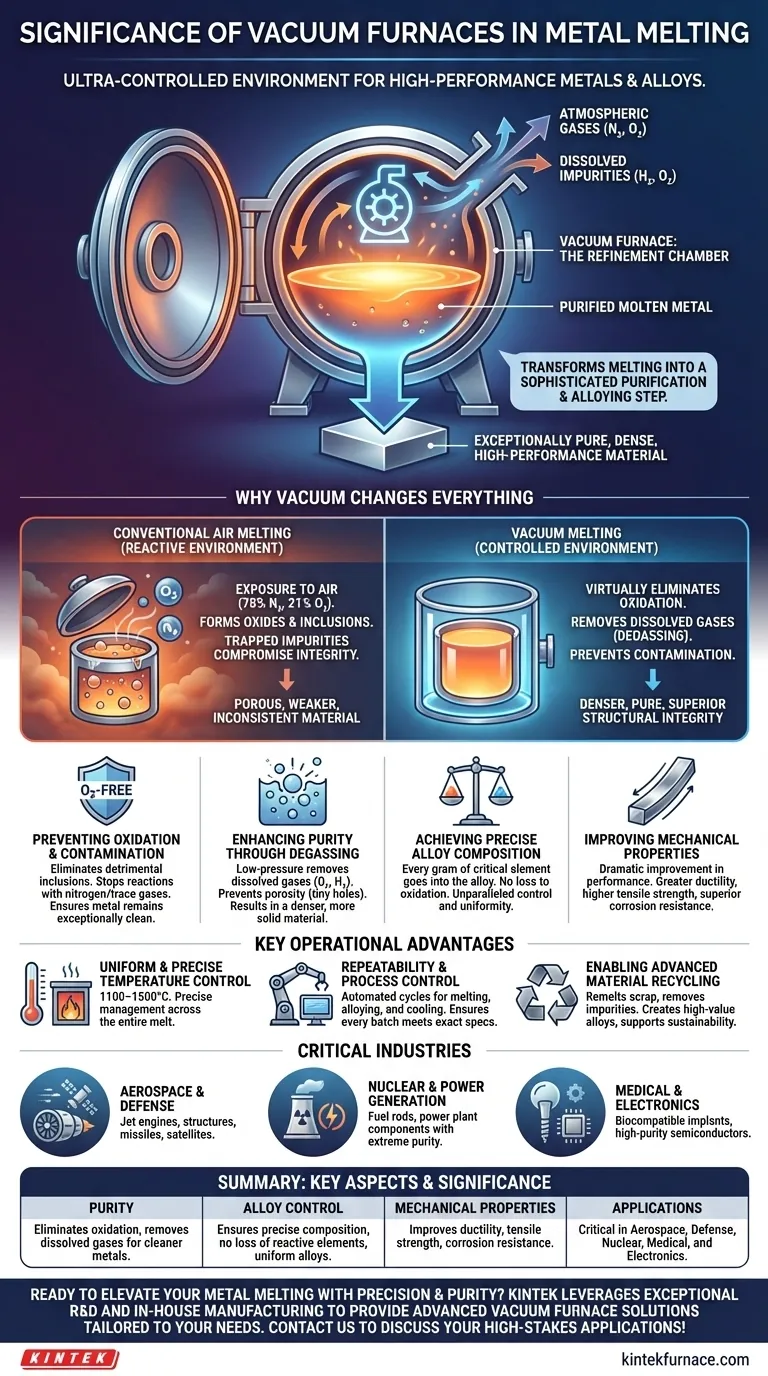
The fundamental significance of vacuum furnaces in metal melting is their ability to create an ultra-controlled environment, free from atmospheric gases. This control allows for the production of exceptionally pure, high-performance metals and alloys with precisely defined characteristics that are impossible to achieve with conventional air-melting techniques. By removing air, you eliminate unwanted chemical reactions, remove trapped impurities, and gain complete authority over the final material composition.
The core function of a vacuum furnace is not just to melt metal, but to actively refine it during the melting process. It transforms melting from a simple phase change into a sophisticated purification and alloying step, which is critical for materials used in the most demanding industries.

Why Melting in a Vacuum Changes Everything
Melting a metal in the open air exposes it to a reactive environment of approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. A vacuum furnace removes this variable, unlocking significant metallurgical advantages.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
In a conventional furnace, molten metal readily reacts with oxygen in the air, forming oxides. These oxides become inclusions—impurities trapped within the metal that compromise its structural integrity.
A vacuum atmosphere virtually eliminates oxidation, preventing the formation of these detrimental inclusions. It also stops reactions with nitrogen and other trace gases, ensuring the metal remains exceptionally clean.
Enhancing Purity Through Degassing
Molten metals can hold a significant amount of dissolved gases, particularly oxygen and hydrogen. As the metal cools and solidifies, these gases are forced out of solution, creating porosity (tiny holes) that severely weakens the final product.
The low-pressure environment of a vacuum furnace actively pulls these dissolved gases out of the liquid metal in a process called degassing. This results in a denser, more solid material with superior structural integrity.
Achieving Precise Alloy Composition
Creating high-performance alloys requires mixing elements in exact, often minute, proportions. In a normal atmosphere, some reactive alloying elements (like titanium or aluminum) can be lost to oxidation.
A vacuum ensures that every gram of an expensive or critical alloying element goes into the final alloy, not into slag or fumes. This allows for unparalleled control and uniformity of the alloy composition, which is essential for meeting strict industry and defense standards.
Improving Mechanical Properties
The direct result of higher purity, lower porosity, and precise composition is a dramatic improvement in the material's performance.
Metals produced in a vacuum furnace consistently exhibit enhanced mechanical properties, including greater ductility (ability to deform without fracturing), higher tensile strength, and superior corrosion resistance.
Key Operational and Process Advantages
Beyond the metallurgical benefits, vacuum furnaces offer distinct operational advantages that are critical for modern manufacturing.
Uniform and Precise Temperature Control
Vacuum furnaces provide exceptionally uniform heating, often within a range of 1100–1500°C (2000–2800°F).
This allows for precise temperature management across the entire melt, which is vital for complex alloys with narrow processing windows.
Repeatability and Process Control
Modern vacuum furnaces are typically computer-controlled. This enables fully automated, repeatable cycles for melting, alloying, and cooling.
This level of metallurgical repeatability ensures that every batch meets the exact same specifications, a non-negotiable requirement for industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Enabling Advanced Material Recycling
The refining capability of vacuum melting makes it highly effective for recycling. It can remelt scrap metal and remove impurities, turning lower-grade material into high-value alloys.
This contributes to sustainability efforts and provides a cost-effective path for creating specialized materials.
Where This Technology is Critical
The unique capabilities of vacuum melting make it indispensable for applications where material failure is not an option.
Aerospace and Defense
This is the largest user of vacuum-melted materials. Components for jet engines, aircraft structures, missiles, and satellites demand the highest possible strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to extreme conditions.
Nuclear and Power Generation
The production of nuclear fuel rods and components for power plants requires materials with extreme purity and predictable performance under radiation and high temperatures.
Medical and Electronics
High-purity metals are essential for medical implants, which must be biocompatible and corrosion-resistant. In electronics, vacuum processing is used to create semiconductors and components for solar cells where even trace impurities can cause failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a melting process depends entirely on the required purity and performance of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: For mission-critical parts in aerospace, nuclear, or medical fields, vacuum melting is the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is precise and repeatable alloying: For developing or producing specialty superalloys with complex chemistries, the control offered by a vacuum furnace is essential.
- If your primary focus is general fabrication or small-scale R&D: Simpler atmospheric or small-scale box furnaces may be sufficient and more cost-effective for applications where ultra-high purity is not the main driver.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic decision to prioritize material quality and performance above all else.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Significance |
|---|---|
| Purity | Eliminates oxidation and contamination, removes dissolved gases via degassing for cleaner metals. |
| Alloy Control | Ensures precise composition with no loss of reactive elements, enabling uniform high-performance alloys. |
| Mechanical Properties | Improves ductility, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance for durable materials. |
| Applications | Critical in aerospace, defense, nuclear, medical, and electronics for reliability and performance. |
Ready to elevate your metal melting processes with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, nuclear, medical, or electronics, our vacuum furnaces ensure superior material quality and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-stakes applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















