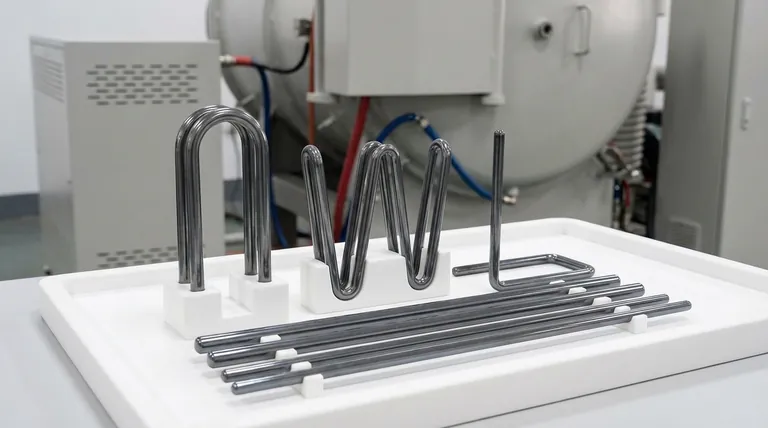
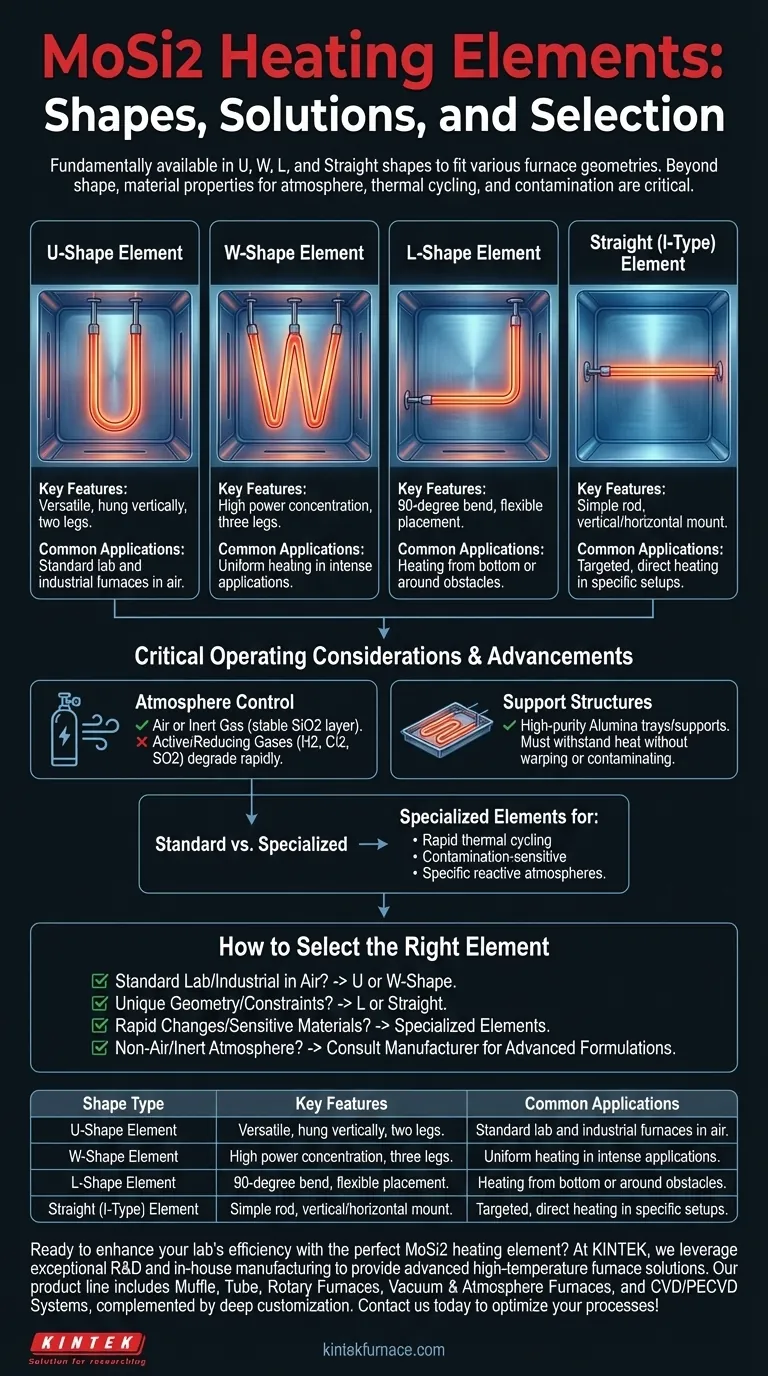
Fundamentally, MoSi2 heating elements are available in several standard configurations. The most common are the W-shape, U-shape, L-shape, and straight (or I-type) elements. Each design is engineered to accommodate different furnace geometries, mounting requirements, and power density needs, allowing for flexible integration into a wide array of high-temperature equipment.
While the element's shape determines its physical fit within a furnace, the true challenge is matching its material properties to your specific process, including the furnace atmosphere, thermal cycling speed, and potential for contamination.

A Closer Look at Each Element Shape
The shape of a MoSi2 element is its most visible feature, directly influencing how it is installed and how it distributes heat. The choice is primarily driven by the design and constraints of your furnace.
The U-Shape Element
This is one of the most common and versatile shapes. It consists of two vertical legs (shanks) connected at the bottom, resembling the letter "U." These elements are typically hung vertically from the top of the furnace chamber.
The W-Shape Element
Similar to the U-shape, the W-shape element consists of three vertical legs. This design can provide a higher power concentration in a given area and is often used in applications requiring more intense, uniform heating.
The L-Shape Element
The L-shape element is bent at a 90-degree angle. This configuration is exceptionally useful for heating from the bottom of a furnace or for navigating around internal obstacles where a straight vertical element would not fit.
The Straight (I-Type) Element
As the name implies, these are simple, straight rods. They can be mounted either vertically or horizontally and are often used when targeted, direct heating is required or in furnaces with specific side-wall or roof-mounting capabilities.
Critical Operating Considerations Beyond Shape
Choosing the right MoSi2 element involves more than just selecting a shape that fits. The operational environment is the single most important factor determining the element's performance and lifespan.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Standard MoSi2 elements are designed to operate exclusively in air or inert gas environments. The protective silica (SiO2) layer that forms on the element's surface at high temperatures is stable in these conditions.
Exposing them to active or reducing gases like hydrogen (H2), chlorine (Cl2), or sulfur dioxide (SO2) will rapidly degrade the element and lead to premature failure.
Required Support Structures
These elements operate at extreme temperatures and must be held in place with materials that can withstand the heat without failing.
High-purity alumina trays and supports are the industry standard. These materials offer excellent thermal stability and are chemically non-reactive, ensuring they do not warp, melt, or contaminate the elements or the process.
Understanding Recent Advancements and Trade-offs
While standard MoSi2 elements have clear limitations, technology has evolved to meet more demanding applications. Understanding these developments is key to avoiding common pitfalls.
Standard vs. Specialized Elements
It is crucial to distinguish between a standard element and one designed for a specific, challenging process. Using a standard element in an incompatible environment is a frequent cause of failure.
New Designs for Demanding Applications
Recent advancements have produced specialized MoSi2 elements optimized for specific needs. These include designs for:
- Rapid thermal cycling in lab and sintering furnaces.
- Contamination-sensitive processes requiring high purity.
- Operation in specific reactive atmospheres, such as nitrogen.
These advanced elements represent a significant step forward, but they must be specified correctly for the intended application. Always verify the element's atmospheric compatibility with the manufacturer.
How to Select the Right Element for Your Application
Your final choice should balance the physical furnace design with the chemical and thermal demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is a standard lab or industrial furnace in air: A U-shape or W-shape element is likely your most reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your furnace has unique geometry or access constraints: Consider L-shape or straight elements for targeted heating or placement around obstacles.
- If your process involves rapid temperature changes or sensitive materials: You must look beyond standard shapes to specialized elements designed for thermal cycling and low contamination.
- If you must operate in any atmosphere other than air or inert gas: Do not use a standard MoSi2 element; consult a manufacturer about advanced formulations designed specifically for your process gas.
Selecting the correct element is a matter of aligning its physical shape and material science with the precise demands of your high-temperature environment.
Summary Table:
| Shape Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| U-Shape | Versatile, hung vertically, two legs | Standard lab and industrial furnaces in air |
| W-Shape | High power concentration, three legs | Uniform heating in intense applications |
| L-Shape | 90-degree bend, flexible placement | Heating from bottom or around obstacles |
| Straight (I-Type) | Simple rod, vertical/horizontal mount | Targeted, direct heating in specific setups |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with the perfect MoSi2 heating element? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Don't let element selection hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your high-temperature processes and extend equipment lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity



















