conductivity and retention. This means they heat up quickly, distribute that heat uniformly, and hold it effectively, requiring less continuous energy to maintain a target temperature.
By minimizing wasted energy during operation, ceramic heaters directly lower electricity consumption. This reduces the load on the power grid and, by extension, cuts down on the carbon emissions associated with electricity generation.
Pillar 2: Exceptional Durability and Longevity
Perhaps the most significant environmental advantage is their long-term durability. Ceramic is an inert material with outstanding resilience.
Unlike many metal elements, ceramic heaters are highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion, especially in applications like water heaters or industrial processes involving moisture. This prevents premature failure and extends their operational lifespan significantly.
This extended service life directly translates to a smaller environmental footprint. Fewer replacements mean less raw material extraction, reduced manufacturing energy, and a significant reduction in landfill waste.
Pillar 3: Material Composition and Recyclability
The materials themselves contribute to the sustainability profile. Ceramics are generally produced from abundant, naturally occurring materials.
The manufacturing processes and materials used often result in a product with higher recyclability compared to more complex or coated metal components. This aligns well with increasingly stringent environmental regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances).
Understanding the Trade-offs
A truly objective analysis requires acknowledging the context and limitations of any technology. While ceramic heaters offer clear benefits, their overall environmental impact is not zero.
The Source of Electricity Matters
A ceramic heater is an electric device. Its ultimate carbon footprint during operation is directly tied to the source of its electricity. If the power grid relies heavily on fossil fuels, using a ceramic heater merely shifts emissions from the point of use to the power plant.
However, as grids increasingly integrate renewable sources like solar and wind, the operational emissions of electric technologies like ceramic heaters approach zero, making them a future-proof choice.
Manufacturing Energy Intensity
Creating ceramics involves firing materials at very high temperatures, which is an energy-intensive process. While the raw materials are abundant, the environmental impact of manufacturing must be considered when evaluating the total lifecycle.
The long service life of a quality ceramic element typically offsets its initial manufacturing footprint over time, but this trade-off is important to recognize.
Not a Universal Solution
While highly versatile, ceramic heaters are not the most efficient solution for every single application. For instance, in some scenarios, technologies like induction heating might achieve even higher efficiency. The key advantage of ceramic often lies in its unique combination of efficiency, durability, and performance in extreme temperature or corrosive environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a heating technology requires aligning its strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational energy use: Ceramic heaters are an excellent choice due to their ability to efficiently convert electricity to heat and maintain temperature with less power.
- If your primary focus is reducing lifecycle waste and replacement costs: The exceptional durability and corrosion resistance of ceramic elements make them a superior long-term investment that minimizes waste.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lowest possible carbon footprint: Pair a high-efficiency ceramic heater with a certifiably renewable electricity source to nearly eliminate its operational environmental impact.
By evaluating both operational efficiency and lifecycle durability, you can make a genuinely sustainable heating decision.
Summary Table:
| Sustainability Aspect | Key Contribution |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High thermal conductivity reduces electricity consumption and emissions |
| Durability | Long lifespan minimizes replacements, lowering material waste |
| Material Recyclability | Made from abundant materials, often recyclable per RoHS standards |
| Operational Impact | Lower energy waste and potential for zero emissions with renewables |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with advanced heating solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique needs, helping you achieve superior energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















