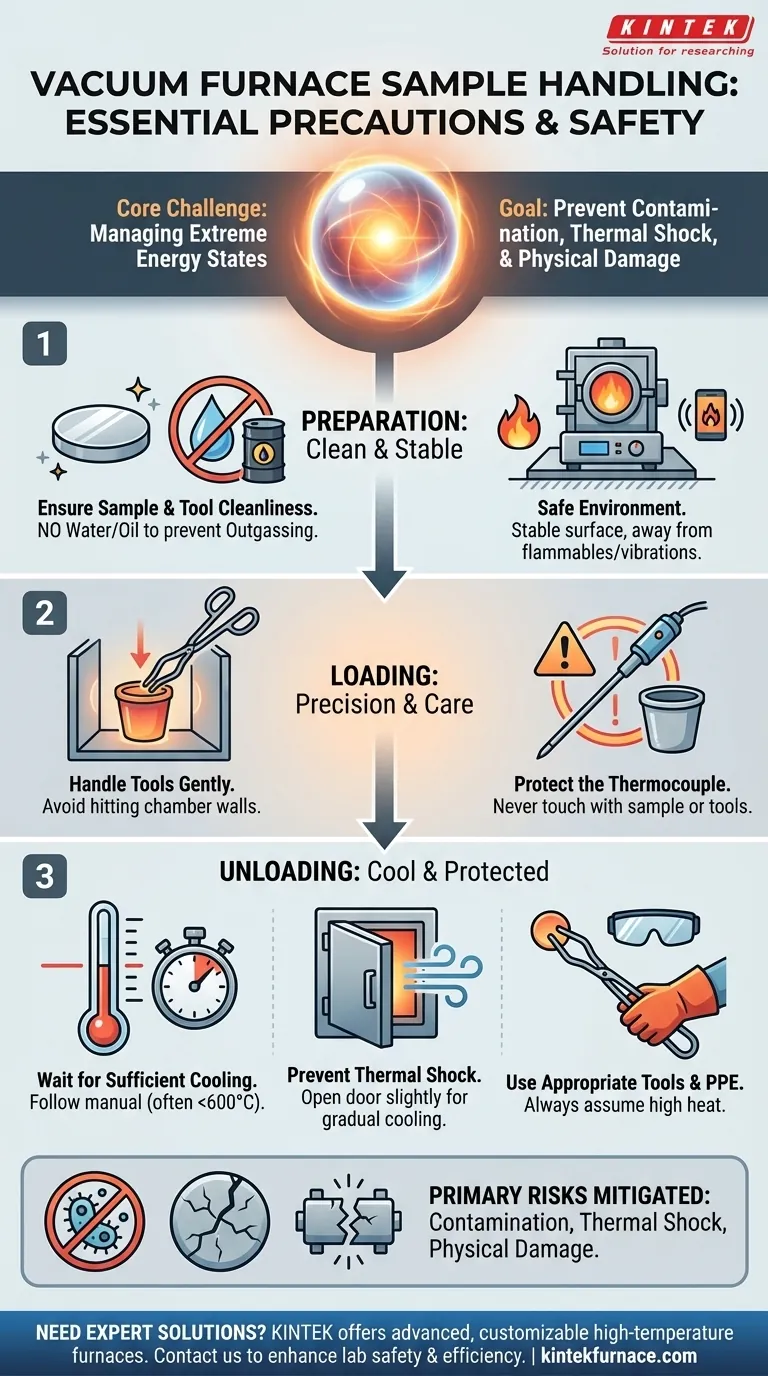
Above all, handling samples in a vacuum furnace requires a deliberate, methodical approach focused on safety and precision. Key precautions involve ensuring your sample and tools are completely free of contaminants like water or oil, handling all items gently to avoid damaging fragile internal components like the thermocouple, and managing the cooling and venting process carefully to prevent thermal shock to both the sample and the furnace.
The core challenge of handling vacuum furnace samples is not the physical act of moving them, but managing the extreme energy states involved. Your primary goal is to prevent three critical failures: contamination from foreign substances, thermal shock from rapid temperature changes, and physical damage from careless handling.
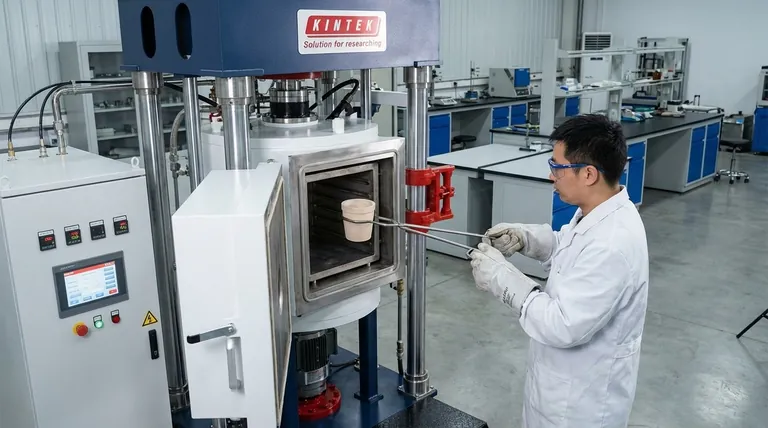

Preparing Your Sample and Furnace
Before you even open the furnace door, proper preparation is essential to prevent catastrophic failure during the heating cycle.
Ensure Sample and Tool Cleanliness
You must not introduce samples or tools that have any trace of water or oil. These substances will vaporize and rapidly expand in the vacuum, a process called outgassing.
This can prevent the furnace from reaching the required vacuum level, contaminate your sample, and in a worst-case scenario, lead to a dangerous pressure buildup or explosion.
Position the Furnace in a Safe Environment
The furnace itself should be located in a stable, secure area. It must be placed away from any flammable, explosive, or excessively wet materials.
Furthermore, ensure the furnace is on a surface that prevents severe vibrations or resonance, which can damage internal components over time.
Placing Samples into the Chamber
The process of loading the furnace is a moment of high risk for the equipment itself. Precision and care are paramount.
Handle Tools with Care
When using crucible tongs or clamps to place a sample inside, you must move gently and deliberately. Striking the interior walls can damage the furnace chamber's insulation or lining.
This damage can lead to inefficient heating, vacuum leaks, and costly repairs.
Protect the Thermocouple
The thermocouple is a temperature-sensing probe that extends into the furnace chamber. It is extremely fragile, especially at high temperatures.
Never allow your sample, crucible, or tools to touch the thermocouple. A slight impact can break its hot junction, rendering it useless and aborting your process.
Removing Samples After the Cycle
Removing the sample is arguably the most hazardous step, with significant risks of personal injury and damage from stored thermal energy.
Wait for Sufficient Cooling
Do not attempt to open the furnace door while the internal temperature is high. A common rule is to wait until the temperature drops below a specific threshold, often cited as 600°C, but following your specific equipment manual is critical.
Opening the door prematurely exposes you to intense radiant heat and risks severe burns.
Prevent Thermal Shock
Once the cycle is complete and power is off, do not immediately open the furnace door fully. This introduces cool room air that can cause thermal shock.
Thermal shock can crack or shatter your sample, the crucible, and even the furnace's internal components. Instead, open the door just a small crack to allow for slow, gradual cooling and pressure equalization.
Use Appropriate Tools and PPE
After the furnace has cooled sufficiently and the door is open, use long-handled crucible tongs to remove your items. Always assume the sample and internal racks are still hot enough to cause serious burns.
Wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses, is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Primary Risks
Your precautions are directly tied to mitigating three fundamental dangers inherent in vacuum furnace operation.
The Risk of Contamination
Any moisture or oil introduced into the chamber compromises the entire process. It ruins the vacuum, deposits unwanted material onto your sample's surface, and can damage vacuum pumps. Cleanliness is an absolute requirement.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
Materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. When this happens too quickly, the resulting internal stress can cause catastrophic failure. The gradual cooling procedure is the only way to prevent this.
The Fragility of Internal Components
The furnace's internal environment is delicate. The thermocouple and insulation are not designed to withstand physical impact. Every movement you make inside the chamber must be slow and controlled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific focus will determine which precautions are most critical in the moment.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: Prioritize waiting for the furnace to cool completely and always using the correct PPE and tools for removal.
- If your primary focus is protecting the equipment: Be most vigilant about never touching the thermocouple and handling tongs gently to avoid hitting the chamber walls.
- If your primary focus is sample integrity: The most important steps are ensuring absolute cleanliness of the sample and preventing thermal shock by cooling gradually.
Operating a vacuum furnace safely is a discipline built on patience and a deep respect for the powerful forces at play.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Type | Key Actions | Primary Risks Mitigated |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Ensure sample and tool cleanliness; position furnace in safe environment | Contamination, equipment damage |
| Loading | Handle tools gently; protect thermocouple from contact | Physical damage to furnace components |
| Unloading | Wait for sufficient cooling; prevent thermal shock; use appropriate PPE | Thermal shock, personal injury |
Need expert vacuum furnace solutions tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise performance for your specific experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing



















