At its core, a vacuum carburizing furnace is an advanced heat treatment system designed to perform much more than just carburizing. Its primary functions include low-pressure carburizing (LPC), carbonitriding, and subsequent oil or high-pressure gas quenching to create extremely hard, wear-resistant surfaces on components. However, its precise control over temperature and atmosphere makes it a highly versatile platform for a wide range of thermal processes.
The true value of a vacuum carburizing furnace lies not just in its ability to carburize, but in its capacity to function as a multi-process heat treatment center. It enables the execution of complex, sequential processes within a single, contamination-free cycle, offering a level of precision and part quality that traditional atmospheric furnaces cannot match.

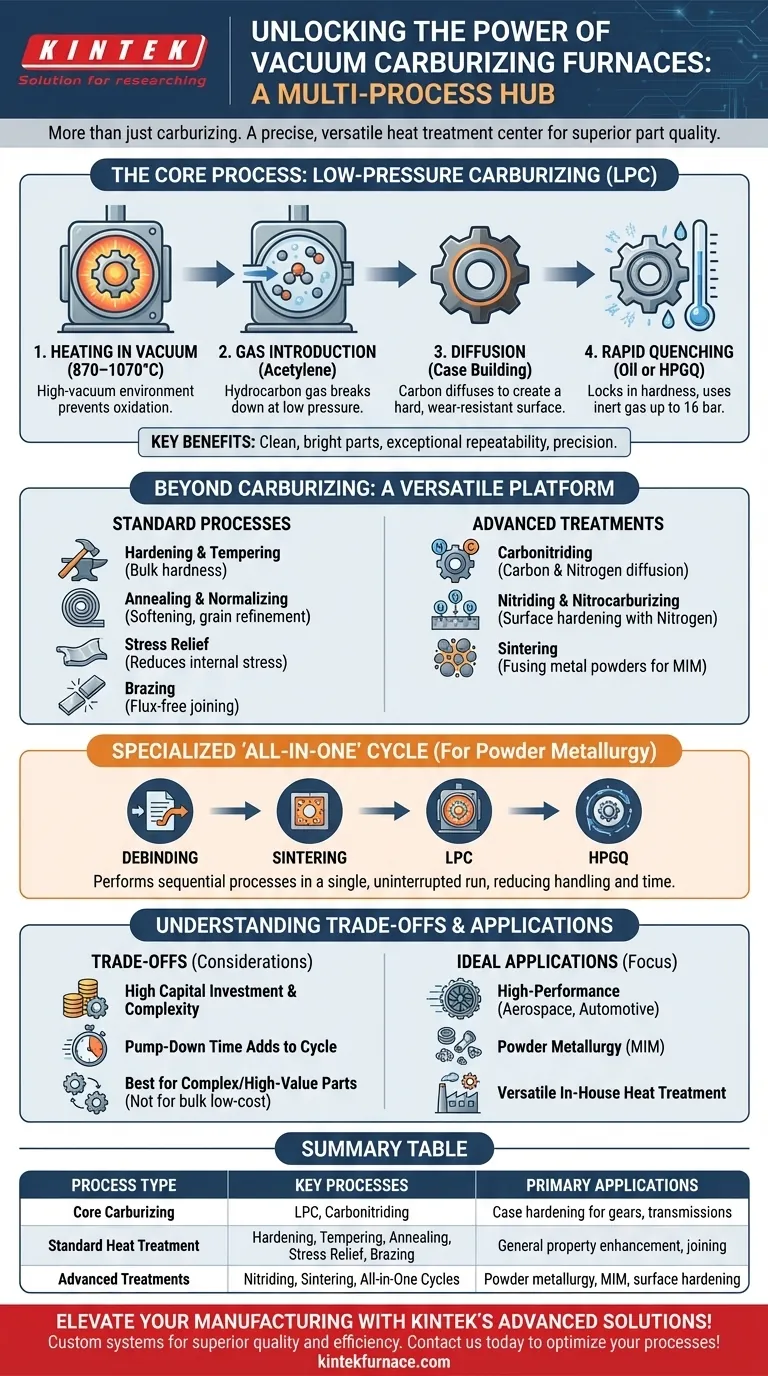
The Core Process: Low-Pressure Carburizing (LPC)
The signature process of this furnace is vacuum or Low-Pressure Carburizing (LPC). This modern case-hardening technique is fundamentally different from traditional methods.
How LPC Works
The process begins by heating steel components inside a high-vacuum chamber, typically between 870–1070°C (1600–1950°F).
Once at temperature, a hydrocarbon gas like acetylene is introduced at a very low pressure (a few millibars). This gas breaks down, allowing elemental carbon to diffuse into the surface of the steel.
This cycle of introducing gas and allowing it to diffuse is repeated to precisely build a carbon-rich layer, known as the "case," to a specified depth.
The Critical Role of Quenching
Adding carbon only prepares the material. To achieve the desired hardness, the parts must be rapidly cooled, or quenched.
Vacuum furnaces integrate this step seamlessly, using either a submerged oil quench or, more commonly, a high-pressure gas quench (HPGQ) with inert gases like nitrogen or helium at pressures up to 16 bar.
Key Benefits of the LPC Process
The vacuum environment prevents surface oxidation, resulting in clean, bright parts that often require no post-process cleaning.
Microprocessor control over the entire cycle ensures that every batch is treated with exceptional repeatability and precision, which is critical for high-performance industries like aerospace.
Beyond Carburizing: A Multi-Process Platform
A vacuum furnace's ability to precisely control temperature and atmosphere makes it suitable for a wide array of thermal processes, consolidating the work of multiple machines into one.
Standard Heat Treatment Processes
Because it is fundamentally a high-temperature vacuum chamber, the furnace can easily execute standard processes like:
- Hardening & Tempering: Achieving specific bulk material hardness and toughness.
- Annealing & Normalizing: Softening material or refining grain structure.
- Stress Relief: Reducing internal stresses caused by manufacturing or welding.
- Brazing: Joining materials using a filler metal in a clean, flux-free environment.
Advanced Surface and Material Treatments
The furnace's capabilities extend to other sophisticated processes:
- Carbonitriding: Similar to carburizing, but both carbon and nitrogen are diffused into the surface for enhanced wear and fatigue resistance.
- Nitriding & Nitrocarburizing: Surface hardening processes that primarily use nitrogen.
- Sintering: Fusing metal powders into a solid mass, often used in Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and powder metallurgy.
Specialized "All-in-One" Cycles
A unique advantage for powder metallurgy is the ability to run an "all-in-one" cycle. The furnace can perform debinding, sintering, low-pressure carburizing, and high-pressure gas quenching sequentially in a single, uninterrupted run, dramatically reducing handling and total cycle time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, this technology is not the universal solution for all heat-treating needs. Objectivity requires acknowledging its specific trade-offs.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment compared to conventional atmospheric furnaces. They require sophisticated vacuum pump systems, advanced controls (PLCs, SCADA), and specialized maintenance.
Cycle Time Considerations
The time required to pump the chamber down to a deep vacuum must be factored into the total cycle time. For simple, single-step processes, this can sometimes make the overall time longer than an atmospheric equivalent.
Process Suitability
Vacuum carburizing is ideal for complex geometries and high-value components where precision, cleanliness, and the absence of surface oxidation are critical. For simple, bulk treatment of low-cost parts, traditional atmospheric furnaces may be more economical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right thermal process depends entirely on your final goal.
- If your primary focus is high-performance components (e.g., aerospace gears, automotive transmissions): The superior case uniformity, cleanliness, and process repeatability of LPC is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is powder metallurgy parts: The furnace's ability to perform an "all-in-one" cycle from sintering to case hardening offers unmatched efficiency and part integrity.
- If your primary focus is versatile, in-house heat treatment: A vacuum furnace consolidates many processes into one machine, providing maximum flexibility for a diverse range of high-quality parts.
Ultimately, a vacuum carburizing furnace empowers you with a level of process control and part quality essential for modern, high-specification manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Processes | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Core Carburizing | Low-Pressure Carburizing (LPC), Carbonitriding | Case hardening for gears, transmissions in aerospace and automotive |
| Standard Heat Treatment | Hardening, Tempering, Annealing, Stress Relief, Brazing | General material property enhancement, joining |
| Advanced Treatments | Nitriding, Sintering, All-in-One Cycles | Powder metallurgy, MIM, surface hardening |
Elevate your manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior part quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your heat treatment processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What technological features enhance the efficiency of vacuum furnaces? Boost Performance with Advanced Control & Energy Savings
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- How do vacuum furnaces contribute to long-term cost savings? Reduce Costs with Efficiency and Quality
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance



















