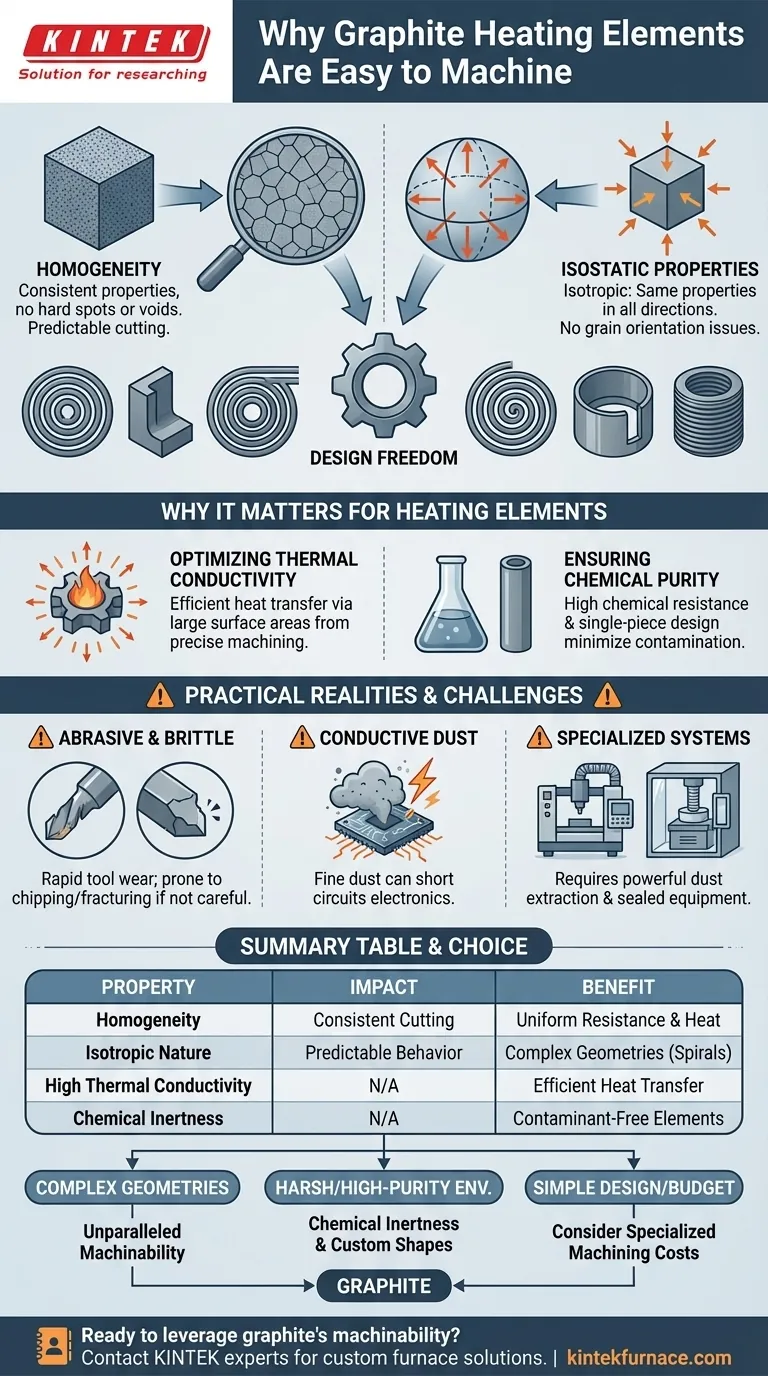
At its core, graphite’s excellent machinability stems from two key material characteristics: homogeneity and isostatic properties. This unique combination allows it to be shaped with remarkable precision, a critical factor in manufacturing uniform and efficient heating elements for high-temperature applications.
While often selected for its extreme temperature resistance, graphite's true advantage lies in how its uniform internal structure translates directly into design freedom. This machinability is what enables the creation of complex, high-performance heating elements that would be difficult or impossible to fabricate from other materials.
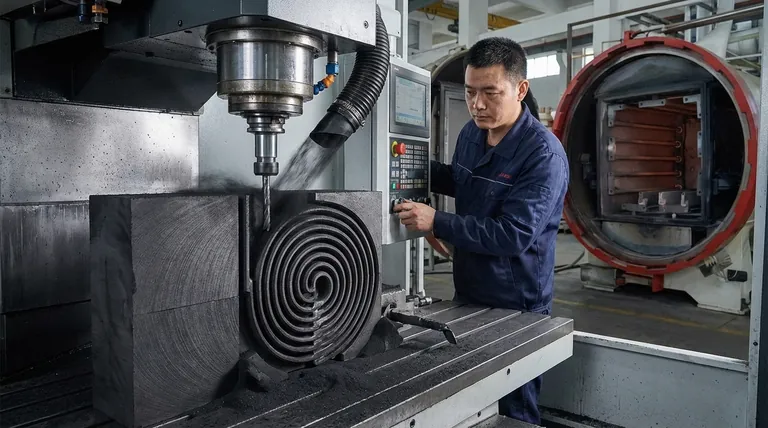

The Foundation of Graphite's Machinability
The term "easy to machine" requires a deeper look. With graphite, it refers to the material's predictability and consistency during the cutting process, which is a direct result of its microstructure.
Uniformity Through Homogeneity
Homogeneity means the graphite's properties are consistent throughout the entire block of material. There are no hard spots, voids, or inclusions that can disrupt the machining process.
This uniformity ensures that cutting tools engage with the material predictably, leading to smooth surface finishes and consistent dimensional accuracy from one part to the next.
Predictability from Isostatic Properties
Modern high-quality graphite is formed through isostatic pressing, where pressure is applied equally from all directions. The resulting material is isotropic, meaning its mechanical and thermal properties are the same regardless of orientation.
For a machinist, this is a significant advantage. It eliminates the variables seen in anisotropic materials (like wood or extruded metals), where strength and cutting behavior can change dramatically depending on the direction of the cut.
The Practical Result: Design Freedom
Because graphite can be machined so predictably, engineers can design heating elements with highly complex geometries.
This includes thin walls, fine threads, and intricate spiral or serpentine patterns. These complex shapes are not for aesthetics; they are essential for controlling electrical resistance and ensuring uniform heat distribution within a furnace.
Why This Matters for Heating Elements
Graphite's machinability is not just a manufacturing convenience; it is fundamentally linked to its performance as a heating element. The ability to shape it precisely unlocks its other superior thermal properties.
Optimizing Thermal Conductivity
Graphite possesses high thermal conductivity, allowing it to transfer heat quickly and evenly. Easy machining allows the creation of elements with a large surface area, maximizing the efficiency of this heat transfer into the furnace environment.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
In many high-temperature processes, such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical purity is paramount. Graphite's high chemical resistance prevents it from corroding or reacting with process gases.
Its machinability allows for the creation of integrated, single-piece elements, minimizing the need for joints or fasteners made from other materials that could introduce contaminants.
Understanding the Practical Realities
While the material properties of graphite make it easy to shape, the process itself is highly specialized and presents unique challenges. It is not a material that can be machined in a typical metalworking shop.
Abrasive and Brittle Nature
Graphite is highly abrasive, leading to rapid tool wear if incorrect cutting tool materials and coatings are used. It is also brittle and can easily chip or fracture if improper feeds, speeds, or toolpaths are employed.
The Problem of Conductive Dust
The biggest challenge in machining graphite is the fine, electrically conductive dust it produces. This dust can infiltrate machine electronics and control cabinets, causing short circuits and catastrophic equipment failure.
The Need for Specialized Systems
Because of the dust, graphite machining must be performed on machines specifically designed or modified for the task. This includes powerful, sealed vacuum systems for dust extraction and positive air pressure systems to protect sensitive electronics. Skilled machinists with experience in managing these factors are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material for a heating element involves balancing performance requirements, design complexity, and manufacturing constraints.
- If your primary focus is achieving complex geometries for uniform heating: Graphite's unparalleled machinability makes it the superior choice for creating intricate designs that ensure consistent thermal performance.
- If your primary focus is operation in a harsh chemical or high-purity environment: The combination of graphite's chemical inertness and the ability to machine custom, single-piece shapes makes it an ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is a simple design on a tight budget: Be aware that while the raw material can be cost-effective, the need for specialized machining can add costs that must be factored into your decision.
Ultimately, understanding these properties empowers you to leverage graphite not just as a material, but as a complete engineering solution for high-performance thermal systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | Impact on Machinability | Benefit for Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Homogeneity | Consistent cutting with no hard spots or voids | Uniform electrical resistance and heat distribution |
| Isotropic Nature | Predictable behavior from any cutting direction | Complex geometries (thin walls, spirals) are possible |
| High Thermal Conductivity | N/A (a resulting benefit) | Efficient heat transfer when combined with machined shapes |
| Chemical Inertness | N/A (a resulting benefit) | Enables creation of contaminant-free, single-piece elements |
Ready to leverage graphite's superior machinability for your high-temperature furnace?
At KINTEK, we combine our deep expertise in thermal engineering with advanced in-house manufacturing to turn your unique requirements into reality. Whether you need a standard Tube Furnace or a highly customized CVD/PECVD System, our team uses high-quality graphite and other advanced materials to craft heating elements with precise geometries for optimal performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness



















