At its core, a vacuum furnace is an engineered system of specialized materials, each chosen to withstand extreme conditions. Key materials include refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten for heating, ceramics such as alumina and quartz for containment, and high-temperature steel alloys for structural components and retorts.
The selection of materials for a vacuum furnace is not about finding a single "best" material, but about creating a balanced system. Each component's material is precisely chosen for its specific role in managing extreme temperatures, maintaining vacuum purity, and ensuring chemical inertness for the process at hand.
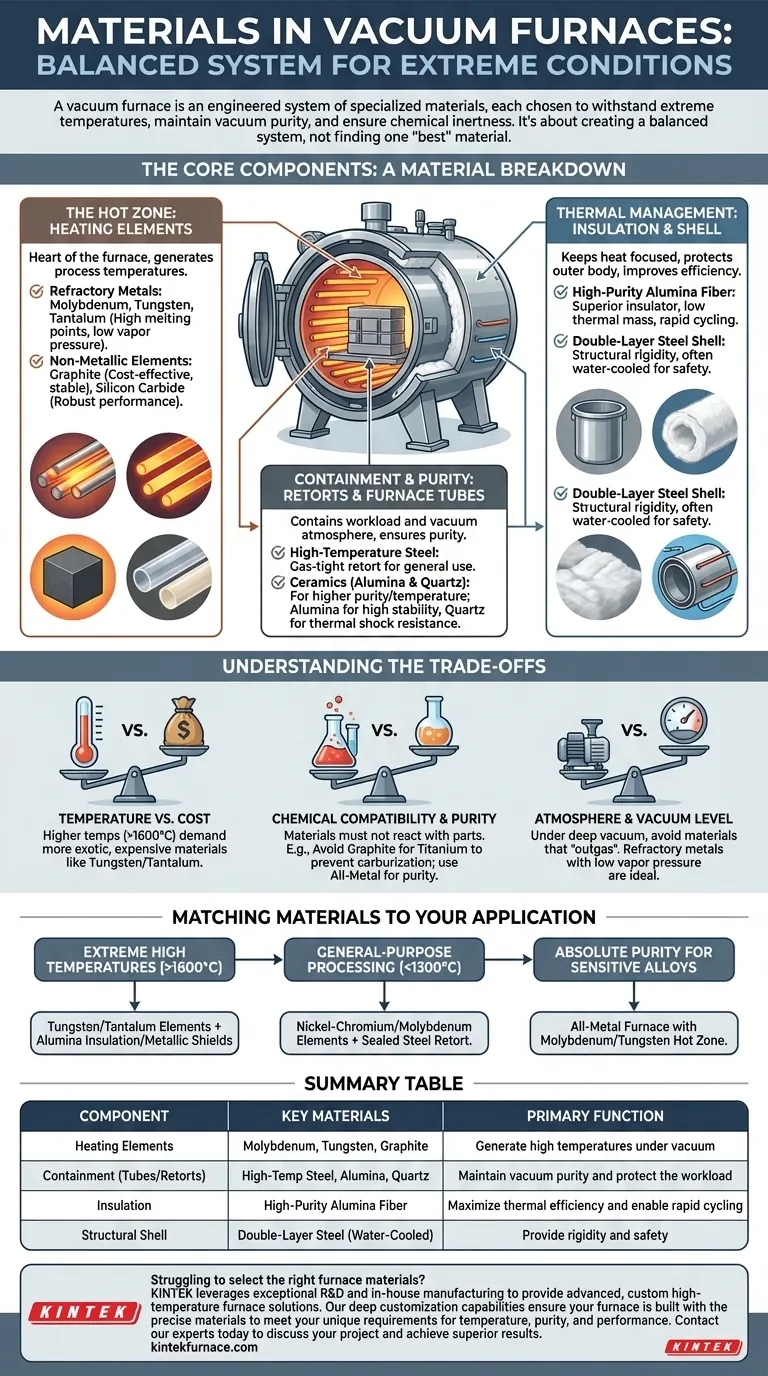
The Core Components: A Material Breakdown
A vacuum furnace is composed of several critical zones, each with its own material requirements. Understanding the function of each zone clarifies why specific materials are used.
The Hot Zone: Heating Elements
The heating elements are the heart of the furnace, responsible for generating the required process temperatures. They must operate reliably at thousands of degrees while under vacuum.
The most common materials are either metallic or non-metallic.
- Refractory Metals: Molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum are the primary choices. Their extremely high melting points and low vapor pressure prevent them from degrading or contaminating the vacuum environment at high temperatures.
- Non-Metallic Elements: Graphite and silicon carbide are excellent alternatives. Graphite is cost-effective and structurally stable at high heat, while silicon carbide offers robust performance in specific atmospheres.
Containment and Purity: Retorts and Furnace Tubes
This layer contains the workload and the vacuum atmosphere, protecting it from the heating elements and vice-versa. The material must be gas-tight and chemically non-reactive with the parts being processed.
- High-Temperature Steel: For many general-purpose applications, a gas-tight retort made of high-temperature resistant steel provides a durable and efficient containment solution.
- Ceramics (Alumina & Quartz): For processes demanding higher purity or temperature, furnace tubes are made from alumina or quartz. Alumina is exceptionally stable at very high temperatures (up to 1700°C), while quartz offers high purity and thermal shock resistance at slightly lower temperatures.
Thermal Management: Insulation and Shell
Surrounding the hot zone is a package of insulation designed to keep heat focused on the workload and protect the outer furnace body.
- High-Purity Alumina Fiber: This material is a superior insulator with low thermal mass. This allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles, significantly improving energy efficiency compared to older, heavier refractory bricks.
- Double-Layer Steel Shell: The external body is typically a double-layer steel shell. This structure provides the necessary structural rigidity and often incorporates a water-cooling circuit to keep the exterior safe to the touch and protect seals and instruments from overheating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right materials is a game of balancing performance, process compatibility, and cost. There is no single solution that fits all applications.
Temperature vs. Cost
Higher operating temperatures demand more exotic and expensive materials. A furnace with molybdenum elements is a workhorse for temperatures up to around 1600°C. Pushing beyond that to 2000°C or higher necessitates the use of more expensive tungsten or tantalum.
Chemical Compatibility and Purity
The furnace materials cannot react with the parts being processed. Using a graphite furnace to process titanium, for example, is a mistake as it can lead to carbon pickup (carburization), making the parts brittle. In such cases, an all-metal furnace with molybdenum or tungsten elements is required to maintain material purity.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Level
Under a deep vacuum, materials can "outgas," releasing trapped gases or even their own vapor, which contaminates the process. Refractory metals like molybdenum have exceptionally low vapor pressure, making them ideal for high-vacuum applications. The material choice must ensure the integrity of the vacuum level required for the treatment, such as vacuum sintering or annealing.
Matching Materials to Your Application
Your choice of furnace, and therefore its material composition, should be driven entirely by your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme high temperatures (>1600°C): You will need a furnace with tungsten or tantalum heating elements and high-purity alumina insulation or metallic radiation shields.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose processing (<1300°C): A cost-effective furnace with nickel-chromium or molybdenum elements and a sealed steel retort is often the most balanced choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity for sensitive alloys: An all-metal furnace using molybdenum or tungsten for all hot zone components is the industry standard to prevent any carbon contamination.
Ultimately, understanding how each material contributes to the system's performance is key to selecting a furnace that will achieve your goals safely and efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Materials | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Molybdenum, Tungsten, Graphite | Generate high temperatures under vacuum |
| Containment (Tubes/Retorts) | High-Temp Steel, Alumina, Quartz | Maintain vacuum purity and protect the workload |
| Insulation | High-Purity Alumina Fiber | Maximize thermal efficiency and enable rapid cycling |
| Structural Shell | Double-Layer Steel (Water-Cooled) | Provide rigidity and safety |
Struggling to select the right furnace materials for your specific high-temperature process? At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, custom high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether your application requires Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, or specialized CVD/PECVD Systems, our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace is built with the precise materials to meet your unique requirements for temperature, purity, and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in CoNiCrAlY coatings? Repairing Cold-Sprayed Microstructures
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance



















