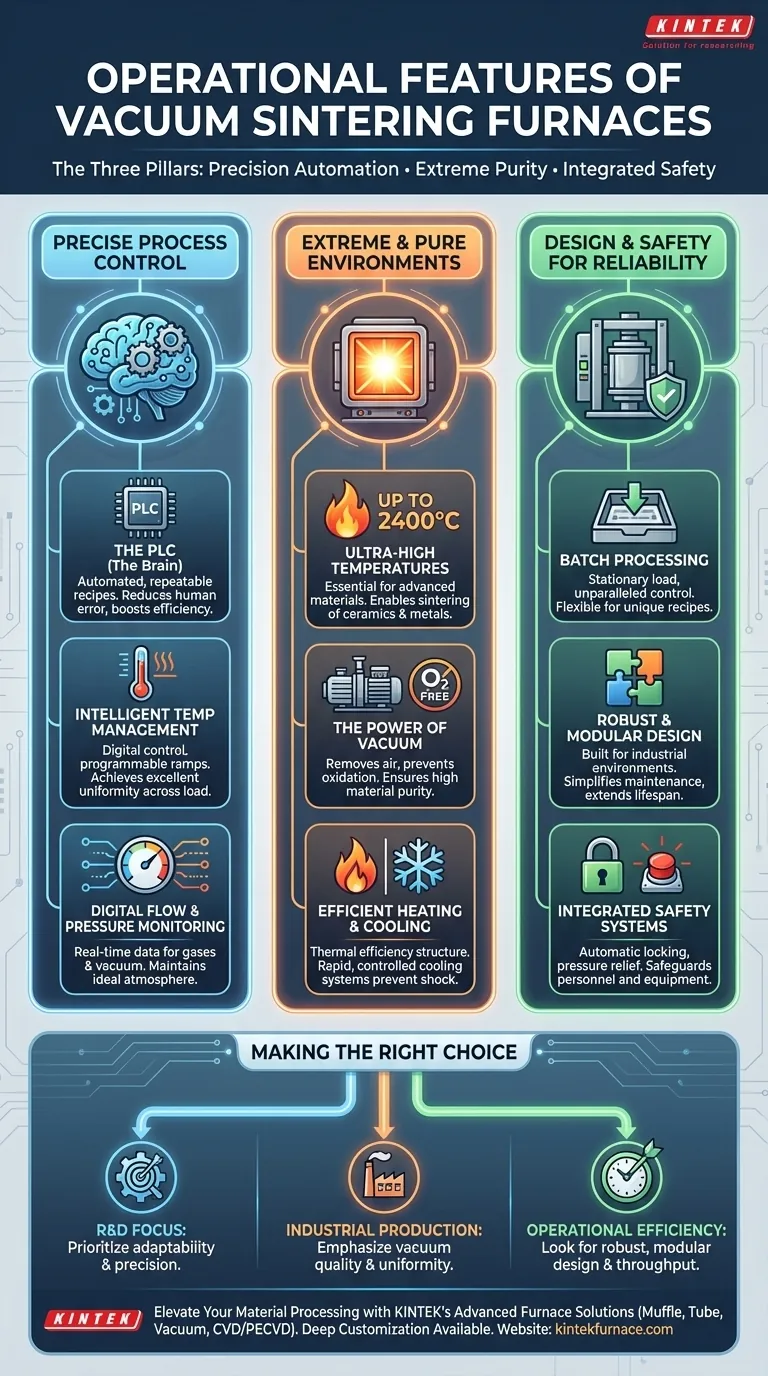
At their core, the operational features that distinguish vacuum sintering furnaces revolve around three principles: precision process automation, the ability to create extreme and pure environments, and integrated safety systems. These furnaces utilize PLC control systems for automated operation, achieve ultra-high temperatures (up to 2400°C) in an oxygen-free environment, and employ comprehensive monitoring to ensure reliability and protect the equipment.
A vacuum sintering furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a highly controlled system engineered to manipulate material properties at a molecular level. Its key features are designed to eliminate environmental variables like oxygen and precisely manage the entire thermal cycle, from heating to cooling.
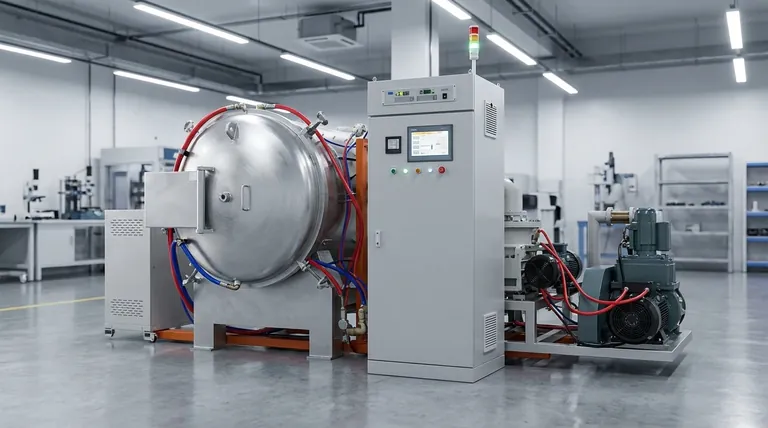

The Core of Operation: Precise Process Control
The primary differentiator of a modern vacuum furnace is its ability to execute a complex process recipe with minimal manual intervention. This is achieved through a synergy of software and hardware.
The PLC: The Brain of the Furnace
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) serves as the central nervous system. It automates the entire sintering cycle based on pre-programmed recipes.
This automation reduces the potential for human error and dramatically increases production efficiency and process repeatability, which is critical for consistent quality.
Intelligent Temperature Management
Furnaces use digital display intelligent temperature control, often guided by thermocouples placed on the furnace or the load itself. This allows for precise programming of temperature ramps, soaks, and cooling rates.
Achieving excellent temperature uniformity across the entire load is a key operational goal, ensuring every part undergoes the exact same thermal treatment.
Digital Flow and Pressure Monitoring
Systems are equipped with digital flow monitoring for gases and cooling water. This provides real-time data for efficient operation and acts as a safety check.
Constant monitoring of vacuum levels and gas pressure is fundamental. The PLC uses this data to control pumps and valves, maintaining the ideal processing atmosphere.
Creating the Ideal Sintering Environment
The "vacuum" in vacuum sintering is the key to producing superior materials. The furnace's features are built to create and maintain this specialized environment under extreme conditions.
Achieving Ultra-High Temperatures
A defining feature is the ability to reach ultra-high temperatures, often as high as 2400°C. This capability is essential for sintering advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and other high-performance materials.
The Power of the Vacuum
By removing air and other atmospheric impurities, the furnace prevents oxidation and contamination of the material during heating.
This is non-negotiable for applications in aerospace, medical, and electronics, where material purity and integrity are paramount. Some furnaces, like vacuum induction furnaces, use this principle to produce extremely high-purity castings.
Efficient Heating and Cooling
The internal structure is designed for thermal efficiency, with low thermal conductivity and excellent heat fusion to minimize energy loss.
Controlled cooling is just as important as heating. Many furnaces use an internal circulation pure water cooling system to safely and rapidly bring the load back to room temperature without thermal shock.
Understanding the Design and Trade-offs
The operational features are a direct result of a design philosophy that prioritizes reliability, safety, and serviceability.
Batch Processing: The Industry Standard
Most vacuum furnaces are batch furnaces, where a stationary load undergoes a complete, pre-programmed cycle. This eliminates the need for complex and failure-prone load transfer mechanisms within the hot zone.
The trade-off is that this is not a continuous process, but it provides unparalleled control and flexibility, as each batch can have a unique recipe tailored to the part geometry and material.
Robust Construction and Modular Design
These furnaces are built for industrial environments, featuring resistance to vibration, heat, and corrosion. This ensures a long service life.
A modular design is a key operational feature that simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and extending the equipment's lifespan.
Integrated Safety Systems
Safety is not an add-on; it is integrated into the PLC's control logic. Features include automatic door locking during operation and monitoring of temperature and pressure to prevent dangerous conditions.
Emergency pressure release valves and other automated shutdowns are in place to safeguard personnel and prevent catastrophic equipment damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The importance of each operational feature depends entirely on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize furnaces with maximum adaptability, precision temperature control, and the ability to handle small, varied loads.
- If your primary focus is high-purity industrial production: Emphasize the quality of the vacuum system, temperature uniformity, and the reliability of the PLC for repeatable, automated cycles.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and uptime: Look for a robust, modular design for easy maintenance, comprehensive safety systems, and efficient cooling cycles to maximize throughput.
Ultimately, these operational features work in concert to give you precise control over the creation of advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| PLC Control | Automated operation for precise, repeatable sintering cycles. |
| Ultra-High Temperatures | Capable of reaching up to 2400°C in oxygen-free environments. |
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination for material purity. |
| Safety Systems | Integrated monitoring with automatic shutdowns and pressure release. |
| Modular Design | Easy maintenance and troubleshooting to minimize downtime. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on R&D, high-purity production, or operational efficiency, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how our tailored solutions can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering



















