At a fundamental level, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements can be used in both vertical and horizontal orientations. This flexibility allows them to be adapted to a wide variety of furnace and kiln designs. The element's ability to generate heat is not dependent on its orientation.
The question is not whether you can mount SiC elements horizontally or vertically, but how you support them in each orientation. The core challenge is managing their inherent brittleness and preventing mechanical failure at high operating temperatures.

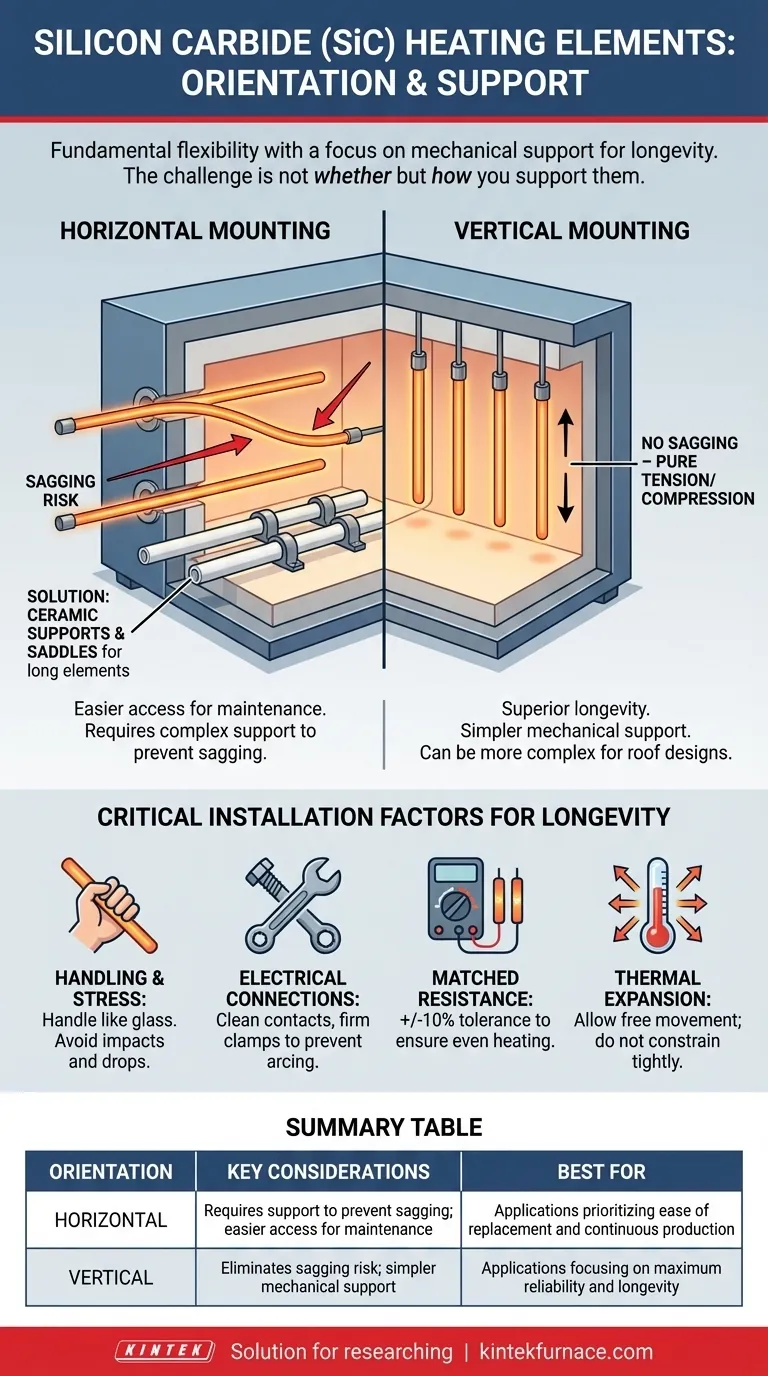
Understanding Orientation and Mechanical Support
The choice between vertical and horizontal mounting is less about thermal performance and more about the mechanical engineering of your furnace. SiC is a strong but brittle ceramic, and its longevity depends entirely on proper installation.
Horizontal Mounting
This is a very common orientation, where elements pass through the furnace walls.
The primary concern with horizontal mounting is sagging. At peak operating temperatures, even rigid silicon carbide can bend under its own weight over time, especially with longer elements.
To prevent this, longer horizontal elements must be supported by high-alumina ceramic support tubes or saddles placed at appropriate intervals within the furnace chamber.
Vertical Mounting
This orientation involves hanging the elements from the furnace roof or supporting them from the floor.
Vertical mounting is often mechanically simpler because it eliminates the risk of sagging. The element is in pure tension or compression, leveraging its structural strength most effectively.
Care must still be taken to ensure the clamps are not overtightened and that the element can expand and contract freely with temperature changes.
Critical Installation Factors for Longevity
Regardless of orientation, several factors are critical to the performance and lifespan of your SiC elements. Getting these details wrong is the most common source of premature failure.
Handling and Mechanical Stress
Silicon carbide elements are hard but brittle, similar to glass. They must be handled with extreme care during installation. Dropping them or striking them against a hard surface will likely cause a fracture.
Proper Electrical Connections
The connection between the element's cold ends and the power strap is a frequent point of failure. Ensure contact surfaces are clean and that clamps are tightened firmly to prevent electrical arcing, which can quickly destroy the element terminal.
Matched Electrical Resistance
For multi-element installations, it is critical that all elements in a given circuit have closely matched electrical resistance values (typically within a +/-10% tolerance). Mismatched elements will lead to uneven heating and cause some elements to run hotter, drastically shortening their life.
Thermal Expansion
The design must allow for the element's thermal expansion and contraction. If an element is constrained too tightly, the thermal stress will cause it to break as it heats up.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each orientation presents a different set of design considerations. There is no single "best" choice; the right answer depends on your specific furnace design and operational priorities.
The Case for Horizontal Mounting
Horizontal elements are often easier to access and replace without having to cool down the entire furnace or dismantle its roof structure. This makes them a practical choice for continuous production environments where downtime is costly. However, they demand a more complex support system inside the furnace to prevent sagging.
The Case for Vertical Mounting
Vertical elements offer superior longevity by completely avoiding the risk of sagging. This makes them ideal for applications requiring maximum reliability and in furnaces where element replacement is infrequent. The trade-off may be a more complex furnace structure, particularly for roof-hanging designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by your primary design objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Vertical mounting is generally the superior choice as it eliminates the primary mechanical failure mode of sagging.
- If your primary focus is ease of maintenance and replacement: Horizontal mounting often provides easier access to elements through the furnace walls.
- If your primary focus is designing a new furnace: Consider vertical mounting first for its inherent reliability, but weigh it against the complexity of your chamber design and loading process.
- If your primary focus is retrofitting an existing furnace: Your choice is largely dictated by the existing element openings, internal clearances, and support structures.
Ultimately, a successful installation depends on respecting the material's properties through careful handling and robust mechanical support.
Summary Table:
| Orientation | Key Considerations | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Requires support to prevent sagging; easier access for maintenance | Applications prioritizing ease of replacement and continuous production |
| Vertical | Eliminates sagging risk; simpler mechanical support | Applications focusing on maximum reliability and longevity |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's performance with custom high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced heating elements and furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup for durability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















