In short, heating elements are physically supported from the furnace sidewalls, suspended from the roof, or laid on the furnace floor. This is accomplished using specialized components like ceramic hooks, high-temperature alloy hangers, or by embedding the elements into pre-formed refractory tiles designed to hold them securely.
The method used to support a heating element is not just about holding it in place. It is a critical design choice that directly impacts temperature uniformity, energy efficiency, and the operational lifespan of both the element and the furnace itself.
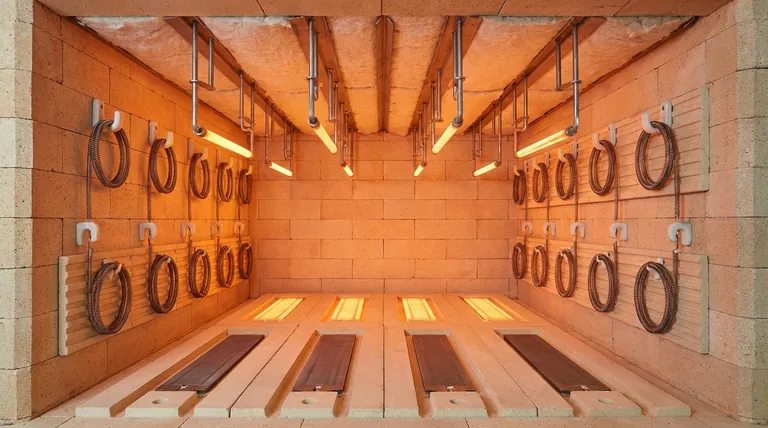

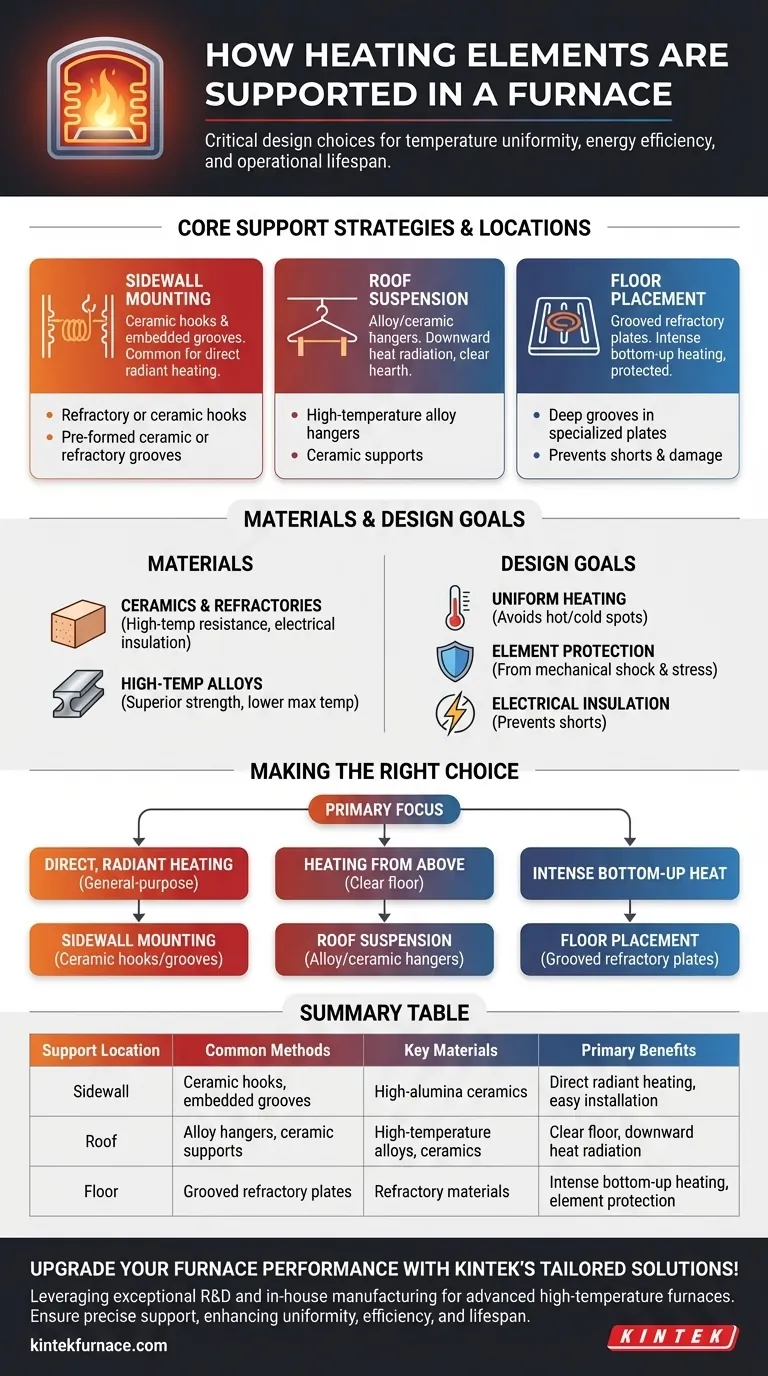
Core Support Strategies and Locations
The placement of a heating element is determined by the furnace's design and its intended application. The goal is always to position the element for optimal heat transfer to the workload while protecting it from damage.
Sidewall Mounting
This is one of the most common configurations. Elements are mounted vertically or horizontally along the interior walls of the furnace.
Supports often include refractory or ceramic hooks that hold coiled wire elements in place. Alternatively, elements can be seated within pre-formed ceramic or refractory grooves built directly into the furnace wall. This protects the element from mechanical damage and ensures consistent spacing.
Roof Suspension
In some furnace designs, particularly those requiring a clear hearth or heating from above, elements are hung from the furnace roof.
This is achieved using high-temperature alloy hangers or ceramic supports that can withstand the furnace's peak temperature without degrading. Suspending elements allows for excellent heat radiation downward onto the workload.
Floor Placement
For applications that require intense bottom-up heating, elements can be laid on the furnace floor.
To prevent short-circuiting and protect the elements from damage by the workload or debris, they are almost always placed within deep grooves in specialized refractory floor plates. This secures the element while allowing heat to radiate upwards efficiently.
The Materials That Make It Possible
The materials used to support heating elements must be able to withstand extreme conditions without failing. The choice depends on the maximum operating temperature and the chemical environment inside the furnace.
Ceramics and Refractories
High-alumina ceramics and other refractory materials are the most common choice for element supports. They offer extremely high-temperature resistance and are excellent electrical insulators. They are used to create hooks, hangers, tubes, and form tiles that hold elements like resistance wires or silicon carbide rods.
High-Temperature Alloys
In furnaces that operate at lower temperatures, supports can be made from high-temperature metal alloys. These materials provide superior mechanical strength and ductility compared to ceramics but have a lower maximum service temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Goals
A support system is not passive; it is an active part of the furnace's performance. The wrong choice can lead to premature element failure and inconsistent results.
The Goal: Uniform Heating
The distribution of elements—whether they are on the walls, roof, or floor—is engineered to create an even temperature zone. A poorly designed support system can cause elements to sag or shift, creating hot and cold spots within the chamber and compromising process results.
The Goal: Element Protection
Many heating elements, such as those made from silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide, are brittle. The support system must protect them from mechanical shock and stress. It must also allow the element to expand and contract thermally during heat-up and cool-down cycles to prevent cracking.
The Goal: Electrical Insulation
The support system's primary safety function is to prevent the heating element from touching the furnace shell or any conductive material, which would cause an electrical short. This is why ceramic and refractory materials, which are excellent electrical insulators at high temperatures, are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal support strategy is directly linked to the furnace's purpose and the type of heating element used.
- If your primary focus is direct, radiant heating in a general-purpose furnace: Sidewall mounting using ceramic hooks or embedded grooves is the most common and effective method.
- If your primary focus is heating from above or keeping the floor clear: Roof suspension using robust ceramic or alloy hangers is the ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is intense heat from the bottom up: Floor elements seated within protective, grooved refractory plates provide durability and powerful heating.
Ultimately, selecting the correct support method is a critical engineering decision that ensures reliable furnace performance and protects your investment in the heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Support Location | Common Methods | Key Materials | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sidewall | Ceramic hooks, embedded grooves | High-alumina ceramics | Direct radiant heating, easy installation |
| Roof | Alloy hangers, ceramic supports | High-temperature alloys, ceramics | Clear floor, downward heat radiation |
| Floor | Grooved refractory plates | Refractory materials | Intense bottom-up heating, element protection |
Upgrade your furnace performance with KINTEK's tailored solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise support for your heating elements, enhancing temperature uniformity, efficiency, and lifespan. Contact us today to discuss how we can meet your unique experimental needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















