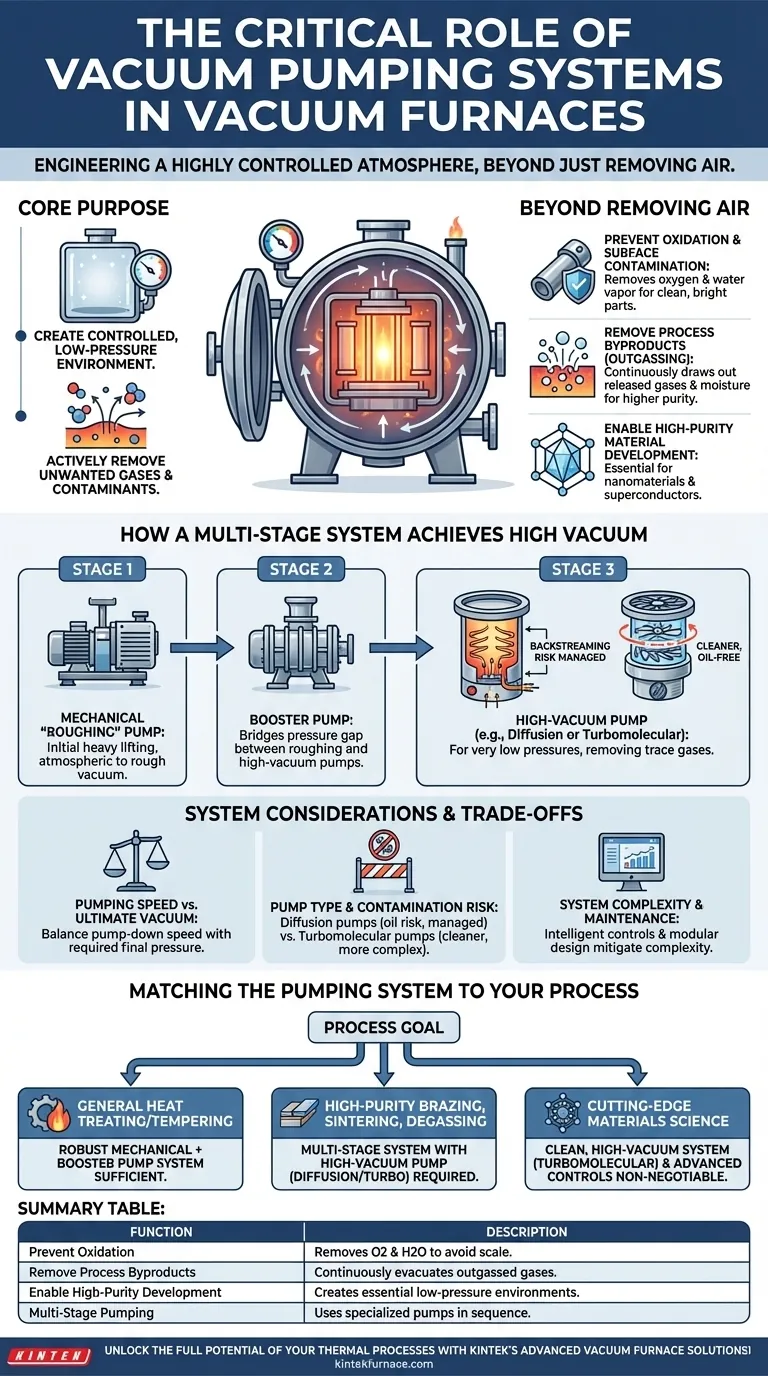
At its core, a vacuum pumping system serves two critical functions: creating a controlled, low-pressure environment and actively removing unwanted gases and contaminants released during the heating process. By systematically evacuating the furnace chamber, the pumping system prevents oxidation and unwanted chemical reactions, ensuring the final product meets stringent purity and structural standards.
The ultimate purpose of a vacuum pumping system is not merely to create an empty space, but to engineer a highly controlled atmosphere. By systematically removing reactive gases like oxygen and process-generated byproducts, these systems guarantee material purity, prevent surface defects, and enable thermal processes that are impossible in a normal atmosphere.

The Core Purpose: Beyond Just Removing Air
The function of a vacuum pump extends far beyond simply evacuating the chamber. It is an active and continuous process that purifies the entire thermal processing environment.
Preventing Oxidation and Surface Contamination
The most immediate benefit of a vacuum is the removal of atmospheric gases, primarily oxygen and water vapor.
In a normal atmosphere, heating metals causes them to react with oxygen, forming an oxide layer (scale) on the surface. A vacuum furnace prevents this, resulting in clean, bright, oxide-free parts. This is critical for applications like vacuum tempering of tool steels and high-temperature alloys.
Removing Process Byproducts (Outgassing)
As materials are heated, they release trapped gases, moisture, and volatile elements from their bulk and surface—a process known as outgassing.
The vacuum pumping system continuously draws these released byproducts out of the furnace. This purification step is essential for achieving a higher-purity end product, which is a key advantage of vacuum processing.
Enabling High-Purity Material Development
For advanced applications like producing nanomaterials or superconducting materials, even trace impurities can be catastrophic.
A high-vacuum environment is the only way to ensure the extreme purity required for these materials to form and grow correctly. The pumping system creates the ideal high-temperature, high-vacuum conditions for this synthesis.
How a Multi-Stage System Achieves High Vacuum
Achieving a high vacuum is not done with a single pump. Instead, furnaces use a sequence of specialized pumps, each designed to operate efficiently within a specific pressure range.
Stage 1: The Mechanical "Roughing" Pump
This is the first stage and the workhorse of the system. The mechanical pump (or "roughing pump") does the initial heavy lifting, removing the bulk of the air from the chamber and taking the pressure from atmospheric level down to a rough vacuum.
Stage 2: The Booster Pump
Once the mechanical pump's efficiency drops at lower pressures (typically below 20 Torr), a booster pump takes over. It acts as an intermediary, efficiently bridging the pressure gap between the roughing pump and the high-vacuum pump.
Stage 3: The High-Vacuum Pump
To achieve the very low pressures required for sensitive processes, a high-vacuum pump is activated. Common types include diffusion pumps or turbomolecular pumps.
Diffusion pumps have no moving parts and use jets of hot oil vapor to drag remaining gas molecules away. Turbomolecular pumps use high-speed rotating blades to push gas molecules out of the chamber.
Supporting Pumps for System Integrity
In some configurations, a smaller holding pump is used. Its job is often to maintain the correct backing pressure for the diffusion pump, preventing its oil from backstreaming into the furnace chamber and contaminating the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and System Considerations
The choice and configuration of a pumping system involve balancing performance, cost, and process requirements.
Pumping Speed vs. Ultimate Vacuum
A system designed for a very deep (or "hard") ultimate vacuum may not be the fastest at removing the initial bulk air. The design must balance the speed of the pump-down with the final pressure level required by the process.
Pump Type and Contamination Risk
Diffusion pumps are robust and cost-effective but use oil, which poses a minor but real risk of contamination through backstreaming. This risk is managed with baffles, traps, and proper operation.
Turbomolecular pumps are considered "cleaner" because they are oil-free but are more mechanically complex and sensitive to sudden bursts of pressure.
System Complexity and Maintenance
A multi-stage system is highly effective but adds complexity. Modern vacuum furnaces mitigate this with intelligent control systems that automate the pump-down sequence, reducing the chance of operator error. A modular design also simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting, extending the equipment's service life.
Matching the Pumping System to Your Process
The ideal pumping system is directly tied to the metallurgical or chemical goal of the operation.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating or tempering: A robust mechanical and booster pump system is often sufficient to prevent oxidation and achieve the desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is high-purity brazing, sintering, or degassing: You require a multi-stage system with a high-vacuum pump (diffusion or turbo) to effectively remove all contaminants and outgassing byproducts.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge materials science (nanomaterials, superconductors): A clean, high-vacuum system, likely featuring turbomolecular pumps and advanced controls, is non-negotiable to ensure absolute purity and process repeatability.
Ultimately, understanding and controlling your furnace's pumping system is the key to mastering your thermal process and guaranteeing the quality of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Removes oxygen and water vapor to avoid surface scale and contamination during heating. |
| Remove Process Byproducts | Continuously evacuates outgassed gases and volatile elements for higher purity. |
| Enable High-Purity Development | Creates controlled, low-pressure environments essential for nanomaterials and advanced materials. |
| Multi-Stage Pumping | Uses roughing, booster, and high-vacuum pumps to achieve specific pressure ranges efficiently. |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, guaranteeing purity, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your material processing outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum system critical for sealing the quartz tube used in Fe3GeTe2 single crystal preparation?
- How does a high-vacuum pump system facilitate the synthesis of high-quality calcium-based perrhenates? Expert Synthesis
- What materials are used for the heating elements in a vacuum furnace? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the primary function of the vacuum pump system in the magnesium powder evaporation process? Ensure High Purity & Efficiency
- How does a vacuum pumping system contribute to the fabrication of high-quality silicide structures? Ensure Material Purity



















