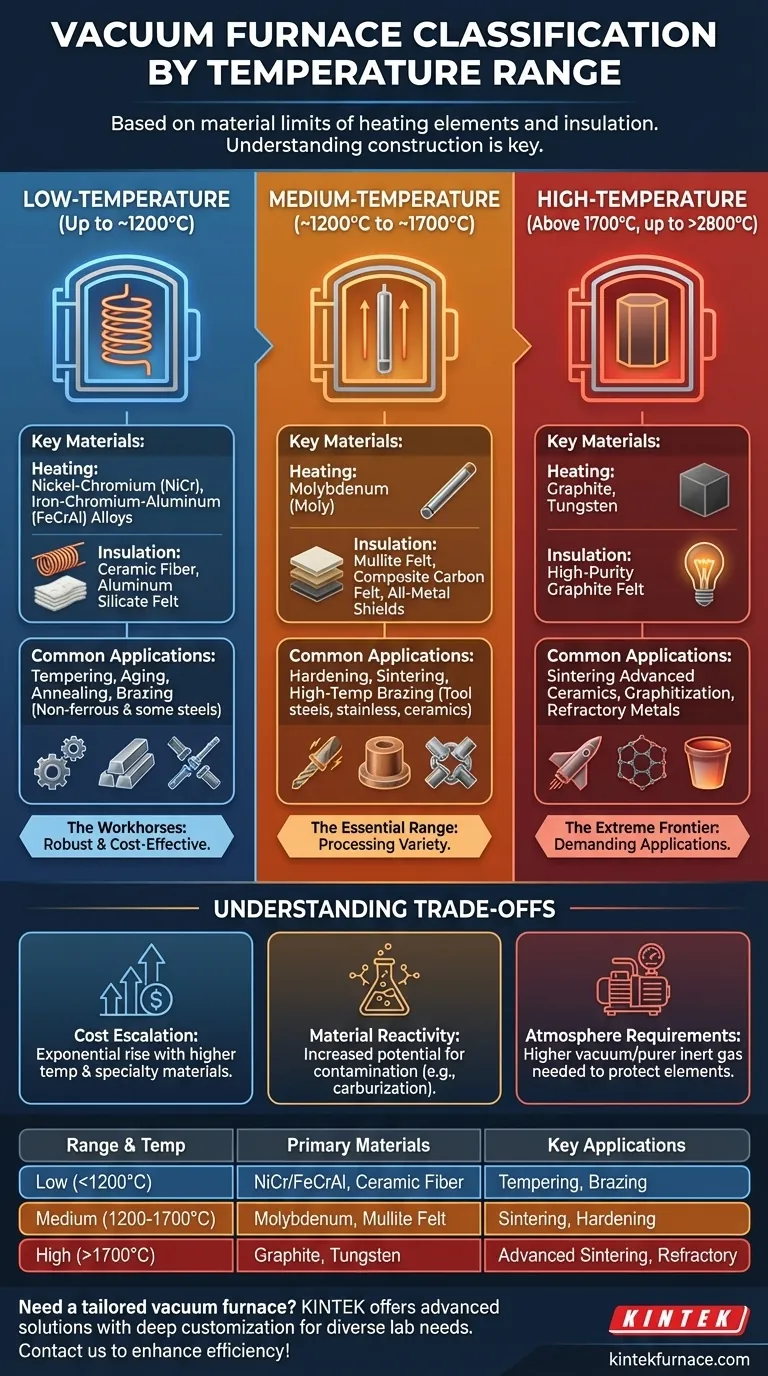
In principle, vacuum furnaces are categorized into three main temperature ranges. Low-temperature furnaces operate up to approximately 1200°C, medium-temperature furnaces reach up to 1700°C, and high-temperature furnaces operate above 1700°C, with some capable of exceeding 2800°C. These divisions are not arbitrary; they are defined by the physical limits of the materials used to construct the furnace's heating elements and insulation.
The classification of a vacuum furnace by temperature is a direct reflection of its internal construction. Understanding the materials used for heating and insulation is more critical than memorizing exact temperature numbers, as this reveals the furnace's true capabilities and limitations.

The Engineering Behind the Temperature Ranges
A furnace's maximum temperature is not a marketing figure but a hard limit imposed by material science. The choice of heating elements and insulation dictates the operational range, cost, and suitable applications for the furnace.
Low-Temperature Furnaces (Up to ~1200°C)
These furnaces are the workhorses for many common thermal processes. They are typically used for applications like tempering, aging, annealing, and brazing of non-ferrous metals and some steels.
The technology is based on robust and cost-effective materials. Heating elements are commonly made of nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys.
For insulation, these furnaces use ceramic fiber or high-temperature aluminum silicate felt, which provide excellent thermal resistance in this range without significant degradation.
Medium-Temperature Furnaces (~1200°C to ~1700°C)
This range is essential for processing a wider variety of materials, including tool steels, stainless steels, and certain ceramics. Common applications include hardening, sintering, and high-temperature brazing.
To achieve these temperatures, furnaces must use refractory metals. The most common heating element is molybdenum (Moly), which has a high melting point but must be protected from oxygen at high temperatures, making the vacuum or inert atmosphere critical.
Insulation shifts to materials like mullite felt or composite carbon felt to handle the increased thermal load. All-metal hot zones with molybdenum or stainless steel shielding are also common.
High-Temperature Furnaces (Above 1700°C)
Reserved for the most demanding applications, these furnaces are used for sintering advanced ceramics, graphitization, and processing refractory metals.
The technology relies on materials with the highest melting points. Graphite is the most common heating element and insulation material due to its stability and strength at extreme temperatures. For specialized applications that cannot tolerate carbon, tungsten is used.
The entire hot zone, including heating elements and insulation, is typically constructed from high-purity graphite felt, which can withstand temperatures well over 2200°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a higher temperature rating than you need introduces significant costs and complexities. It is crucial to match the furnace to the process.
The Escalation of Cost
As the maximum temperature increases, the cost of the furnace rises exponentially. Refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten are far more expensive than NiCr alloys, and the fabrication of high-purity graphite components is a complex, costly process.
Material Reactivity and Contamination
At higher temperatures, the potential for unwanted chemical reactions increases. For example, a graphite heating element will carburize certain metals, making it unsuitable for those processes. An all-metal molybdenum hot zone may be required instead, even if it is more expensive.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Requirements
Protecting heating elements like molybdenum and tungsten from oxidation requires a higher quality vacuum or a purer inert gas backfill. High-temperature operations are less forgiving of leaks or atmospheric impurities, demanding more sophisticated and reliable vacuum pump systems.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final choice should be dictated by the materials you are processing and the thermal profile they require.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treatment or brazing of common alloys: A low-temperature furnace (up to 1200°C) is the most cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is processing tool steels, stainless steels, or basic ceramic sintering: A medium-temperature furnace (up to 1700°C) with molybdenum elements is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research, sintering technical ceramics, or processing refractory metals: A high-temperature furnace (above 1700°C) with graphite or tungsten components is necessary.
Matching the furnace's material science to your process requirements is the key to achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Materials | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low (Up to ~1200°C) | NiCr/FeCrAl alloys, ceramic fiber | Tempering, aging, annealing, brazing of non-ferrous metals |
| Medium (~1200°C to ~1700°C) | Molybdenum, mullite felt | Hardening, sintering, high-temperature brazing of tool steels |
| High (Above 1700°C) | Graphite, tungsten, graphite felt | Sintering advanced ceramics, graphitization, refractory metals |
Need a vacuum furnace tailored to your specific temperature and material requirements? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















