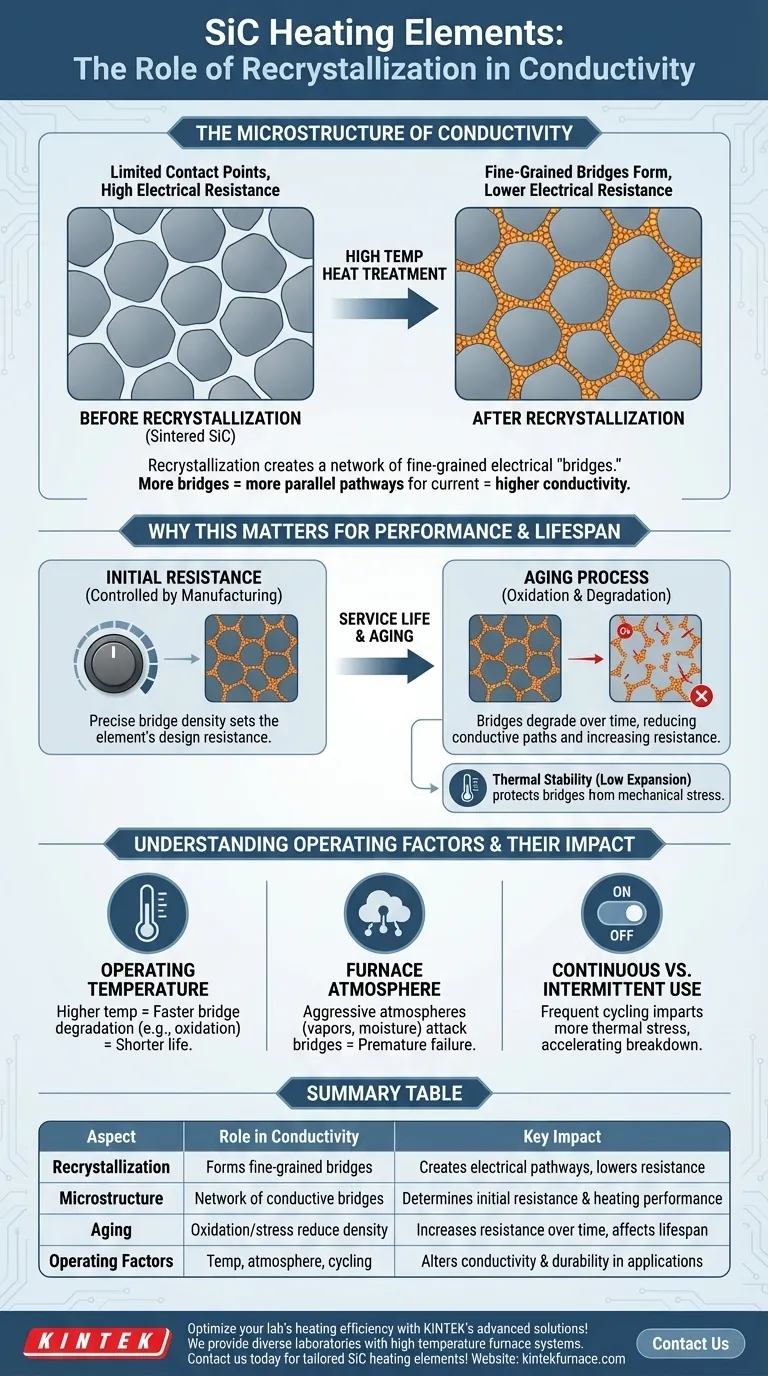
At its core, recrystallization is the fundamental process that transforms sintered silicon carbide (SiC) from a collection of individual grains into a cohesive, electrically conductive material. This process intentionally forms a network of fine-grained bridges between larger SiC grains, creating the precise pathways through which electrical current flows to generate heat. The density and integrity of this network directly determine the heating element's electrical resistance and overall performance.
Recrystallization is not a side effect; it is the central manufacturing principle that governs a SiC element's conductivity. The process creates a microstructure of fine-grained electrical "bridges," and the number of these bridges dictates the element's resistance and heating characteristics.
The Microstructure of Conductivity
To understand the performance of a silicon carbide heating element, you must first visualize its internal structure. It is not a uniform, monolithic crystal but a complex ceramic matrix.
From Grains to a Conductive Network
A SiC heating element begins as a collection of larger, individual silicon carbide grains. In this initial state, the grains are simply packed together, with limited points of contact and very high electrical resistance.
The Role of Recrystallization
During manufacturing, the element is subjected to extremely high temperatures. This heat treatment initiates recrystallization, a process where new, much smaller SiC grains begin to form and grow.
Fine Grains as Electrical Bridges
These new, fine grains nucleate and grow in the spaces between the original, larger grains. They effectively form physical and electrical bridges, connecting the larger grains into a continuous, interconnected network throughout the element's body.
Resistance as a Function of Connections
The flow of electricity is now able to travel across this network of bridges. The element's final resistance is a direct function of this microstructure: more bridges create more parallel pathways for current, resulting in lower overall resistance and higher conductivity.
Why This Matters for Performance and Lifespan
Understanding the role of these microscopic bridges is key to understanding the element's behavior in a real-world industrial environment.
Initial Resistance and Element Design
Manufacturers precisely control the recrystallization process to achieve a specific density of conductive bridges. This sets the element's initial or "cold" resistance, which is a critical parameter for designing the power supply and control system.
The Inevitable Aging Process
Over its service life, a SiC element's resistance gradually increases. This aging is caused by factors like oxidation, where the furnace atmosphere slowly degrades the fine-grained bridges, reducing the number of available conductive paths.
The Importance of Thermal Stability
Silicon carbide has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This is a critical property that protects the delicate microstructural bridges from mechanical stress as the element heats up and cools down. This inherent stability is a primary reason for the material's durability and long life in applications with frequent thermal cycling.
Understanding the Operating Factors
The environment in which a SiC element operates has a direct impact on the longevity of its recrystallized structure. The factors that influence lifespan do so by affecting the integrity of these conductive bridges.
Impact of Operating Temperature
Higher operating temperatures provide more energy to drive chemical reactions like oxidation. This accelerates the degradation of the conductive network, causing resistance to increase more rapidly and shortening the element's useful life.
Influence of Furnace Atmosphere
Certain atmospheres can be aggressive toward the silicon carbide microstructure. For example, heavy water vapor or certain chemical vapors can attack the SiC grains and the bridging network, leading to premature failure.
Continuous vs. Intermittent Use
While SiC is mechanically robust, frequent cycling (intermittent use) still imparts more thermal stress over time than continuous operation. This stress can contribute to the slow mechanical breakdown of the conductive pathways, especially if other degrading factors are present.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the role of recrystallization allows you to manage your heating elements for optimal performance and longevity.
- If your primary focus is consistent heating: Recognize that the element's performance is tied directly to its microscopic structure, and monitor its resistance over time to predict its end-of-life.
- If your primary focus is maximum lifespan: Control operating conditions, especially temperature and furnace atmosphere, to protect the fine-grained conductive bridges from degradation.
- If your primary focus is reliability: Select high-quality SiC elements whose inherent thermal stability will protect the conductive network across thousands of heating cycles.
By grasping this microscopic principle, you gain macroscopic control over your heating process.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Conductivity | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Recrystallization Process | Forms fine-grained bridges between SiC grains | Creates electrical pathways, lowers resistance |
| Microstructure | Network of conductive bridges | Determines initial resistance and heating performance |
| Aging and Degradation | Oxidation and stress reduce bridge density | Increases resistance over time, affects lifespan |
| Operating Factors | Temperature, atmosphere, cycling influence bridges | Alters conductivity and durability in applications |
Optimize your lab's heating efficiency with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored SiC heating elements can benefit your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















