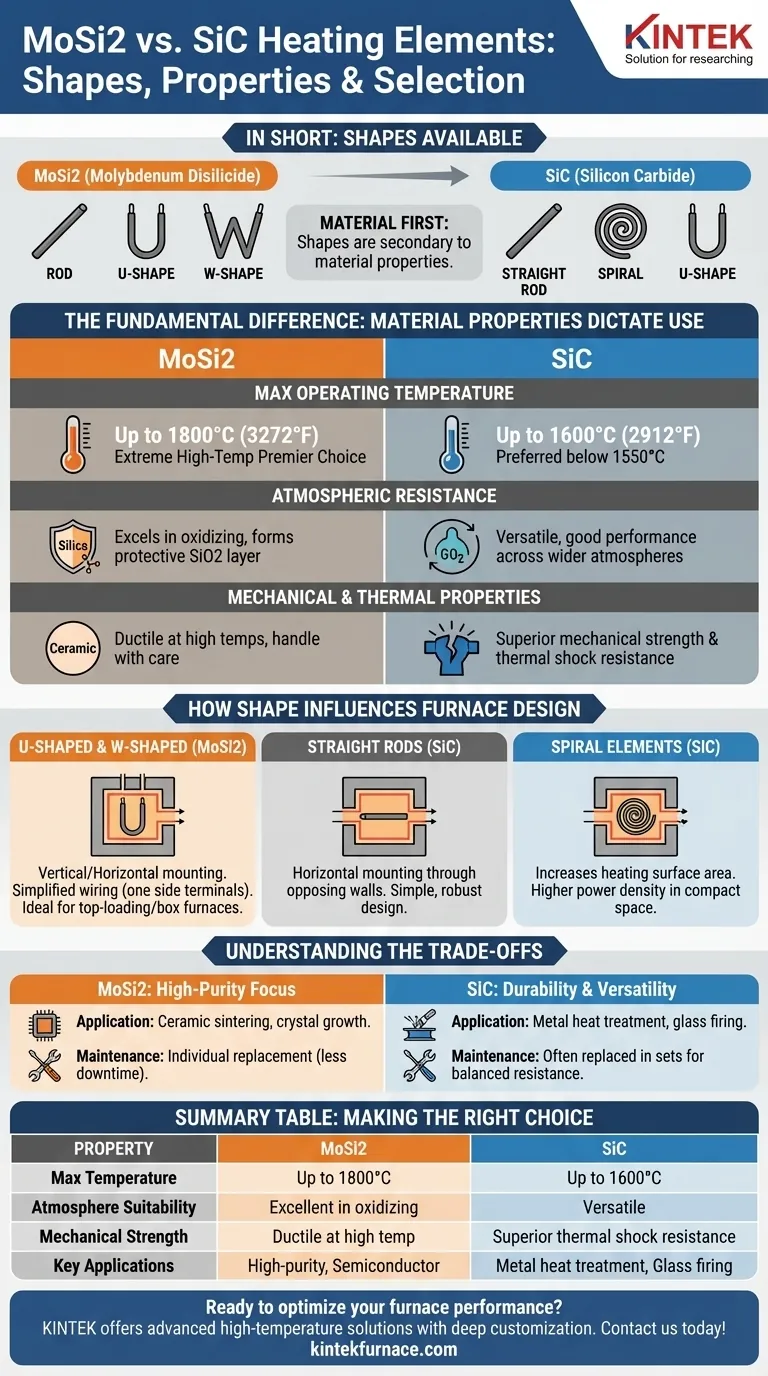
In short, both Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements come in a range of standard and custom shapes designed to fit specific furnace configurations. MoSi2 is commonly available in rod, U-shaped, and W-shaped forms. SiC elements are typically produced as straight rods, spiral elements, and U-shapes, with complex custom forms also available.
The choice of shape is secondary to the more critical decision of selecting the right material. The fundamental properties of MoSi2 and SiC—their maximum temperature, atmospheric compatibility, and mechanical strength—will dictate which material is suitable for your application, which in turn narrows your choice of available shapes.

The Fundamental Difference: Material Properties Dictate Use
Before considering the geometry of a heating element, you must first match the material to your process requirements. The physical and chemical properties of MoSi2 and SiC are distinctly different and govern their use in industrial and laboratory furnaces.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The most significant differentiator is the temperature range. MoSi2 elements are the premier choice for extreme high-temperature applications, capable of operating reliably up to 1800°C (3272°F).
SiC elements have a lower maximum operating temperature, typically capped around 1600°C (2912°F). They are often preferred for processes that run consistently below 1550°C.
Atmospheric Resistance
MoSi2 excels in oxidizing atmospheres. At high temperatures, it forms a protective, self-healing layer of pure silica (SiO2) on its surface, which prevents further oxidation and extends its life.
SiC is more versatile and demonstrates good performance across a wider range of atmospheres, including those that are not purely oxidative. Its robustness makes it a reliable choice in more varied process environments.
Mechanical and Thermal Properties
SiC offers superior mechanical strength and a higher resistance to thermal shock. This makes it a more physically durable element, especially during rapid heating and cooling cycles.
MoSi2 is more ductile at high temperatures compared to SiC, but it is still a ceramic material that must be handled with care. Its key strength lies in its exceptional stability and resistance to degradation at peak temperatures.
How Shape Influences Furnace Design
Once you have selected the appropriate material, the element's shape becomes a critical factor in furnace design, influencing heat distribution, electrical connections, and ease of maintenance.
Common Shapes and Their Purpose
U-Shaped and W-Shaped elements, common for MoSi2, are designed for either vertical or horizontal mounting. Their primary advantage is that both electrical terminals are on one side, simplifying furnace construction and wiring, especially for top-loading or box furnaces.
Straight Rods, a standard for SiC, are simple, robust, and typically mounted horizontally through opposing furnace walls. This is a straightforward design for many common furnace types.
Spiral Elements, primarily seen with SiC, are engineered to increase the heating surface area within a compact volume. This allows for higher power density and more efficient heat transfer in space-constrained designs.
Customization and Dimensions
Heating elements are not one-size-fits-all components. They are specified with precise dimensions to ensure proper fit and performance, including:
- Heating Zone (D1/Le): The diameter and length of the active heating section.
- Cooling Zone (D2/Lu): The diameter and length of the terminal ends, which operate at a lower temperature.
- Center Distance (A): The spacing between the legs of a U-shaped or W-shaped element.
These dimensions can be customized to meet the exact requirements of your furnace chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves balancing performance, cost, and operational constraints. Objectively weighing these factors is key to long-term success.
Application and Cost
MoSi2 is the standard for high-purity, high-temperature processes like ceramic sintering, crystal growth, and semiconductor manufacturing. Its cost is justified by its unique temperature capabilities.
SiC is a workhorse material used in a vast range of applications, including metal heat treatment, glass firing, and electronics production, where its durability and versatility provide excellent value.
Maintenance and Lifespan
A significant operational difference is in maintenance. MoSi2 elements can typically be replaced individually if one fails, minimizing downtime and replacement cost.
In many designs, SiC elements may need to be replaced in sets to maintain balanced electrical resistance within the furnace. Understanding how to operate elements within their specified limits is critical for extending the lifespan of either type.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct element, start with your process temperature and atmosphere, then consider the physical layout of your furnace.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-temperature operation (above 1600°C) in an oxidizing atmosphere: MoSi2 is the definitive and often only choice.
- If your primary focus is operational versatility and thermal shock resistance below 1600°C: SiC provides superior mechanical durability and is suitable for a broader range of atmospheric conditions.
- If your primary focus is simplifying furnace wiring and enabling individual element replacement: U-shaped or W-shaped MoSi2 elements offer a distinct advantage in serviceability.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is about aligning the material's inherent strengths with the precise demands of your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Property | MoSi2 Heating Elements | SiC Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1800°C | Up to 1600°C |
| Common Shapes | Rod, U-shaped, W-shaped | Straight rod, Spiral, U-shaped |
| Atmosphere Suitability | Excellent in oxidizing | Versatile across various atmospheres |
| Mechanical Strength | Ductile at high temperatures | Superior thermal shock resistance |
| Key Applications | High-purity processes, semiconductor | Metal heat treatment, glass firing |
Ready to optimize your furnace performance? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with MoSi2 or SiC elements, we can help you select the perfect shape and material for maximum efficiency and durability. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can elevate your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















