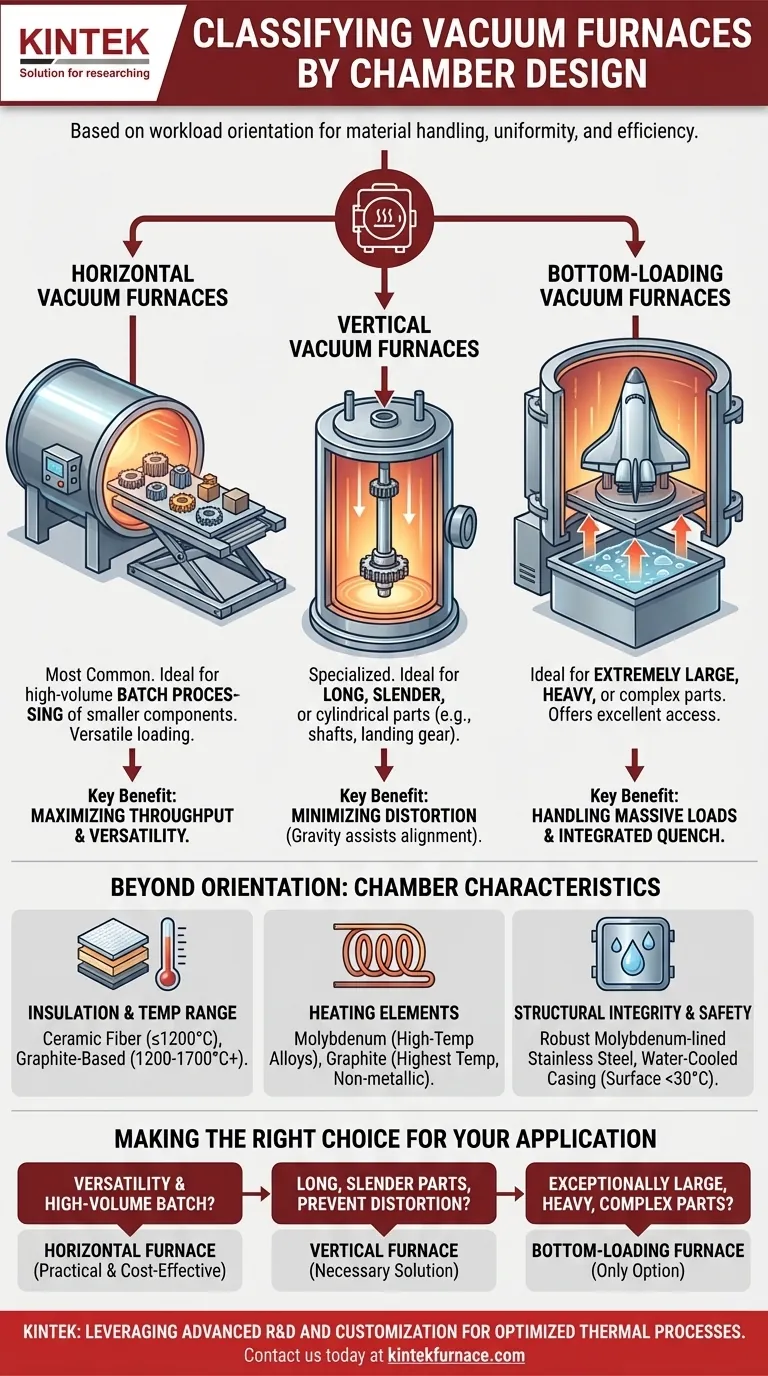
At its core, a vacuum furnace is classified by how the material, or "workload," is oriented and loaded into its chamber. The three primary designs are horizontal, vertical, and bottom-loading, each one tailored for different part geometries, sizes, and processing requirements.
The choice between a horizontal, vertical, or bottom-loading furnace is not a matter of preference but a critical engineering decision. It directly impacts material handling, processing uniformity, the risk of part distortion, and overall operational efficiency.
The Three Core Chamber Designs
The fundamental difference between furnace types is their loading orientation. This single design choice has significant consequences for the entire heat-treating process.
Horizontal Vacuum Furnaces
Horizontal furnaces are the most common design, where the workload is loaded into the chamber on a horizontal plane. Loading is often done manually or with a dedicated loader for heavier parts.
This configuration is highly versatile and well-suited for processing a wide variety of parts, especially in batch operations where many smaller components are treated simultaneously.
Vertical Vacuum Furnaces
In a vertical furnace, the workload is loaded on a vertical axis, either hung from the top or supported from the bottom. This design is specialized for specific part geometries.
Its primary advantage is minimizing distortion and sag in long, slender, or cylindrical parts (like shafts or landing gear) during the high-temperature heating cycle. Gravity works with the part's orientation, not against it.
Bottom-Loading Vacuum Furnaces
A bottom-loading furnace is a type of vertical furnace where the chamber base is lowered, a workload is placed onto it, and the entire assembly is then raised into the furnace body.
This design is ideal for processing extremely large, heavy, or complex-shaped components, such as aerospace structures or large dies. It offers excellent access for loading and is often integrated with a quench tank directly below for rapid, uniform cooling.
Beyond Orientation: Other Key Chamber Characteristics
While orientation is the primary classification, the chamber's internal construction is equally critical to its function.
Insulation and Temperature Range
The chamber's insulation dictates its maximum operating temperature and energy efficiency. Ceramic fiber is common for lower temperatures (up to 1200°C), while graphite-based insulation is required for medium (1200-1600°C) and high-temperature (above 1700°C) applications.
Heating Element Selection
Furnaces are almost exclusively electrically heated. The choice of heating element material depends on the required temperature and operating atmosphere.
Elements are typically made from either high-temperature metallic alloys like molybdenum or non-metallic materials like graphite. Graphite is preferred for the highest temperatures but may not be suitable for all processes.
Structural Integrity and Safety
To withstand the immense pressure difference and high internal heat, chambers are built with robust structures, often using molybdenum-lined stainless steel. The outer casing is typically water-cooled to keep the surface temperature safe for operators, usually below 30°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace design requires balancing the needs of the part, the process, and the operation.
Part Geometry vs. Distortion Risk
For parts prone to bending or sagging at high temperatures, a vertical furnace offers a clear advantage over a horizontal design. The force of gravity is aligned with the part's strongest axis, preserving its geometry.
Throughput vs. Part Size
Horizontal furnaces excel at high-volume batch processing of smaller components, maximizing throughput. Conversely, bottom-loading furnaces are built for capacity, handling single massive parts that would be impossible to load otherwise.
Process Integration
The furnace design can directly impact subsequent process steps. Bottom-loading furnaces provide the fastest path to a liquid quench, as the load can be lowered directly into a tank positioned underneath, ensuring rapid and uniform cooling that is critical for achieving specific material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is versatility and high-volume batch processing: A horizontal furnace is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing long, slender parts while preventing distortion: A vertical furnace is the necessary solution.
- If your primary focus is treating exceptionally large, heavy, or complex components: A bottom-loading furnace is the only design that meets these demands.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's physical design with the specific requirements of your material and process goal is the key to a successful thermal treatment.

Summary Table:
| Chamber Design | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Versatile, batch processing, manual or loader loading | High-volume smaller components, general heat treatment |
| Vertical | Minimizes distortion, vertical axis loading | Long, slender, or cylindrical parts (e.g., shafts, landing gear) |
| Bottom-Loading | Handles large/heavy parts, integrated quench, easy access | Aerospace structures, large dies, complex-shaped components |
Struggling to choose the right vacuum furnace for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether you need high-volume batch processing, distortion-free treatment for slender parts, or handling of massive components. Let us help you optimize your thermal processes—contact us today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















