In high-temperature applications, alkali, alkaline oxides, and certain melting metals are severely damaging to silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements. These substances initiate chemical reactions and corrosion above specific temperatures, leading to the formation of new compounds, a degradation of the element's structure, and a significant reduction in both heating efficiency and operational lifespan.
The longevity and performance of silicon carbide heating elements hinge entirely on chemical compatibility within the furnace. Contamination from alkali, alkaline oxides, or specific molten metals initiates irreversible chemical reactions at high temperatures, leading to structural failure and a rapid loss of heating efficiency.

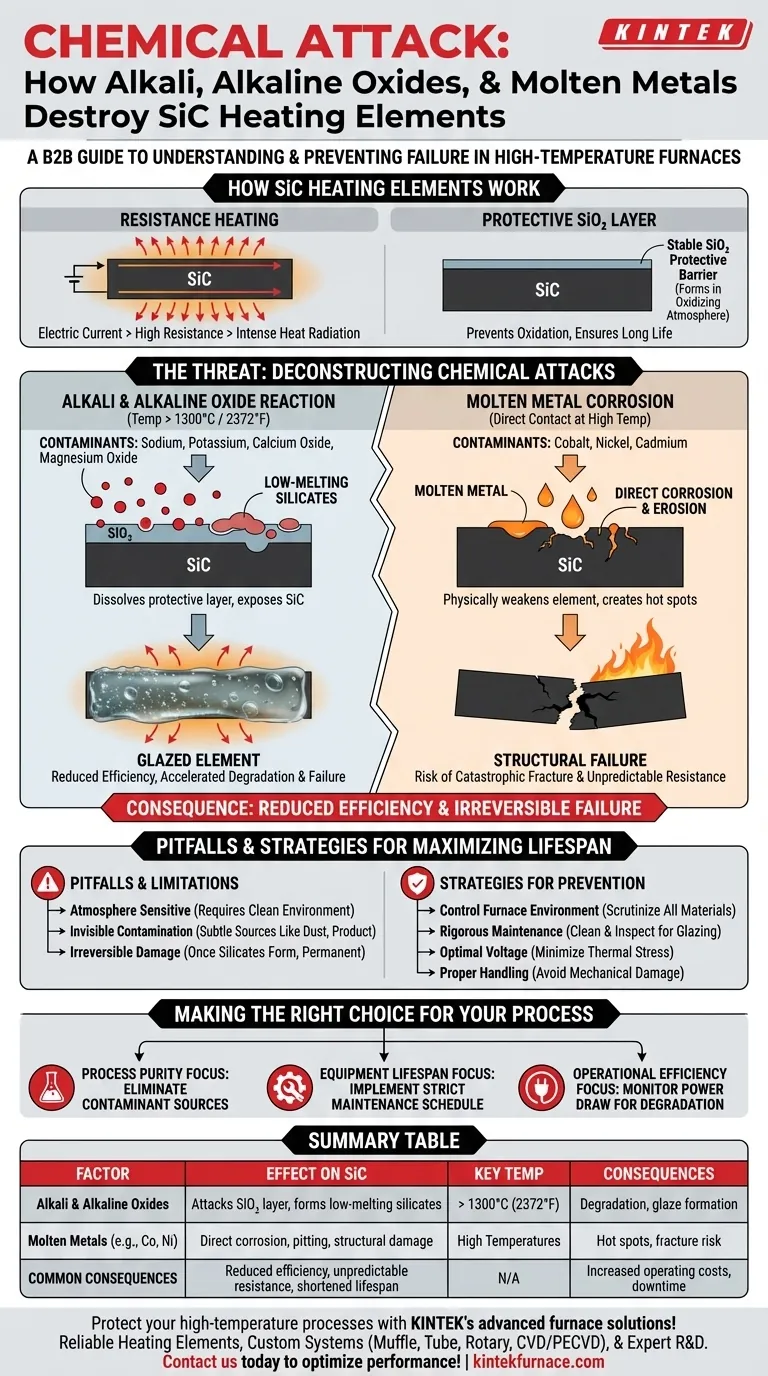
How SiC Elements Work
The Principle of Resistance Heating
Silicon carbide elements function by passing an electric current through the SiC material. Due to its inherent electrical resistance, the element heats up intensely and radiates this thermal energy to heat the furnace and its contents. The temperature is precisely controlled by adjusting the electrical current supplied to the element.
The Protective Silica Layer
Under normal operating conditions in an oxidizing atmosphere, a thin, stable layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) naturally forms on the surface of the SiC element. This glassy layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing further oxidation of the underlying silicon carbide and ensuring a long service life. The chemical attacks discussed here primarily target this vital protective layer.
Deconstructing the Chemical Attacks
The Alkali and Alkaline Oxide Reaction
At temperatures exceeding 1300°C (2372°F), contaminants like alkali (e.g., sodium, potassium) and alkaline earth oxides (e.g., calcium oxide, magnesium oxide) become highly reactive. They attack the protective SiO₂ layer, reacting with it to form various low-melting-point silicates.
This reaction effectively dissolves the protective layer, exposing fresh SiC to the furnace atmosphere. The process creates a "glaze" on the element, reduces its ability to radiate heat efficiently, and ultimately leads to accelerated degradation and failure.
Molten Metal Corrosion
Certain molten metals, such as cobalt, nickel, and cadmium, are directly corrosive to the silicon carbide material itself. When these metals come into contact with the element at high temperatures, they can cause pitting, erosion, and deep structural damage.
This is a direct chemical attack that physically weakens the heating element, creating hot spots and increasing the risk of a catastrophic fracture during operation.
The Consequence: Inefficiency and Failure
Both types of chemical attack lead to the same outcomes. The element's electrical resistance changes unpredictably, its structural integrity is compromised, and its ability to radiate heat is reduced. This forces the power supply to work harder to maintain the target temperature, decreasing overall energy efficiency and shortening the element's lifespan.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Limitations
Atmosphere is a Critical Variable
While SiC elements are known for their high strength and excellent performance, they are not chemically inert. Their suitability is highly dependent on the furnace's internal atmosphere and the specific materials being processed. Contamination can be airborne or outgas directly from the workload.
Contamination is Often Invisible
The source of harmful alkali or oxides can be subtle. It may come from the product being heated, refractory dust from the furnace insulation, or even handling materials used during loading and unloading. What seems like a minor contaminant at room temperature can become a major problem at 1300°C.
Degradation is Irreversible
Once the chemical reaction begins and silicates are formed, the damage is permanent. There is no practical way to repair an element that has suffered from significant chemical attack. The only solution is prevention.
Strategies for Maximizing Element Lifespan
Control Your Furnace Environment
The most effective strategy is to prevent these harmful substances from entering the furnace chamber in the first place. Scrutinize all materials being processed for potential sources of alkali, oxides, or volatile metals.
Implement Rigorous Maintenance
Regular furnace cleaning and inspection are critical. Look for signs of element glazing, discoloration, or deposits on the furnace walls. Early detection of contamination allows you to address the source before extensive damage occurs.
Operate at Optimal Voltages
Operating the furnace at the lowest possible voltage required to achieve your target temperature can reduce thermal stress on the elements. This may slow the rate of chemical reactions and extend the element's useful life.
Ensure Proper Handling and Installation
Mechanical damage, such as chips or scratches incurred during installation, can create weak points on the element's surface. These spots are more susceptible to initiating a chemical attack, so careful handling is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
By understanding these failure mechanisms, you can better control your high-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is process purity: You must ensure the materials being heated do not release alkali, alkaline oxides, or volatile metals at operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment lifespan: Implement a strict maintenance schedule to clean the furnace interior and inspect elements for signs of chemical attack or "glazing."
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Monitor power consumption closely, as an increasing power draw to maintain temperature is a key indicator of element degradation from chemical reactions.
Ultimately, understanding and controlling your furnace's chemical environment is the most critical factor in achieving reliable performance from your silicon carbide heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on SiC Heating Elements | Key Temperature Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
| Alkali & Alkaline Oxides | Attack protective SiO₂ layer, form low-melting silicates, leading to degradation | Above 1300°C (2372°F) |
| Molten Metals (e.g., cobalt, nickel) | Cause direct corrosion, pitting, and structural damage, creating hot spots | Varies by metal, typically high temperatures |
| Consequences | Reduced heating efficiency, unpredictable resistance changes, shortened lifespan | N/A |
Protect your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions to prevent chemical damage and extend equipment lifespan. Contact us today to optimize your furnace environment and achieve superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















