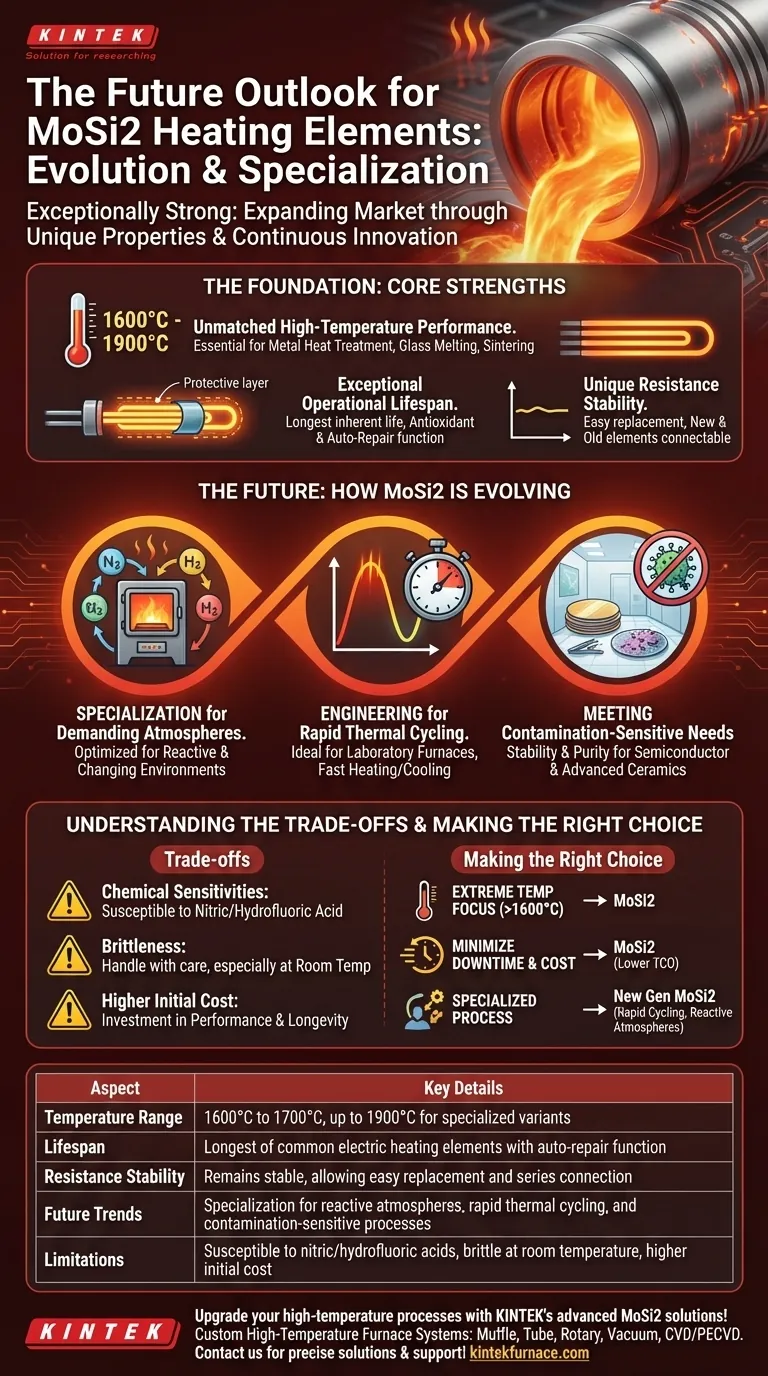
The future outlook for MoSi2 heating elements is exceptionally strong. Their market is expanding due to a unique combination of extreme high-temperature capability, long operational lifespan, and continuous innovation. Rather than being replaced, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) technology is becoming more specialized, solving challenges in advanced industrial and laboratory applications where other heating elements cannot perform.
The core takeaway is that the future of MoSi2 isn't about its relevance, but its evolution. It is solidifying its position as the premium, go-to solution for the most demanding high-temperature processes, driven by ongoing advancements that broaden its application range.

The Foundation: Why MoSi2 Remains a Core Technology
MoSi2 elements are not just maintaining their place in the market; their fundamental properties ensure they remain a critical component in high-temperature industries.
Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
MoSi2 elements operate comfortably at temperatures between 1600°C and 1700°C, with specialized variants capable of reaching up to 1900°C.
This makes them indispensable for applications like metal heat treatment, glass melting, and high-temperature sintering where conventional metallic elements would fail.
Exceptional Operational Lifespan
These elements possess the longest inherent lifespan of all common electric heating elements, which significantly reduces furnace downtime and maintenance costs.
A key feature is their antioxidant and auto-repair function. In an oxidizing atmosphere, a protective layer of silica glass forms on the surface, which "heals" itself if damaged, contributing to its durability.
Unique Resistance Stability
The electrical resistance of MoSi2 remains remarkably stable throughout its long service life.
This unique property allows new elements to be connected in series with older ones without causing imbalances. It also simplifies replacement, which can often be done while the furnace is still hot, further minimizing production halts.
The Future: How MoSi2 is Evolving
The strong outlook for MoSi2 is not just based on its existing strengths but on significant, ongoing progress in its design and application.
Specialization for Demanding Atmospheres
Recent advancements have produced MoSi2 elements specifically optimized for use in reactive atmospheres, such as nitrogen, or in processes with changing atmospheres.
This overcomes a traditional limitation and opens up new applications in advanced materials manufacturing and chemical processing.
Engineering for Rapid Thermal Cycling
New designs are engineered to withstand rapid thermal cycling without degradation.
This makes them ideal for modern laboratory furnaces and high-temperature sintering processes that require fast heating and cooling rates to achieve specific material properties.
Meeting the Needs of Contamination-Sensitive Processes
Innovations are also focused on creating elements for contamination-sensitive high-temperature environments.
The stability and purity of these advanced MoSi2 elements are critical for industries like semiconductor manufacturing and advanced ceramics, where even minor impurities can ruin a product batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To make an informed decision, it's crucial to understand the specific limitations and considerations associated with MoSi2 technology.
Chemical Sensitivities
While resistant to most acids and alkalis, MoSi2 elements are susceptible to attack from nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. Care must be taken to ensure the process environment is compatible.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
Like many advanced ceramics, MoSi2 elements are brittle at low temperatures. This requires careful handling during installation and maintenance to prevent mechanical shock or fracture.
Higher Initial Cost
MoSi2 elements typically have a higher upfront cost compared to other heating technologies like silicon carbide or metallic elements. This cost is an investment in performance, longevity, and reduced operational downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element depends entirely on your operational goals and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature capability (above 1600°C): MoSi2 is the definitive choice, offering performance and stability where other materials cannot.
- If your primary focus is minimizing downtime and long-term cost: The exceptionally long lifespan and ease of replacement make MoSi2 a compelling option for a lower total cost of ownership.
- If your primary focus is a specialized or sensitive process: Look to the new generations of MoSi2 elements, as they are being actively engineered for challenges like reactive atmospheres and rapid cycling.
Ultimately, MoSi2 technology is not just persisting; it is defining the future of high-performance electric heating.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 1600°C to 1700°C, up to 1900°C for specialized variants |
| Lifespan | Longest of common electric heating elements with auto-repair function |
| Resistance Stability | Remains stable, allowing easy replacement and series connection |
| Future Trends | Specialization for reactive atmospheres, rapid thermal cycling, and contamination-sensitive processes |
| Limitations | Susceptible to nitric/hydrofluoric acids, brittle at room temperature, higher initial cost |
Upgrade your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced MoSi2 solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with custom high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your demanding applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















