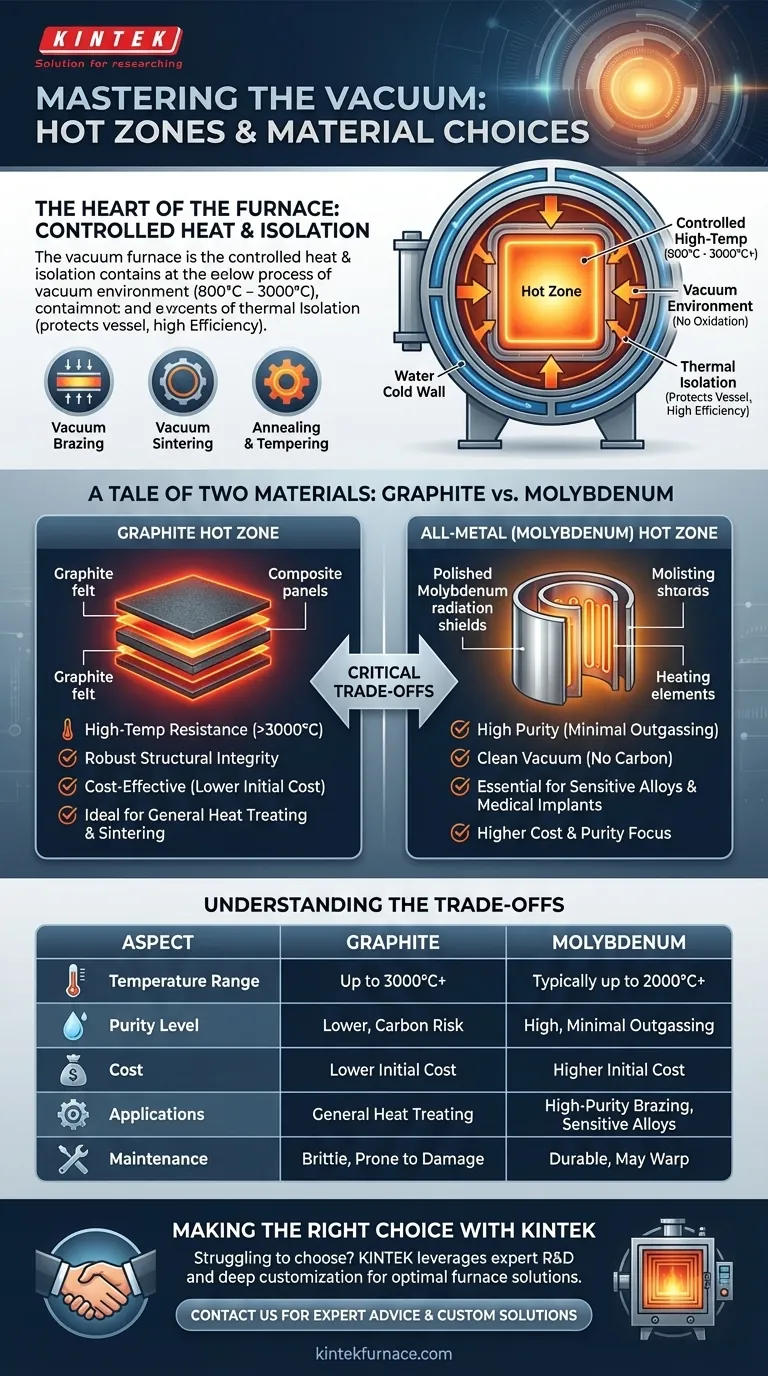
At the heart of any vacuum furnace is the hot zone, the insulated inner chamber where all heating takes place. Its purpose is to contain and uniformly apply extreme heat to a workpiece in a vacuum, while protecting the rest of the furnace. The most common materials used for its heat shields and insulation are high-purity graphite and refractory metals, primarily molybdenum.
The choice between a graphite or an all-metal (molybdenum) hot zone is a critical engineering decision. It directly dictates the furnace's maximum temperature, vacuum purity, operational costs, and suitability for specific metallurgical processes like brazing or sintering.
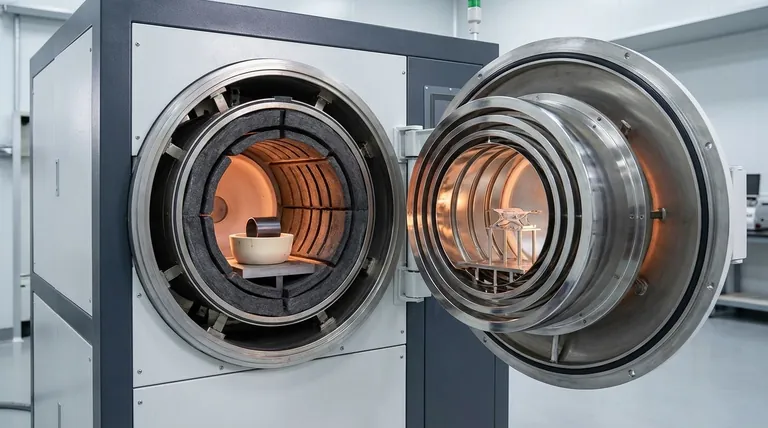

The Role of the Hot zone in Vacuum Processing
The hot zone is more than just a box that gets hot; it is a precisely engineered system designed for thermal control and isolation.
A Controlled High-Temperature Environment
The primary function of the hot zone is to generate and contain the heat required for a specific process, which can range from 800°C to over 3,000°C.
By operating in a vacuum, this heating occurs without the risk of oxidation or contamination from atmospheric gases, which is critical for processing reactive metals and advanced materials.
Isolating Heat from the Vessel
The hot zone is constructed as a self-contained unit suspended inside the main furnace chamber. This creates a gap between the hot insulation package and the water-cooled "cold wall" of the furnace vessel.
This physical separation is the key to thermal efficiency. It dramatically reduces heat loss, allowing the system to reach and maintain extreme temperatures while keeping the outer vessel cool and structurally sound.
Enabling Key Thermal Processes
The specific design of the hot zone enables a range of industrial applications. These include:
- Vacuum Brazing: Joining metals using a filler material at temperatures below the base metals' melting point.
- Vacuum Sintering: Fusing metal or ceramic powders into a solid mass.
- Annealing & Tempering: Heat treating to alter a material's microstructure, improving its ductility and reducing hardness.
A Tale of Two Materials: Graphite vs. Molybdenum
The choice of hot zone material is the most significant factor in a furnace's performance. The decision almost always comes down to graphite or an all-metal design featuring molybdenum.
The Graphite Hot Zone
Graphite is an extremely popular choice due to its high-temperature resistance, structural integrity at heat, and relatively lower cost.
It is often used in the form of rigid felt or carbon-carbon composite insulation panels. These are excellent for general-purpose heat treating and high-temperature sintering of materials like stainless steel or certain ceramics.
The All-Metal (Molybdenum) Hot Zone
All-metal hot zones use layers of refractory metals, primarily molybdenum and sometimes tungsten, as both heating elements and radiation shields.
These zones are prized for their cleanliness. Molybdenum does not produce carbon-bearing vapor, making it essential for processes where even minute carbon contamination is unacceptable, such as brazing sensitive aerospace superalloys or processing medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither material is universally superior. The correct choice depends entirely on the process requirements, creating a series of critical trade-offs.
Temperature vs. Purity
Graphite-based hot zones can often reach higher maximum temperatures than standard molybdenum designs, making them ideal for some sintering and melting applications.
However, molybdenum provides a much cleaner vacuum environment. For applications demanding the highest purity and lowest outgassing, such as in the semiconductor or medical fields, an all-metal hot zone is the only viable option.
Process Compatibility
The materials being processed can react with the hot zone itself. For example, brazing certain alloys in a graphite hot zone can lead to carbon pickup, creating brittle carbides in the final joint. An all-metal hot zone prevents this.
Conversely, some materials can react negatively with molybdenum, making graphite the preferred choice. Understanding this chemical compatibility is paramount.
Maintenance and Longevity
Graphite components can become brittle and are susceptible to mechanical damage. All-metal shields, while durable, can warp or become embrittled after thousands of thermal cycles.
Modern furnace designs often feature hot zones that are easily removable as a single unit, which significantly simplifies maintenance and repair for either material type.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a hot zone is about aligning the furnace's capability with your specific industrial or research goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity brazing or processing sensitive alloys: An all-metal (molybdenum) hot zone is the correct choice to prevent carbon contamination and ensure a clean vacuum.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering or general-purpose heat treating: A graphite hot zone is typically the more robust, cost-effective, and higher-temperature solution.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced ceramics or medical implants: The decision requires careful analysis of chemical compatibility, with all-metal zones often being preferred for purity-sensitive applications.
Ultimately, understanding the design and material of the hot zone is the key to mastering your thermal process and achieving repeatable, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Graphite Hot Zone | Molybdenum Hot Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 3000°C+ | Typically up to 2000°C+ |
| Purity Level | Lower, risk of carbon contamination | High, minimal outgassing |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Applications | General heat treating, high-temp sintering | High-purity brazing, sensitive alloys, medical implants |
| Maintenance | Brittle, prone to damage | Durable, may warp over cycles |
Struggling to choose the right hot zone for your vacuum furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or materials research, we ensure optimal performance and purity. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your thermal processes and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety



















