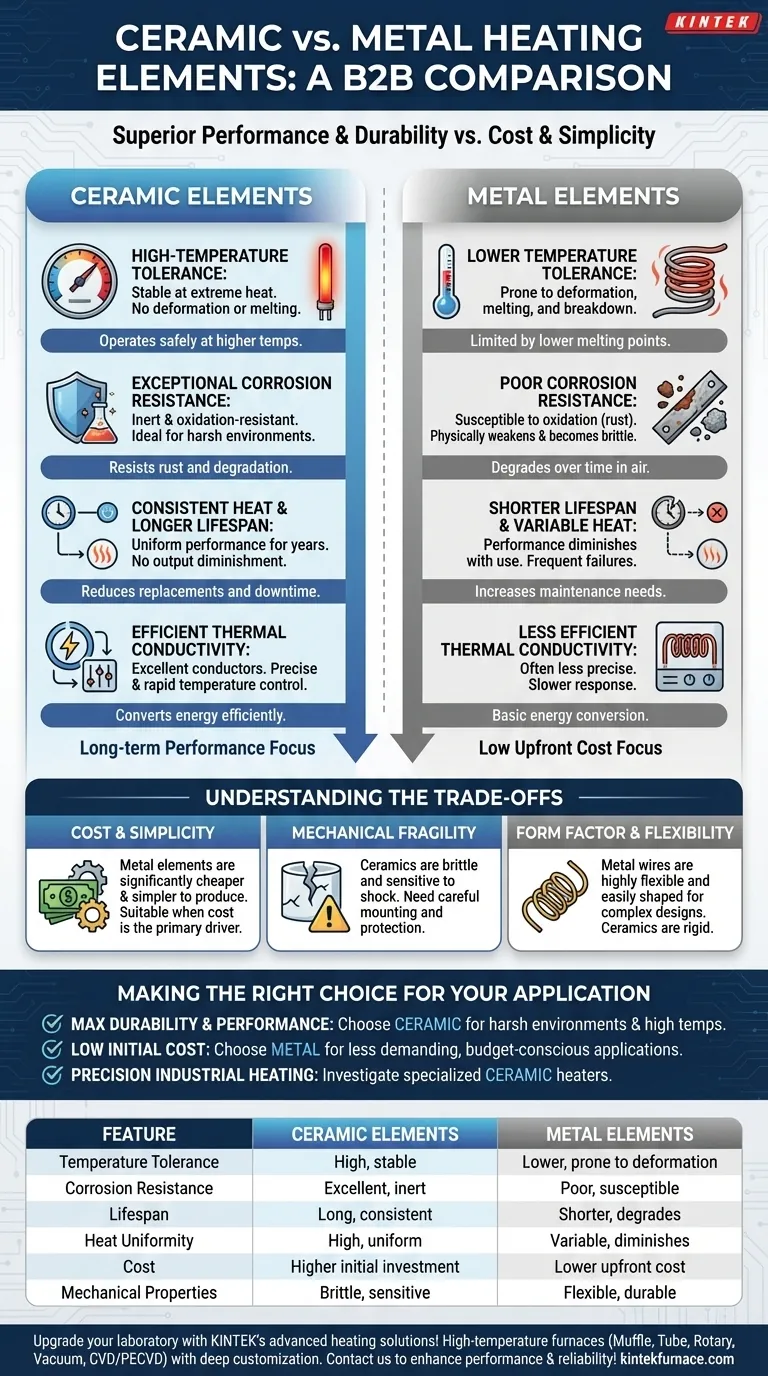
In a direct comparison, ceramic heating elements consistently outperform their metal counterparts in nearly every key metric. Ceramics tolerate significantly higher temperatures, resist corrosion and oxidation, maintain their structural integrity for longer, and provide more uniform and stable heat over their extended lifespan.
While metal heating elements are susceptible to degradation from heat and oxidation, ceramic elements are engineered for longevity and resilience. The choice hinges on whether your priority is long-term performance and reliability or minimizing upfront cost.
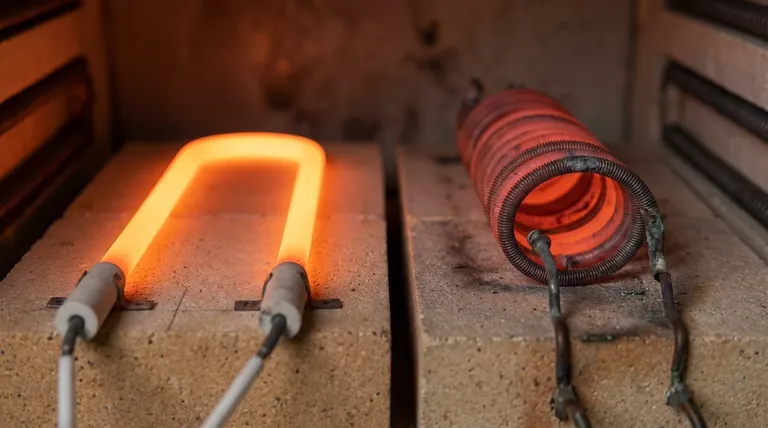

The Core Differences: Durability and Performance
The fundamental advantages of ceramic heaters stem from their material properties. Unlike metals, which are prone to gradual failure, advanced ceramics are designed for stability in extreme conditions.
Superior High-Temperature Tolerance
Ceramic elements possess much higher melting points than traditional metallic heating elements. This allows them to operate at higher temperatures without deforming, melting, or breaking down.
This inherent stability means they can generate more heat safely and reliably.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
Metal elements, when repeatedly heated and cooled in the presence of air, inevitably oxidize. This process, similar to rust, physically weakens the metal, making it brittle and eventually causing it to fail.
Ceramic materials are inert and highly resistant to oxidation and chemical corrosion. This makes them ideal for use in harsh industrial environments and ensures they do not degrade over time.
Consistent Heat and Longer Lifespan
Because they do not oxidize or weaken, ceramic heating elements provide consistent, uniform heating performance for many years. Their output does not diminish with use.
This resistance to thermal fatigue and degradation directly translates to a significantly longer service life, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated downtime.
Efficient Thermal Conductivity
Advanced ceramic materials are excellent thermal conductors, efficiently converting electrical energy into usable heat. This property allows for precise and rapid temperature control across a wide range of applications, from industrial furnaces to high-tech manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While ceramic offers superior performance, metal elements remain common for specific reasons. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for making a sound technical decision.
The Cost and Simplicity Factor
Traditional resistance wire heaters (typically a nickel-chromium alloy) are often significantly cheaper and simpler to produce. For many consumer-grade appliances where low cost is the primary driver and long-term performance is secondary, a metal element is sufficient.
Mechanical Fragility
Ceramics are harder but also more brittle than ductile metals. They can be more susceptible to cracking or shattering from severe mechanical shock or impact. In applications with high vibration or risk of physical impact, the heater's mounting and protection are critical.
Form Factor and Flexibility
Metal heating wires offer exceptional flexibility. They can be easily coiled, shaped, and integrated into complex or compact designs, such as in toasters or handheld hair dryers. Ceramic heaters are typically manufactured into more rigid forms like rods, tubes, or plates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific operational demands and goals of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance in harsh environments: A ceramic element is the clear choice for its superior resistance to high temperatures and corrosion.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost for a less demanding application: A traditional metal element remains a viable and economical option, accepting the shorter lifespan as a trade-off.
- If your primary focus is precision industrial heating: You should investigate specific types of ceramic heaters (e.g., Silicon Carbide) designed for specialized tasks like semiconductor or glass manufacturing.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is about aligning the material's inherent properties with your long-term performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ceramic Heating Elements | Metal Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Tolerance | High, stable at extreme temperatures | Lower, prone to deformation |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, inert and oxidation-resistant | Poor, susceptible to oxidation |
| Lifespan | Long, consistent performance over years | Shorter, degrades with use |
| Heat Uniformity | High, stable and uniform | Variable, can diminish over time |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Mechanical Properties | Brittle, sensitive to shock | Flexible, durable against impact |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your heating performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range where MoSi2 heating elements should not be used for long periods? Avoid 400-700°C to Prevent Failure
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- How can high temperature heating elements be customized for different applications? Tailor Elements for Peak Performance



















