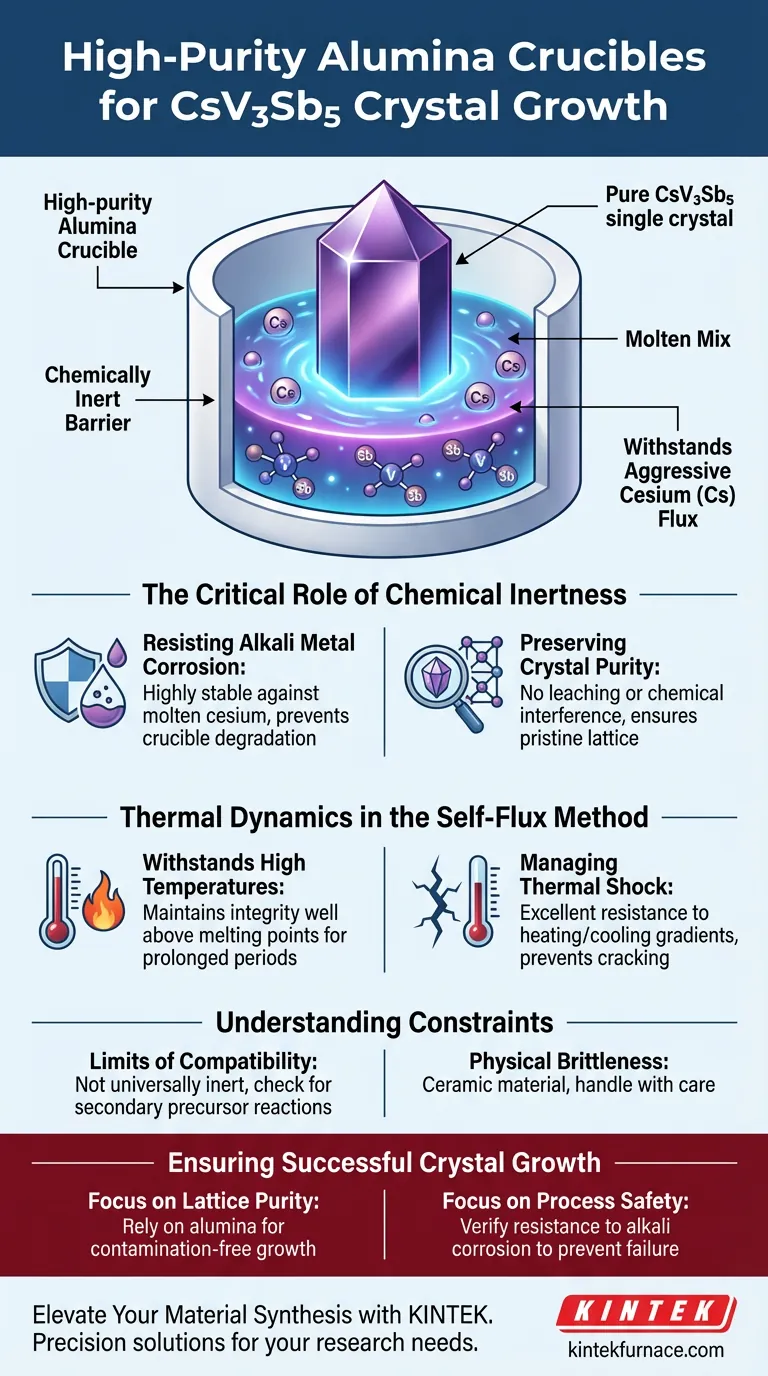
High-purity alumina crucibles are the preferred containment vessel for growing CsV3Sb5 single crystals because they provide a chemically inert barrier against aggressive reactants. Specifically, these crucibles withstand the corrosive nature of the alkali metal flux (cesium) at high temperatures, preventing the container from degrading or introducing impurities that would compromise the crystal lattice.
The success of the self-flux method hinges on the container's ability to remain invisible to the reaction. High-purity alumina is selected not just for its heat resistance, but because it refuses to chemically interact with the corrosive cesium flux, ensuring the final crystal remains pure.

The Critical Role of Chemical Inertness
Resisting Alkali Metal Corrosion
The growth of CsV3Sb5 involves the use of alkali metal fluxes, specifically cesium (Cs). These metals are highly reactive and chemically aggressive, particularly in a molten state.
Standard laboratory crucibles often degrade or react when exposed to these harsh conditions. High-purity alumina offers exceptional chemical stability, effectively acting as a shield against this corrosion.
Preserving Crystal Purity
The primary objective in single crystal growth is achieving a pristine lattice structure. Any reaction between the flux and the crucible wall can introduce foreign atoms into the melt.
Alumina’s stability ensures that the crucible material does not leach into the growth environment. This prevents chemical interference, allowing the CsV3Sb5 crystal to form without unintentional doping or defect formation.
Thermal Dynamics in the Self-Flux Method
Withstanding High Temperatures
The self-flux method requires prolonged periods of high heat to ensure the raw materials are fully dissolved.
High-purity alumina acts as a reliable carrier for these materials, maintaining its structural integrity at temperatures well above the melting points of the precursors.
Managing Thermal Shock
Crystal growth is rarely a static thermal process; it involves specific heating and cooling gradients to encourage nucleation.
Alumina possesses excellent thermal shock resistance. This property ensures the crucible does not crack or shatter during the temperature fluctuations required to precipitate the crystals from the flux.
Understanding the Constraints
The Limits of Compatibility
While alumina is exceptionally stable against alkali metals like cesium and potassium, it is not universally inert.
Researchers must ensure that no other secondary precursors in the mix have a specific affinity for reacting with aluminum oxide.
Physical Brittleness
Despite its thermal robustness, high-purity alumina remains a ceramic material.
It is inherently brittle and susceptible to mechanical failure if handled roughly, regardless of its chemical resistance.
Ensuring Successful Crystal Growth
To maximize the quality of your CsV3Sb5 samples, align your equipment choices with your experimental priorities:
- If your primary focus is Lattice Purity: Rely on high-purity alumina to prevent the leaching of contaminants that occurs with less stable crucible materials.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Ensure your crucible choice is specifically verified for resistance to alkali metal corrosion to prevent containment failure at high heat.
By matching the containment material to the chemical aggression of the flux, you ensure a controlled environment essential for high-quality materials synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for CsV3Sb5 Growth |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from aggressive alkali metal (Cesium) flux. |
| High Purity | Prevents leaching of impurities into the crystal lattice structure. |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains structural integrity at high temperatures over long periods. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands precise heating and cooling gradients without cracking. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in single crystal growth starts with the right containment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance high-purity alumina crucibles and lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique research needs. Ensure the purity of your CsV3Sb5 samples and prevent containment failure with our specialized laboratory solutions.
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace and crucible requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Yongqing Cai, Kai Chen. Emergence of quantum confinement in topological kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5. DOI: 10.1038/s43246-024-00461-z
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory vacuum system contribute to high-purity high-entropy alloys? Essential Insights
- Why are YSZ milling balls selected for mixing Mn2AlB2 precursor powders? Ensure High-Purity MAB Phase Synthesis
- How does a sealed high-purity graphite reaction box function? Optimize Sb-Ge Thin Film Selenization
- Why are alumina or ceramic crucibles selected for KCdCl3 perovskite? Ensure High Purity and Thermal Stability
- Why is zirconia grinding media preferred for NN-10ST ceramic powders? Ensure Purity & Dielectric Performance
- What are the technical advantages of using ceramic crucibles for moxa floss pyrolysis? Ensure Precise Thermal Analysis
- How does the impeller in a water circulating vacuum pump function to create a vacuum? Discover the Liquid Piston Mechanism
- How do specialized molds or supports contribute to the standardization of sludge samples? Unlock Precision in Drying




