In the field of advanced material fabrication, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) serves a critical role by enabling the creation of high-quality, uniform thin films at significantly lower temperatures than traditional methods. It uses an energized plasma to drive the chemical reactions needed for deposition, giving engineers precise control over the final film's properties on a wide variety of materials.
PECVD's fundamental advantage is its ability to decouple the deposition energy source from heat. By using plasma instead of high temperatures, it allows for the growth of dense, pure, and highly-controlled films on substrates that would be damaged or destroyed by conventional thermal processes.
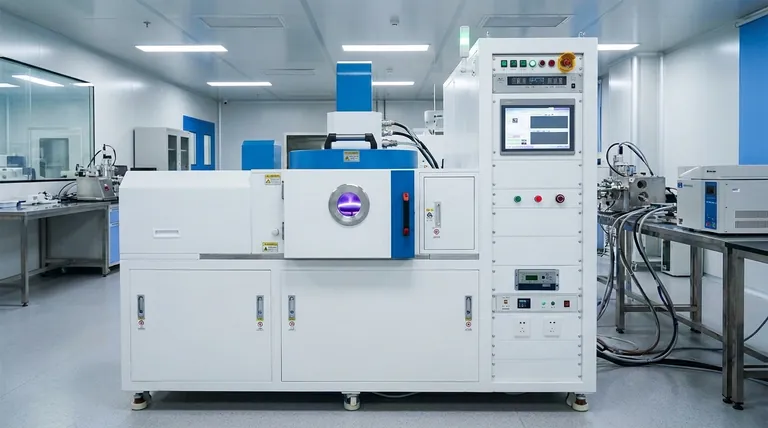

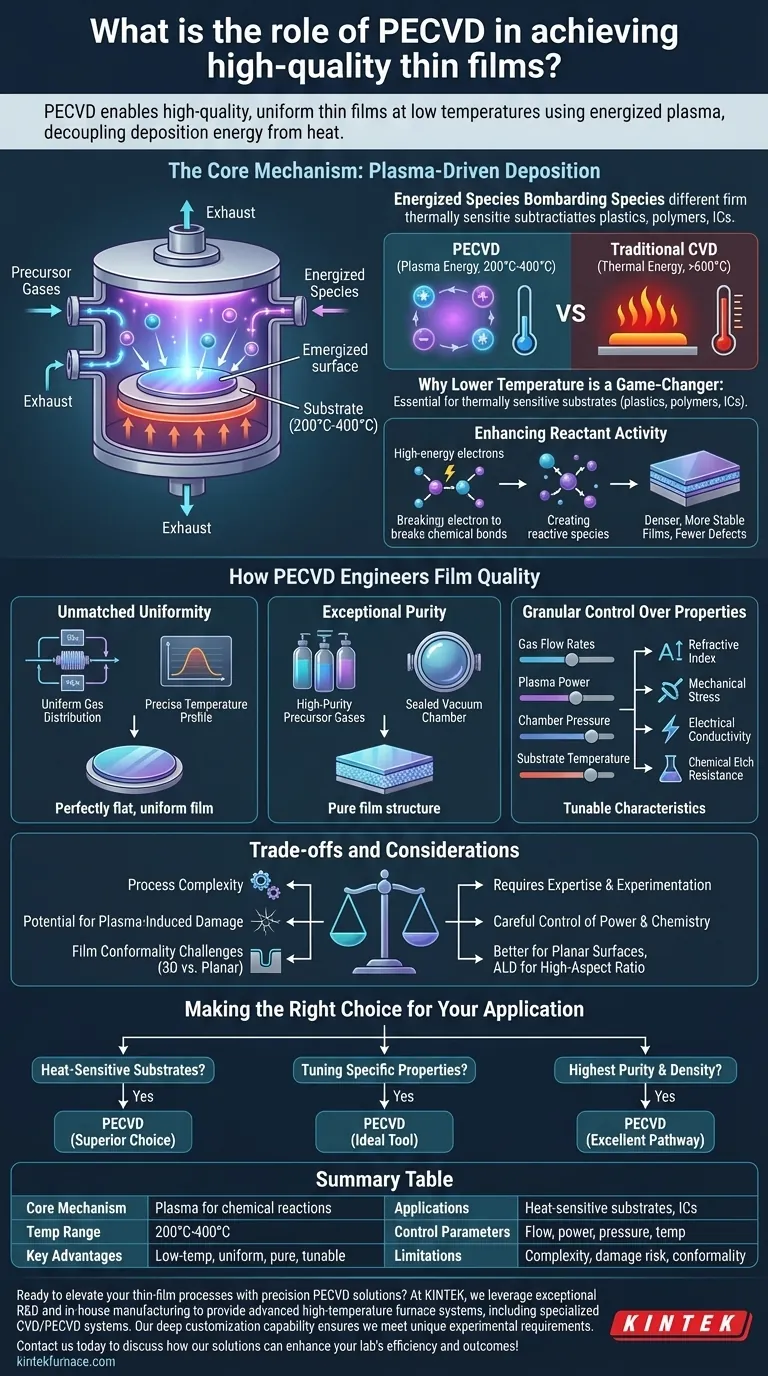
The Core Mechanism: Plasma-Driven Deposition
The defining feature of PECVD is its use of plasma—an ionized gas containing electrons, ions, and neutral species. This plasma provides the energy needed to break down precursor gases and initiate the film-forming chemical reactions.
Why Lower Temperature is a Game-Changer
Traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) relies on high thermal energy (often >600°C) to drive reactions. PECVD achieves the same outcome at much lower temperatures, typically between 200°C and 400°C.
This low-temperature capability is essential for depositing films on thermally sensitive substrates, such as plastics, polymers, or complex integrated circuits that cannot withstand high heat without damage.
Enhancing Reactant Activity
The high-energy electrons within the plasma efficiently break the chemical bonds of the precursor gases. This creates highly reactive species that readily deposit onto the substrate surface.
This enhanced reactivity allows for better control over the film's microstructure and chemical composition, leading to denser, more stable films with fewer defects.
How PECVD Engineers Film Quality
Achieving a "high-quality" film is not accidental; it is the result of meticulously controlling the deposition environment. PECVD systems are designed to provide this control at several key levels.
Achieving Unmatched Uniformity
High-quality films must be consistent across the entire substrate. PECVD reactors are engineered with uniform gas distribution systems and precise temperature profiles.
This hardware design ensures that every part of the substrate is exposed to the same reaction conditions, resulting in highly uniform film thickness and consistent properties from edge to edge.
Ensuring Exceptional Purity
Film purity is paramount, especially in semiconductor and optical applications. The process starts with high-purity precursor gases.
Because the deposition occurs in a controlled, sealed vacuum chamber, the introduction of atmospheric or environmental impurities is minimized, leading to a film with the desired chemical makeup.
Gaining Granular Control Over Properties
PECVD allows for the fine-tuning of a film's final characteristics by adjusting key process parameters. These include:
- Gas flow rates
- Plasma power
- Chamber pressure
- Substrate temperature
By manipulating these variables, engineers can precisely dial in properties like refractive index, mechanical stress, electrical conductivity, and chemical etch resistance to meet exact application requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PECVD is not without its complexities. Acknowledging its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Process Complexity
The large number of controllable parameters that give PECVD its flexibility also adds to its complexity. Developing a stable, repeatable process recipe requires significant expertise and experimentation.
Potential for Plasma-Induced Damage
The same high-energy plasma that enables low-temperature deposition can sometimes cause surface damage to extremely sensitive materials. This risk can be mitigated through careful control of plasma power and chemistry but remains a factor to consider.
Film Conformalilty
While excellent for planar surfaces, achieving a perfectly uniform coating (or "conformal" coverage) over complex, high-aspect-ratio 3D structures can be more challenging with PECVD compared to other methods like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD).
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use PECVD should be driven by the specific requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is depositing on heat-sensitive substrates: PECVD is almost always the superior choice due to its fundamentally low-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is tuning specific optical or electrical properties: The granular control over process parameters makes PECVD an ideal tool for engineering custom film characteristics.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity and film density: PECVD provides an excellent pathway, delivering results far superior to many physical deposition methods.
By understanding its core principles and trade-offs, you can effectively leverage PECVD to achieve precise and reliable thin-film outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Uses plasma for chemical reactions, decoupling energy from heat |
| Temperature Range | 200°C to 400°C, much lower than traditional CVD (>600°C) |
| Key Advantages | Low-temperature deposition, uniform films, high purity, tunable properties |
| Applications | Ideal for heat-sensitive substrates like plastics and integrated circuits |
| Control Parameters | Gas flow rates, plasma power, chamber pressure, substrate temperature |
| Limitations | Process complexity, potential plasma-induced damage, conformality challenges |
Ready to elevate your thin-film processes with precision PECVD solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including our specialized CVD/PECVD systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're working with sensitive substrates or need tailored film properties. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















