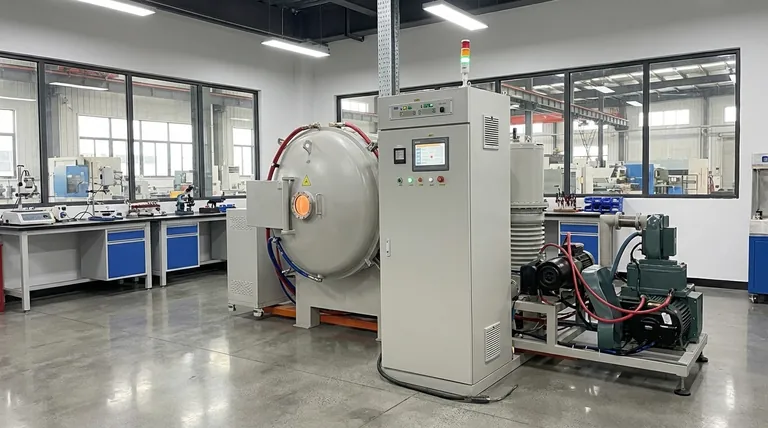
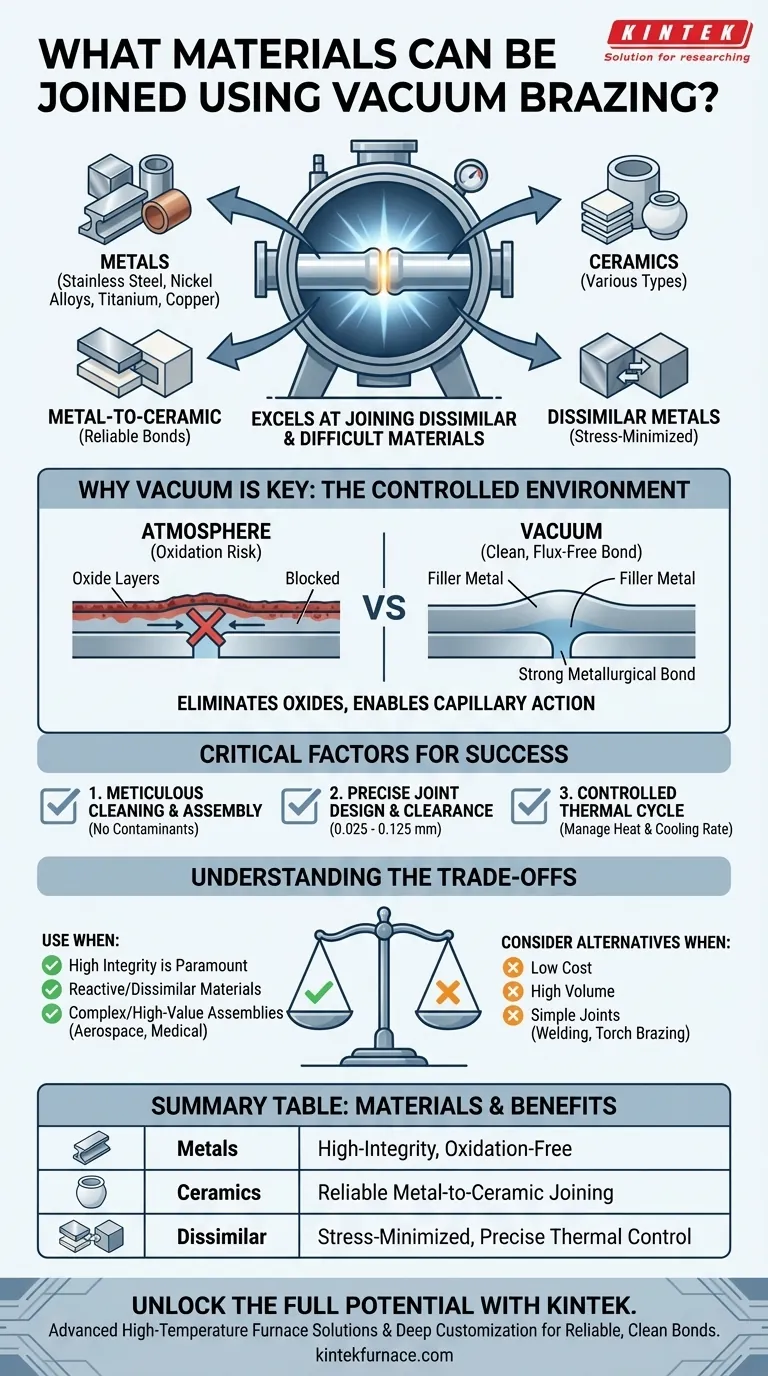
In short, vacuum brazing excels at joining a wide range of materials that are often difficult or impossible to join with other methods. Its primary strength lies in creating high-integrity bonds between dissimilar metals, including stainless steel, nickel alloys, titanium, and copper. Crucially, it is also one of the few processes capable of reliably joining metals to ceramics.
The true value of vacuum brazing is not just the materials it can join, but its ability to produce exceptionally clean, strong, and flux-free bonds in complex assemblies by performing the process in a controlled, oxygen-free environment.

Why Vacuum Is the Key to Versatility
The power of vacuum brazing comes from the environment in which it's performed. By removing the atmosphere from the furnace, the process eliminates the risk of oxidation that plagues many other high-temperature joining methods.
Eliminating Oxides and Contamination
When metals are heated, their surfaces react with oxygen in the air to form oxides. These oxide layers act as a barrier, preventing the filler metal from properly wetting and bonding to the parent materials, leading to a weak or failed joint.
A high-vacuum environment removes this threat. This allows the molten brazing alloy to flow freely via capillary action into the joint, creating a direct, strong metallurgical bond without the need for corrosive chemical fluxes.
Enabling the Joining of Dissimilar Materials
This clean, controlled process is what makes joining dissimilar materials possible. Different materials expand and contract at different rates (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion), which can create immense stress during heating and cooling.
Vacuum brazing allows for extremely precise control over the thermal cycle. This ensures that complex assemblies, even those made of different metals or metal-and-ceramic combinations, can be heated and cooled at a rate that minimizes internal stress, preventing distortion or cracking.
Critical Factors for a Successful Bond
While versatile, vacuum brazing is a highly technical process that demands meticulous control. Success is not just about choosing the right materials; it's about mastering the entire process from start to finish.
Meticulous Cleaning and Assembly
The parts to be joined must be scrupulously clean before entering the furnace. Any oils, grease, or surface contaminants will vaporize in the vacuum and can interfere with the bond. Assembly must take place in a clean environment for the same reason.
Precise Joint Design and Clearance
The gap between the materials being joined, known as the joint clearance, is critical. It must be large enough to allow the filler metal to flow in but small enough to enable strong capillary action.
For most applications, this clearance is typically between 0.025 mm and 0.125 mm (0.001" to 0.005").
Controlled Thermal Cycle
Every stage of the heating and cooling process must be precisely managed. This ensures the filler metal melts and flows at the correct temperature and that the final assembly cools slowly enough to prevent thermal shock or the buildup of residual stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum brazing offers unparalleled quality, but it comes with specific requirements that make it unsuitable for every application.
The Need for Specialized Equipment
The process requires a high-vacuum furnace, which is a significant capital investment. These systems are complex to operate and maintain, requiring skilled technicians.
Intolerance for Process Deviations
There is very little room for error. A successful braze depends on the strict and repeatable control of all process variables, from cleaning and assembly to the final thermal profile. Any deviation can compromise the integrity of the entire assembly.
Higher Per-Part Cost
Due to the specialized equipment, long cycle times, and need for expert oversight, vacuum brazing is generally more expensive than other joining methods like welding or torch brazing. Its cost is justified by the high performance and reliability of the final joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use vacuum brazing when the integrity of the joint is paramount and other methods are insufficient.
- If your primary focus is joining reactive or dissimilar materials: Vacuum brazing is one of the best choices for bonding titanium, nickel superalloys, or metals to ceramics.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, high-value assemblies: The process is ideal for producing clean, flux-free joints in intricate components for aerospace, medical, or semiconductor applications.
- If your primary focus is low cost and high volume for simple joints: You should consider alternative methods like torch brazing, induction brazing, or welding, as vacuum brazing may be over-specified.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is a precision manufacturing process chosen for performance, not for convenience.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Stainless steel, Nickel alloys, Titanium, Copper | High-integrity bonds, oxidation-free |
| Ceramics | Various ceramics | Reliable metal-to-ceramic joining |
| Dissimilar Combinations | Metal-metal, metal-ceramic | Stress-minimized bonds, precise thermal control |
Unlock the full potential of vacuum brazing for your high-performance assemblies! At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and semiconductor. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering reliable, clean bonds for complex components. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















