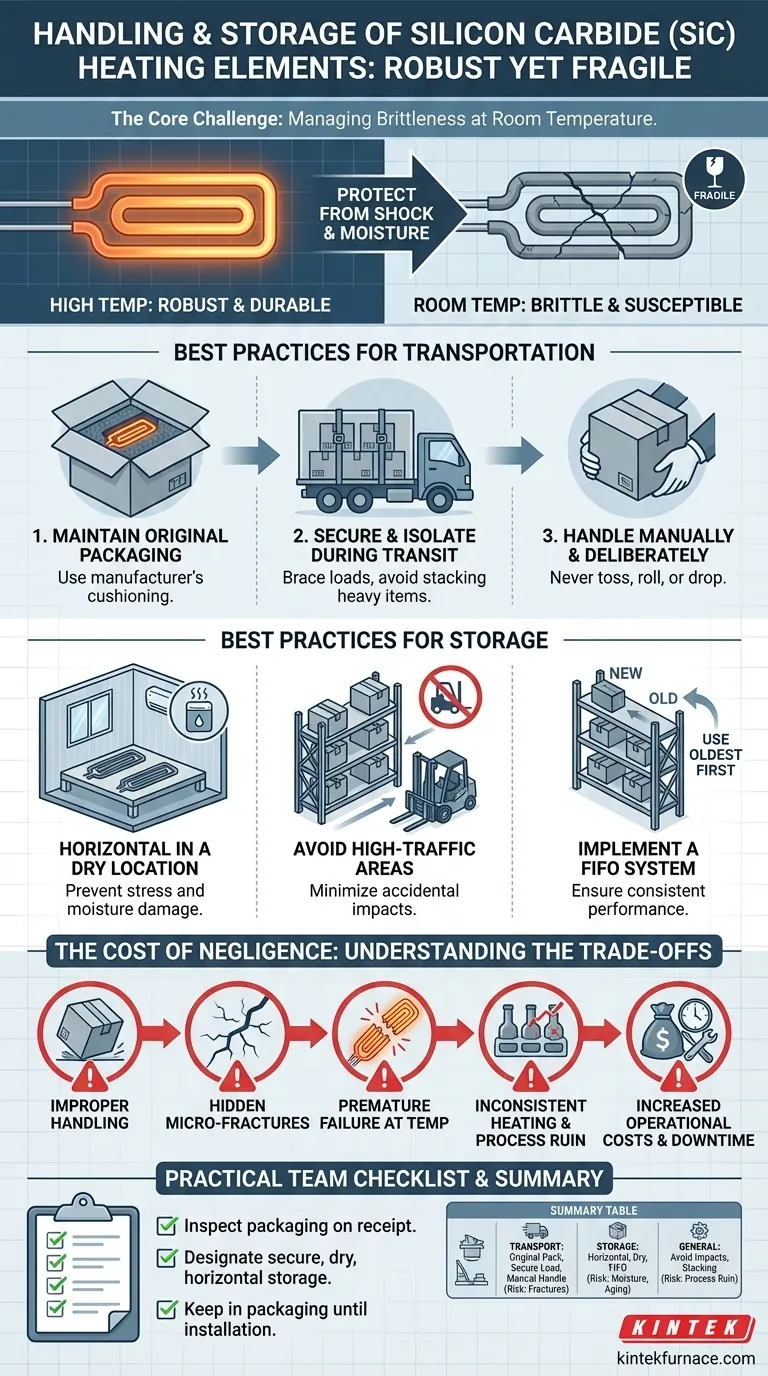
At its core, handling Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements is about protecting a component that is simultaneously robust and fragile. While incredibly durable at high temperatures, these elements are hard and brittle at room temperature, making them highly susceptible to mechanical shock. Therefore, all storage and transportation procedures are designed to prevent impacts, vibration, and exposure to moisture to preserve their structural and electrical integrity.
The central challenge is managing SiC's dual nature: its strength against heat does not translate to mechanical toughness at ambient temperatures. Proper handling is not just about preventing visible breakage; it's about avoiding microscopic cracks that cause premature failure once the element is in service.

The Core Challenge: Brittleness at Room Temperature
Silicon Carbide's value comes from its ability to operate at extreme temperatures without deforming. However, this same crystalline structure makes it behave much like a ceramic coffee mug before it's heated—strong, but unforgiving if dropped.
The Primary Risk: Mechanical Shock
The single greatest threat to a SiC element during handling is mechanical shock. A short drop, a sharp knock, or even strong vibrations during transit can create micro-fractures.
These fractures are often invisible to the naked eye. However, once the element is installed and brought up to temperature, these tiny points of weakness become stress concentrators, leading to catastrophic failure.
The Secondary Risk: Moisture
While less immediate than impact, moisture can also pose a risk. Storing elements in a damp environment can, over time, potentially affect the material properties and protective glazes, especially around the terminal ends.
Best Practices for Transportation and Handling
To mitigate these risks, a disciplined approach is required from the moment the elements leave the manufacturer until they are installed in the furnace.
Maintain Original Packaging
The manufacturer's packaging is specifically engineered to protect the elements. It uses foam cutouts and bracing to cushion the components and prevent movement. Always keep elements in their original box until the moment of installation.
Secure and Isolate During Transit
When moving crates of SiC elements, ensure they are securely braced within the vehicle to prevent shifting, rattling, or falling. Do not stack heavy items on top of the packages, as this can crush the internal supports and damage the elements.
Handle Manually and Deliberately
Never toss, roll, or slide a box containing SiC elements. Each package should be carried carefully by hand to its destination. This simple discipline prevents the accidental impacts that cause most handling-related failures.
Best Practices for Storage
Proper storage is an extension of proper handling, designed to protect the elements from both mechanical and environmental threats over time.
Store Horizontally in a Dry Location
Store the packages flat in a dry, climate-controlled area. Storing them vertically can place unnecessary stress on the elements, especially longer ones. A dry environment prevents any potential degradation from moisture.
Avoid High-Traffic Areas
Keep stored elements away from forklift paths, busy walkways, or areas where they might be accidentally struck. A designated, low-traffic shelf or storage rack is ideal.
Implement a FIFO System
Because a SiC element's electrical resistance naturally increases with age and use, it is wise to use a "First-In, First-Out" (FIFO) inventory system. This ensures that the oldest stock is used first, promoting more consistent performance across all furnace elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Cost of Negligence
Failing to adhere to these handling procedures has significant consequences that go far beyond the replacement cost of a single element.
Hidden Damage and Premature Failure
The most common outcome of improper handling is not immediate, visible breakage. It is the hidden micro-fracture that causes an element to fail weeks or months after installation, often at peak operating temperature.
Inconsistent Heating and Process Ruin
As noted, SiC elements are chosen for their ability to provide uniform and precise heating. A damaged or prematurely aging element will have a different resistance, creating cold spots in the furnace. In applications like metal treatment or ceramics, this can ruin an entire batch, costing far more than the element itself.
Increased Operational Costs
Every unexpected failure leads to furnace downtime, lost production, and emergency maintenance labor. Careful handling is a low-cost insurance policy against these significant and avoidable operational expenses.
A Practical Checklist for Your Team
To ensure reliability, integrate these principles into your team's standard operating procedures.
- If your primary focus is receiving new elements: Inspect the packaging for any signs of crushing, punctures, or impact before accepting the shipment and make a note of any damage.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage: Designate a specific, dry, and secure location for the elements and clearly label shelves to enforce a "First-In, First-Out" policy.
- If your primary focus is installation: Insist that elements remain in their protective packaging until they are at the furnace, ready to be installed, minimizing the risk of a last-minute accident.
Ultimately, treating Silicon Carbide elements with care before they are installed is fundamental to ensuring they deliver the high-temperature performance and reliability your process depends on.
Summary Table:
| Handling Aspect | Key Practices | Risks if Neglected |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Use original packaging, secure loads, handle manually | Micro-fractures, premature failure |
| Storage | Store horizontally in dry, low-traffic areas, implement FIFO | Moisture damage, inconsistent heating |
| General Handling | Avoid impacts, vibrations, and stacking heavy items | Increased costs, process ruin |
Ensure your laboratory's high-temperature processes run smoothly with KINTEK's reliable solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Protect your investments—contact us today for expert advice and tailored heating element handling support!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















