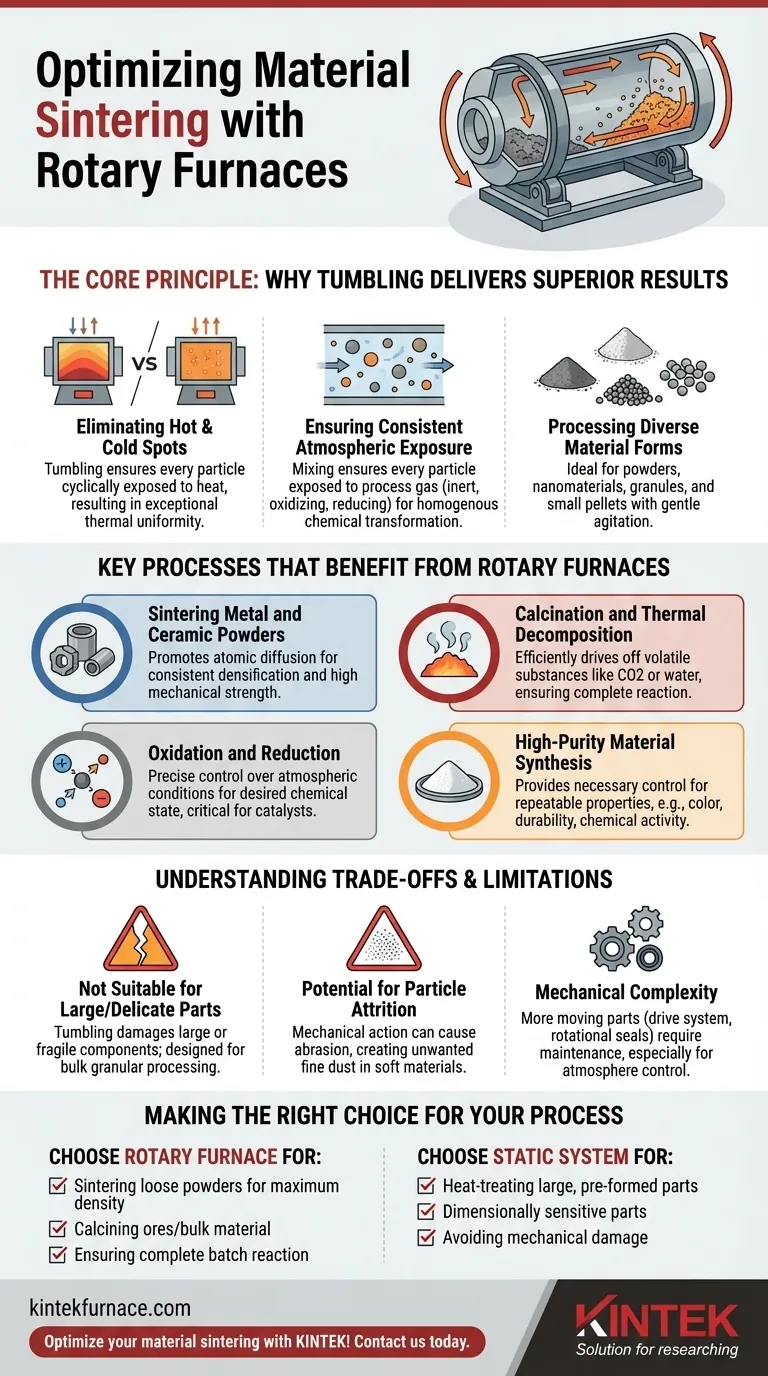
For material sintering, rotary furnaces are exceptionally beneficial for processing unbound powders, particularly metals and ceramics. The continuous rotation ensures that each particle is uniformly exposed to heat and the controlled atmosphere, which is critical for achieving consistent densification, high mechanical strength, and improved corrosion resistance in the final sintered product.
The core advantage of a rotary furnace is not just the heat it provides, but the dynamic, continuous mixing it imparts. This tumbling motion guarantees uniform processing, making it the superior choice for any thermal process where every particle of a bulk material must be treated identically.
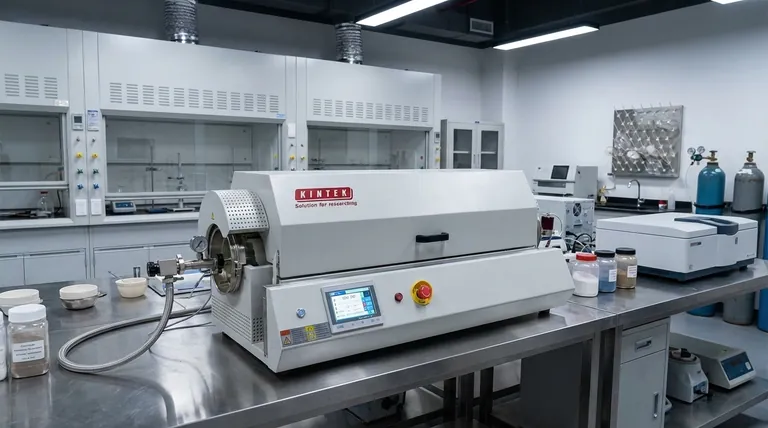

The Core Principle: Why Tumbling Delivers Superior Results
A rotary furnace, also known as a rotary kiln or tube furnace, is fundamentally a cylindrical chamber that rotates along its horizontal axis. This simple design is the key to its effectiveness in high-temperature material processing.
Eliminating Hot and Cold Spots
In a static furnace, material at the edges of a container heats faster than the material in the center. This temperature gradient leads to inconsistent processing. A rotary furnace solves this by constantly tumbling the material, ensuring every particle is cyclically exposed to the heat source, resulting in exceptional thermal uniformity.
Ensuring Consistent Atmospheric Exposure
Many sintering and synthesis processes require a precisely controlled atmosphere, such as an inert (nitrogen, argon), oxidizing, or reducing environment. The mixing action ensures that every particle is consistently exposed to the process gas, preventing unwanted side reactions and guaranteeing a homogenous chemical transformation throughout the batch.
Processing Diverse Material Forms
This method is ideal for materials that can flow and tumble. It is used extensively for powders, nanomaterials, granules, and small pellets. The design inherently provides gentle yet thorough agitation for these forms.
Key Processes That Benefit from Rotary Furnaces
The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes rotary furnaces indispensable for several critical industrial processes.
Sintering Metal and Ceramic Powders
This is a primary application. By heating powders below their melting point, the furnace promotes atomic diffusion between particles. The uniform heating ensures consistent grain growth and densification, leading to a strong, non-porous final material.
Calcination and Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a process of heating a solid material to drive off volatile substances, such as removing carbon dioxide from limestone or water from hydrated minerals. The tumbling action efficiently liberates these trapped gases and ensures the reaction proceeds to completion for the entire batch.
Oxidation and Reduction
In processes like catalyst manufacturing, the oxidation state of a material is critical to its function. A rotary furnace allows for precise control over an oxidizing or reducing atmosphere. The continuous mixing ensures the entire volume of material achieves the desired chemical state.
High-Purity Material Synthesis
Manufacturing advanced materials like specialized pigments or catalysts requires exact temperature profiles and clean environments. Rotary furnaces provide the necessary control to produce materials with highly specific and repeatable properties, such as color, durability, and chemical activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper process selection.
Not Suitable for Large or Delicate Parts
The tumbling motion that is so beneficial for powders would destroy large, pre-formed, or fragile green-state components. The process is fundamentally designed for bulk processing of granular or powdered materials, not individual parts.
Potential for Particle Attrition
The mechanical action of tumbling can cause abrasion between particles. For very soft or brittle materials, this can lead to the creation of unwanted fine dust or alter the morphology of the particles, which may be undesirable for some applications.
Mechanical Complexity
Compared to a simple static box furnace, a rotary furnace involves more moving parts, including a drive system and rotational seals. These components require more maintenance to ensure reliable, long-term operation, especially the seals needed to maintain a controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the physical form of your material and your primary processing goal.
- If your primary focus is sintering loose powders for maximum density and strength: A rotary furnace is the ideal choice due to its unparalleled heating uniformity.
- If your primary focus is calcining ores or driving chemical reactions in a bulk material: A rotary furnace excels at ensuring the entire batch is processed completely and evenly.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating large, pre-formed, or dimensionally sensitive parts: A static system like a box, belt, or pusher furnace is the correct tool to avoid mechanical damage.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace comes down to understanding that the rotary design is engineered to perfect the processing of bulk solids.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Sintering Metal and Ceramic Powders | Consistent densification, high mechanical strength, uniform grain growth |
| Calcination and Thermal Decomposition | Efficient gas removal, complete reaction for entire batch |
| Oxidation and Reduction | Precise atmospheric control, homogenous chemical transformation |
| High-Purity Material Synthesis | Repeatable properties, specific characteristics like color and durability |
Optimize your material sintering with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by strong deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to achieve superior results in powder processing and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















