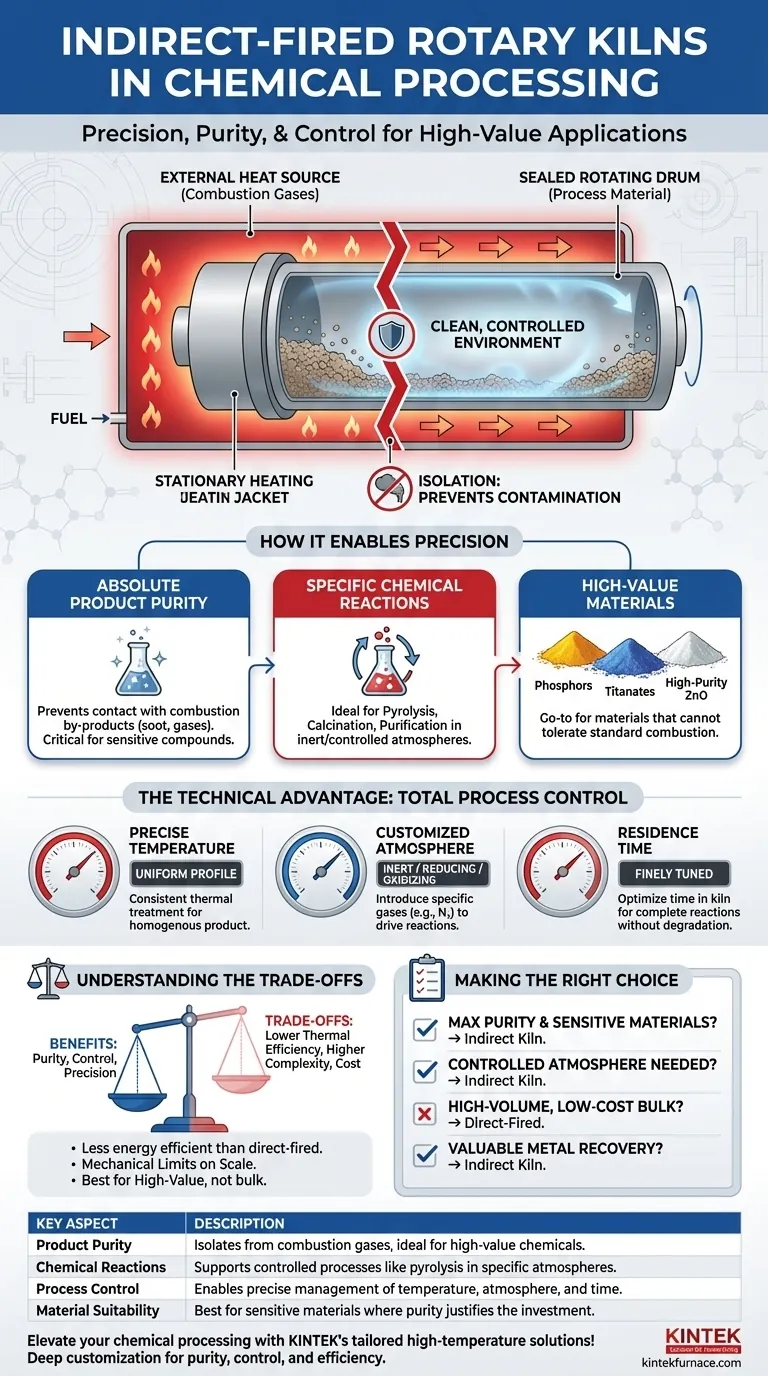
In chemical processing, indirect-fired rotary kilns are used for the synthesis, decomposition, and specialized thermal treatment of compounds where product purity is paramount. By heating the material through the shell of the rotating drum rather than through direct contact with combustion gases, these kilns prevent contamination and allow for precise control over the processing atmosphere.
An indirect-fired rotary kiln is selected when the primary goal is not just to heat a material, but to transform it under exact, repeatable conditions without introducing impurities. Its value lies in control, making it indispensable for high-value and sensitive chemical applications.
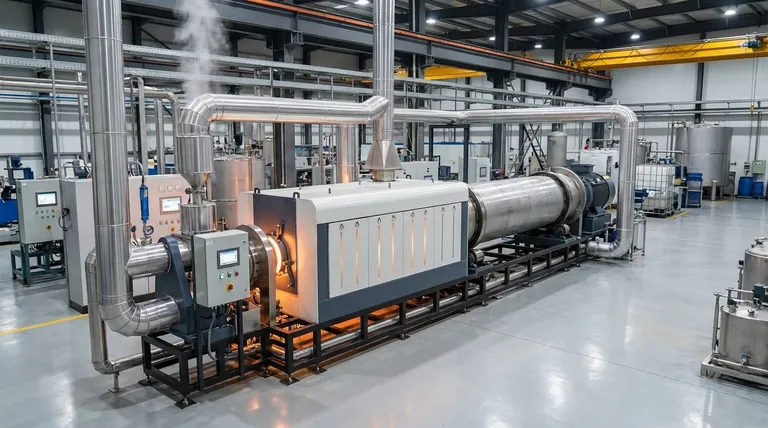

How Indirect Kilns Enable Precision Chemical Transformations
The fundamental design of an indirect kiln—separating the heat source from the process material—is what unlocks its unique capabilities in the chemical industry. This separation is the key to achieving high levels of purity and enabling specific, sensitive reactions.
Ensuring Absolute Product Purity
In an indirect kiln, the material tumbles inside a sealed rotating cylinder that is heated from the outside. This design prevents any contact with combustion by-products like soot or flue gases.
This isolation is critical when processing chemicals where even trace amounts of contamination can render the final product unusable.
Achieving Specific Chemical Reactions
The controlled environment is ideal for driving specific chemical outcomes. These kilns excel at processes like pyrolysis, calcination, and purification.
For example, they are used for the thermal decomposition of compounds in an inert atmosphere or for carefully controlled synthesis reactions between multiple solid or gaseous inputs.
Processing High-Value and Sensitive Materials
Indirect kilns are the go-to solution for materials that cannot tolerate exposure to a standard combustion atmosphere.
This includes high-value specialty chemicals such as phosphors, titanates, and high-purity zinc oxide, where precise chemical composition and structure define their performance.
The Technical Advantage: Total Process Control
The ability to independently manage process variables gives engineers unparalleled command over the final product characteristics. This level of control is the core technical advantage of the indirect kiln.
Precise Temperature Management
Heating the kiln externally allows for a very uniform and precisely controlled temperature profile along the length of the drum.
This ensures every particle of the material receives the same thermal treatment, leading to a highly consistent and homogenous final product.
Customized Atmospheric Control
Because the processing chamber is sealed, the internal atmosphere can be completely customized. Operators can introduce inert gases (like nitrogen), reducing gases, or oxidizing gases to facilitate specific reactions.
This capability is essential for preventing unwanted oxidation or for intentionally driving reduction reactions, such as reducing barium sulfate (heavy spar).
Controlling Residence Time
The combination of the kiln's rotation speed, its angle of inclination, and its length determines the residence time—how long the material spends inside.
This variable can be finely tuned to ensure a chemical reaction proceeds to completion without overheating or degrading the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, indirect-fired kilns are not a universal solution. Their design brings inherent trade-offs that must be considered against process requirements and economic realities.
Thermal Efficiency
Indirect heating is inherently less thermally efficient than direct-fired methods, where hot gases pass directly through the material. Heat must first transfer through the kiln shell, resulting in greater energy loss to the surrounding environment.
This often translates to higher fuel consumption and operational costs compared to direct-fired alternatives.
Mechanical Complexity and Scale
The external furnace or heating jacket adds mechanical complexity and can limit the maximum achievable diameter of the kiln. This can make them less suitable for extremely high-throughput applications where direct-fired "brute force" heating is more economical.
Material Suitability
The higher capital and operational costs associated with indirect kilns mean they are typically reserved for processes where the added value from purity and control justifies the investment. They are generally not the first choice for processing low-cost bulk materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use an indirect-fired rotary kiln must be based on a clear understanding of your material's sensitivity and your final product requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum product purity and processing sensitive materials: The isolation from combustion gases makes an indirect kiln the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is driving a specific reaction in a controlled atmosphere: An indirect kiln offers unparalleled control over the processing environment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost bulk processing: A direct-fired kiln is likely the more economical and energy-efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is recovering valuable metals from waste streams: The controlled atmosphere of an indirect kiln is essential for processes like volatilization.
Ultimately, selecting an indirect-fired kiln is a strategic decision to prioritize precision and purity over raw throughput and energy cost.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Purity | Prevents contamination by isolating materials from combustion gases, ideal for high-value chemicals. |
| Chemical Reactions | Supports pyrolysis, calcination, and synthesis in controlled atmospheres like inert or reducing gases. |
| Process Control | Enables precise temperature, atmosphere, and residence time management for consistent outcomes. |
| Material Suitability | Best for sensitive, high-value materials where purity and control justify higher costs. |
Elevate your chemical processing with KINTEK's tailored high-temperature solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced indirect-fired rotary kilns and other furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering purity, control, and efficiency for high-value applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- How do pyrolysis rotary kiln reactors function? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Value Conversion
- What are the advantages of a rotary kiln for bio-reductants? Achieve Industrial-Scale Uniformity and Scalability
- What is the working principle of a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- What are the key components and parameters of a rotary kiln? Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing
- Why is an industrial-grade rotary reactor necessary in the oil sludge pyrolysis process? Maximize Yield & Efficiency



















