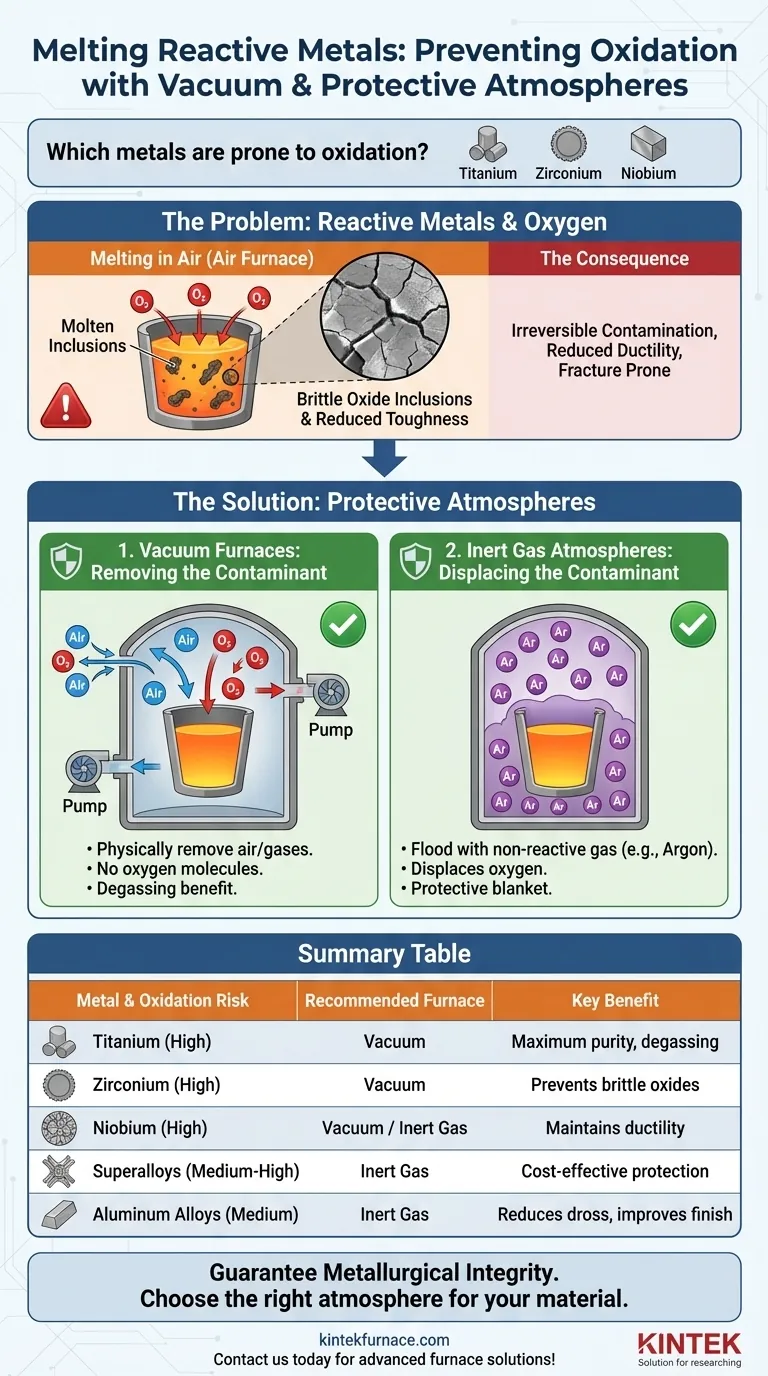
When melting certain metals, controlling the furnace atmosphere is not an option—it is a fundamental requirement. Metals such as titanium, zirconium, and niobium, along with other oxygen-sensitive alloys, are highly reactive and will readily oxidize when melted in the presence of air. To prevent catastrophic contamination and preserve their unique properties, these metals must be melted in a vacuum or under a protective inert gas atmosphere.
The core issue is that the extreme heat of melting dramatically accelerates the chemical reaction between reactive metals and atmospheric oxygen. This contamination compromises the metal's internal structure, and using a vacuum or inert gas furnace is the only effective way to prevent it.

The Challenge of Highly Reactive Metals
To understand why a special atmosphere is necessary, we must first understand what makes these metals "reactive" and the severe consequences of failing to protect them.
What Makes a Metal "Reactive"?
Reactive metals have a very high affinity for oxygen, meaning they form strong, stable chemical bonds with oxygen atoms. At room temperature, this often creates a thin, protective oxide layer on the surface.
However, at melting temperatures, this reactivity increases exponentially. The liquid metal's surface is constantly moving, exposing a fresh, highly active face to any gases in the furnace, ready to absorb contaminants.
The Consequences of Oxidation
When a reactive metal oxidizes during melting, the oxygen doesn't just sit on the surface. It dissolves into the molten metal and forms hard, brittle oxide inclusions throughout the material's internal structure.
This contamination is irreversible and severely degrades the final product's mechanical properties. It leads to reduced ductility and toughness, making the metal prone to fracture and rendering it useless for the high-performance applications it was designed for.
How Protective Atmospheres Solve the Problem
Vacuum and inert gas atmospheres work by removing or displacing the oxygen, starving the chemical reaction before it can begin.
Vacuum Furnaces: Removing the Contaminant
A vacuum furnace uses pumps to physically remove air and other gases from the melting chamber. By creating a very low-pressure environment, there are virtually no oxygen molecules left to react with the molten metal.
This method is extremely effective and is often the preferred choice for the most sensitive materials, like titanium. It also has the added benefit of pulling dissolved gases out of the melt, a process known as degassing, which further increases the purity of the final casting.
Inert Gas Atmospheres: Displacing the Contaminant
This method involves flooding the furnace chamber with a chemically non-reactive gas, most commonly argon.
Because argon is heavier than the air, it sinks and displaces the oxygen, creating a protective blanket over the molten metal. The inert gas will not react with the metal, even at extreme temperatures, effectively shielding it from contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While both methods are effective, the choice between them involves considering the specific metal, the required purity, and operational costs.
Vacuum vs. Inert Gas
A high-vacuum environment offers the highest level of protection by actively removing contaminants. It is the gold standard for metals where even parts-per-million levels of oxygen can cause failure.
An inert gas atmosphere is a highly reliable and often more cost-effective solution for many oxygen-sensitive alloys. It is simpler to implement but requires careful management to ensure a complete and consistent purge of the atmosphere.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
A poorly maintained vacuum system with a leak can be disastrous. It continuously pulls a small stream of oxygen into the chamber, directly feeding it to the molten metal.
Similarly, improper purging with inert gas can leave pockets of air trapped in the furnace, leading to localized oxidation. The purity of the inert gas itself is also critical, as contaminated gas will introduce impurities into the melt.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of atmospheric protection should be dictated by the material you are working with and the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for metals like titanium and zirconium: A high-vacuum furnace is the definitive standard to eliminate gaseous contamination and ensure optimal material properties.
- If your primary focus is melting sensitive superalloys or aluminum alloys cost-effectively: A properly managed inert gas atmosphere using high-purity argon provides excellent protection.
- If your primary focus is improving the quality of even less reactive metals: Using a protective atmosphere can still reduce dross formation, improve surface finish, and yield a cleaner final product.
By controlling the furnace atmosphere, you are not just preventing surface tarnish; you are fundamentally guaranteeing the metallurgical integrity of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Metal | Oxidation Risk | Recommended Furnace Type | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | High | Vacuum | Maximum purity, degassing |
| Zirconium | High | Vacuum | Prevents brittle oxides |
| Niobium | High | Vacuum/Inert Gas | Maintains ductility |
| Superalloys | Medium-High | Inert Gas | Cost-effective protection |
| Aluminum Alloys | Medium | Inert Gas | Reduces dross, improves finish |
Maximize your metal purity and performance with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! We specialize in high-temperature furnaces, including Vacuum, Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're working with reactive metals like titanium or cost-sensitive alloys, our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures reliable, contamination-free melting. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















