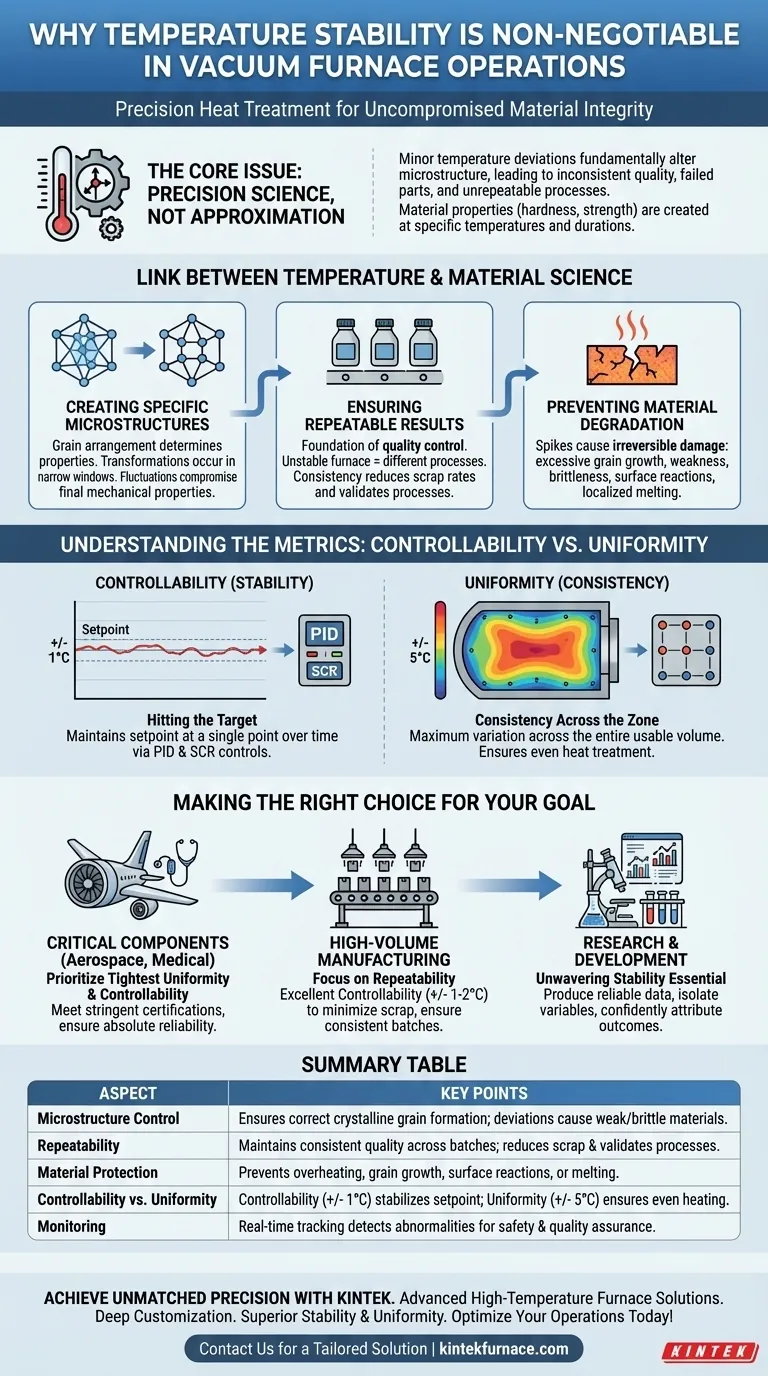
In short, temperature stability is non-negotiable because heat treatment is a precise science, not an approximation. Even minor temperature deviations can fundamentally alter a material's microstructure, leading to inconsistent product quality, failed parts, and unrepeatable manufacturing processes.
The core issue is that the desired physical properties of a material—such as its hardness, strength, and durability—are directly created by holding it at specific temperatures for precise durations. Any instability in temperature introduces a critical variable that undermines the integrity of the entire process.

The Link Between Temperature and Material Science
A vacuum furnace is more than an oven; it is a precision instrument designed to manipulate the atomic structure of materials. Understanding this is key to appreciating why stability is paramount.
Creating Specific Microstructures
The properties of a metal are determined by its microstructure, which is the specific arrangement of its crystalline grains. Processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering are designed to create very specific structures. These transformations only occur correctly within narrow temperature windows. A fluctuation of even a few degrees can result in the wrong structure forming, compromising the material's final mechanical properties.
Ensuring Repeatable Results
In any manufacturing environment, repeatability is the foundation of quality control. If a furnace's temperature fluctuates between batches, you are not running the same process. This leads to one batch meeting specifications while the next fails, increasing scrap rates and making process validation impossible. Stability ensures every part receives the exact same thermal treatment.
Preventing Material Degradation
Uncontrolled temperature spikes, even if brief, can cause irreversible damage. Overheating can lead to excessive grain growth, which often makes a material weaker or more brittle. It can also cause undesirable surface reactions or even localized melting, rendering the part useless.
Understanding the Metrics: Controllability vs. Uniformity
While often discussed together, it's crucial to distinguish between temperature stability (controllability) and temperature uniformity. The specifications of your furnace reveal the difference.
Controllability: Hitting the Target
Controllability, often specified as +/- 1°C, refers to how well the furnace's control system can maintain the setpoint at the location of the primary thermocouple. This is achieved through sophisticated PID loop controls and SCR power regulation, which anticipate and smooth out power delivery to the heating elements. This is a measure of stability over time at a single point.
Uniformity: Consistency Across the Zone
Uniformity, often specified as +/- 5°C, describes the maximum temperature variation across the entire usable volume of the furnace's hot zone. A large part may experience a slightly different temperature on one side than the other. While the control point might be perfectly stable, poor uniformity means different areas of a part are undergoing a different heat treatment process simultaneously.
The Impact of Continuous Monitoring
Achieving both stability and uniformity requires continuous monitoring. Modern systems track temperature and atmosphere in real-time to detect abnormalities instantly. This not only ensures consistent quality but also enhances safety by preventing the formation of hazardous conditions or uneven heating that could damage the furnace or the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your required level of temperature stability directly depends on the sensitivity of your material and the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is critical components (e.g., aerospace, medical): You must prioritize the tightest possible temperature uniformity and controllability to meet stringent industry certifications and ensure absolute reliability.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: Your main concern is process repeatability, so investing in a furnace with excellent controllability (+/- 1-2°C) is key to minimizing scrap and ensuring consistent quality batch after batch.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Unwavering temperature stability is essential for producing reliable data, as it allows you to isolate variables and confidently attribute outcomes to your intended process changes.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control within your vacuum furnace is the first step toward mastering the quality and performance of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Microstructure Control | Ensures correct crystalline grain formation; deviations cause weak or brittle materials. |
| Repeatability | Maintains consistent quality across batches; reduces scrap rates and validates processes. |
| Material Protection | Prevents overheating, grain growth, and irreversible damage like surface reactions or melting. |
| Controllability vs. Uniformity | Controllability (+/- 1°C) stabilizes setpoint; uniformity (+/- 5°C) ensures even heating across the zone. |
| Monitoring | Real-time tracking detects abnormalities for safety and quality assurance. |
Achieve Unmatched Precision in Your Heat Treatment Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, high-volume manufacturing, or R&D, our furnaces deliver superior temperature stability and uniformity to enhance your product quality and efficiency.
Ready to optimize your operations? Contact us today for a tailored solution that ensures reliable, repeatable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density



















