At its core, silicon carbide is used in harsh industrial settings because it provides a rare combination of exceptional chemical resistance and the ability to maintain its structural integrity at extremely high temperatures, far exceeding the limits of many specialized metal alloys.
Silicon carbide is not just a replacement for metal; it's a solution for operational conditions where metals fundamentally fail. It thrives in environments where extreme heat and aggressive chemical corrosion occur simultaneously, making it indispensable for specific, high-value industrial processes.

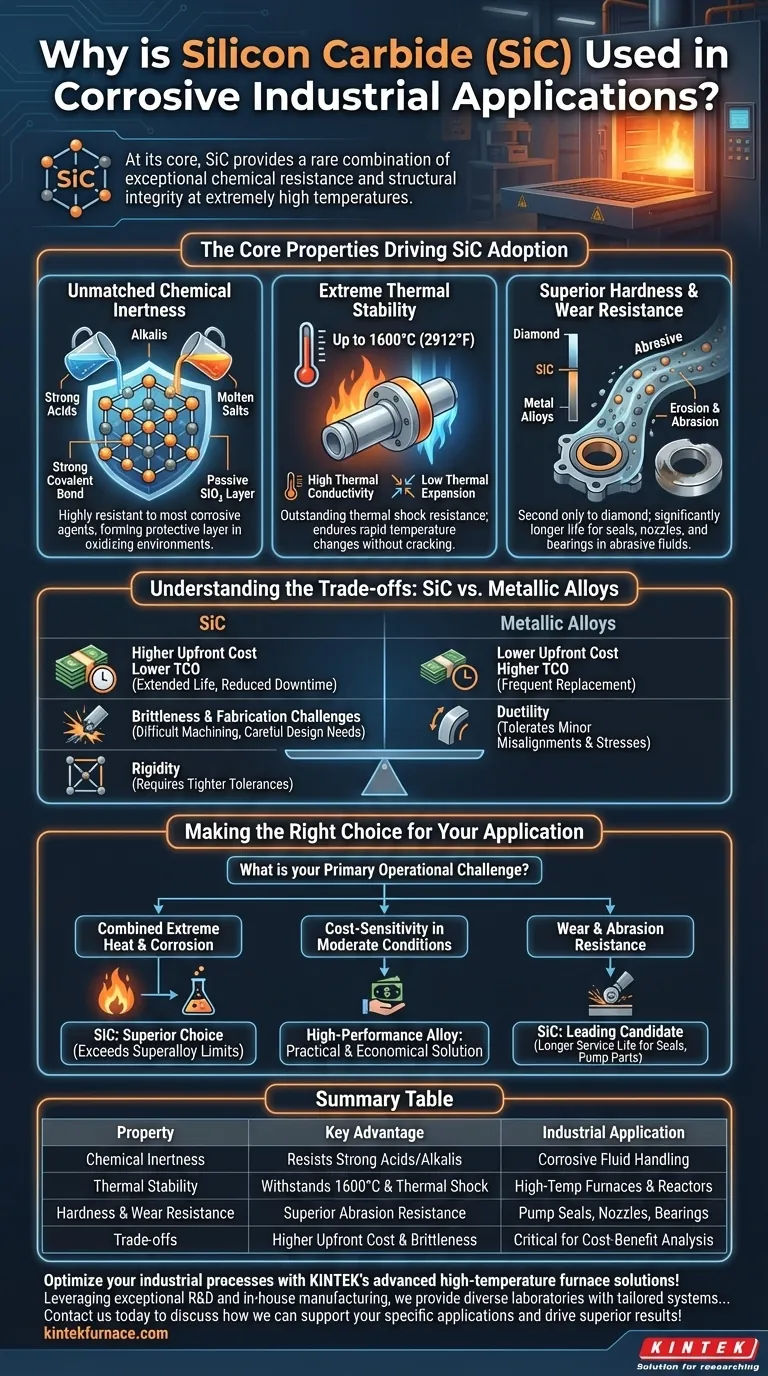
The Core Properties Driving SiC Adoption
To understand why silicon carbide (SiC) is specified for these demanding roles, we must look at its fundamental material properties. It is not just one feature, but the combination of several, that makes it so valuable.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
The primary reason for its use in corrosive environments is its remarkable chemical stability. The powerful covalent bond between silicon and carbon atoms is incredibly strong and difficult for corrosive agents to break.
This makes SiC highly resistant to nearly all strong acids, alkalis, and molten salts, even at elevated temperatures. In many oxidizing environments, it also forms a passive, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), which further shields the underlying material from chemical attack.
Extreme Thermal Stability
Silicon carbide performs exceptionally well under intense heat, with some grades capable of operating in air at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F).
Beyond simply withstanding heat, it has high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion. This combination provides outstanding resistance to thermal shock, meaning it can endure rapid temperature changes without cracking—a common failure point for many other ceramic materials.
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
In many industrial processes, corrosion is accompanied by erosion and abrasion from flowing liquids, slurries, or gases. Silicon carbide is one of the hardest commercially available materials, second only to diamond.
This extreme hardness translates directly into superior wear resistance. Components like pump seals, nozzles, bearings, and valve parts made from SiC last significantly longer than their metal counterparts in abrasive fluid-handling applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SiC vs. Metallic Alloys
While silicon carbide has clear advantages, it is not a universal solution. A trusted advisor must weigh its benefits against its practical limitations, particularly when compared to high-performance alloys like nickel-chromium.
The Cost Factor
The production of high-purity silicon carbide is an energy-intensive and complex process. This results in a significantly higher upfront material cost compared to most metallic alloys.
However, a proper analysis must consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). The extended service life and reduced downtime provided by SiC components can often justify the initial investment in critical applications.
Brittleness and Fabrication Challenges
Like most advanced ceramics, silicon carbide is a brittle material. Unlike metals, which bend and deform under stress (ductility), SiC will fracture catastrophically if subjected to a sharp impact or excessive tensile load.
This brittleness, combined with its extreme hardness, also makes it very difficult and expensive to machine into complex shapes. This adds to the final component cost and requires careful design considerations to avoid stress concentrations.
The Limits of "Flexibility"
When references mention SiC being less "temperature-flexible" than alloys, it often points to this lack of ductility. Metallic components can often tolerate minor misalignments, vibrations, and thermal stresses by deforming slightly.
A system designed with silicon carbide components must be engineered with much tighter tolerances to account for the material's rigidity and prevent mechanical failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational challenge. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for the job.
- If your primary focus is combined extreme heat and corrosion: Silicon carbide is the superior choice, as it operates in conditions where even superalloys degrade.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitivity in moderate conditions: A high-performance nickel-chromium alloy is often the more practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is wear and abrasion resistance: Silicon carbide is a leading candidate for components like seals, nozzles, and pump parts, delivering a much longer service life than hardened steels or alloys.
Choosing the right material is about matching its unique profile to the full spectrum of your operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Advantage | Industrial Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists strong acids, alkalis, and molten salts | Corrosive fluid handling systems |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands up to 1600°C and thermal shock | High-temperature furnaces and reactors |
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Superior abrasion resistance, second only to diamond | Pump seals, nozzles, and bearings |
| Trade-offs | Higher upfront cost and brittleness vs. alloys | Critical for cost-benefit analysis in harsh conditions |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability and efficiency in corrosive environments. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















