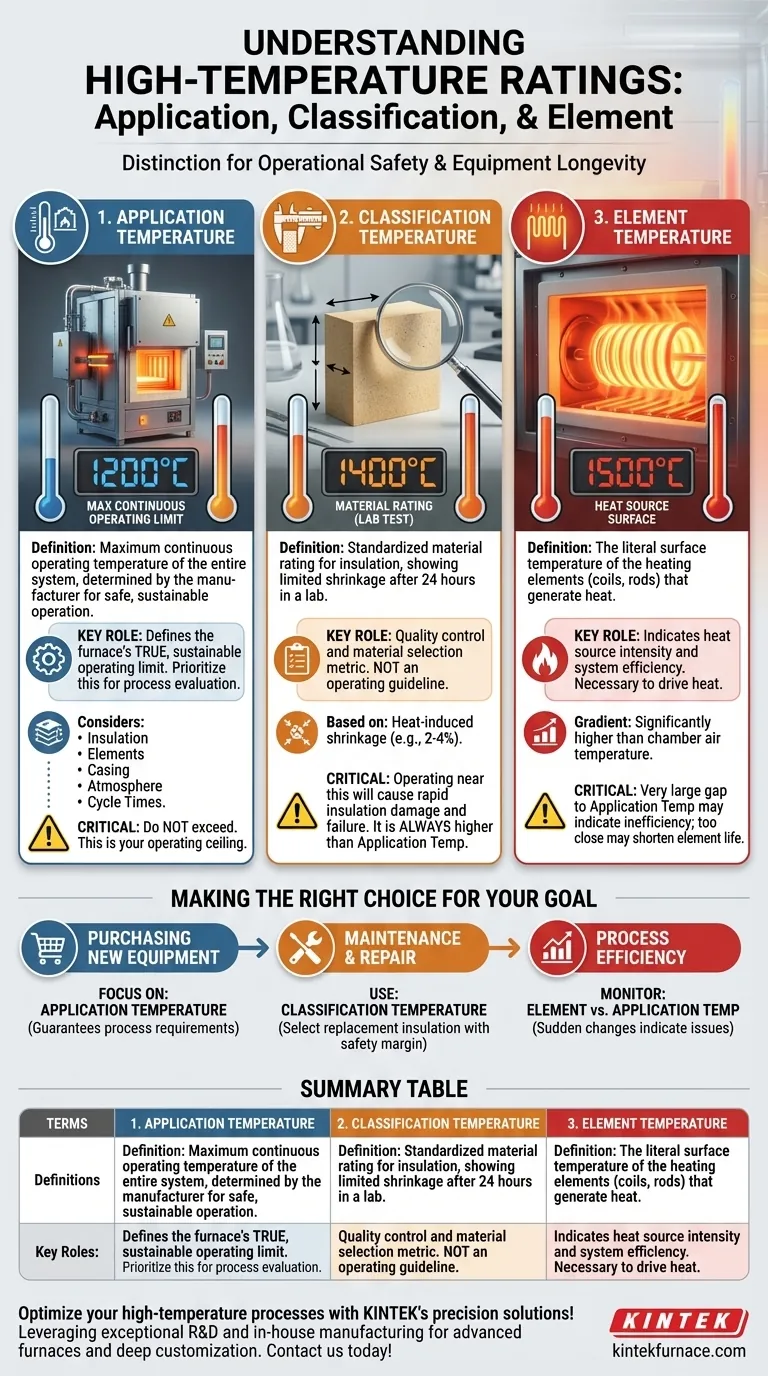
In high-temperature applications, understanding the distinction between application, classification, and element temperature is critical for ensuring operational safety and equipment longevity. Application temperature is the maximum continuous operating temperature of the entire system, classification temperature is a standardized material rating for insulation based on heat-induced shrinkage, and element temperature is the surface temperature of the heating source itself.
While classification and element temperatures are vital engineering specifications for individual components, application temperature is the only rating that defines the furnace's true, sustainable operating limit. Always prioritize application temperature when evaluating equipment for a specific process.

Deconstructing the Ratings: From Component to System
To use high-temperature equipment effectively, you must understand how these ratings relate to one another. They represent different points in the thermal system, from the raw material's limit to the furnace's practical capability.
Classification Temperature: The Insulation's Benchmark
The classification temperature is a standardized property of a refractory or insulation material. It is determined in a laboratory setting.
Specifically, it is the temperature at which the material exhibits a specific, limited amount of linear shrinkage (e.g., 2-4%) after being held at that temperature for 24 hours. This is a quality control and comparison metric, not an operating guideline.
Element Temperature: The Heat Source
The element temperature is the literal surface temperature of the heating elements (e.g., the coils or rods) that generate the heat within the furnace.
This temperature will always be significantly higher than the furnace chamber's air temperature. A steep temperature gradient is necessary to drive heat from the elements into the chamber and the product being processed.
Application Temperature: The Real-World Operating Limit
The application temperature is the most critical number for an operator. It represents the maximum temperature at which the entire furnace or system can be operated continuously and safely.
This rating is a holistic value determined by the manufacturer. It considers the limits of the insulation, the heating elements, the furnace casing, and other components, as well as operational factors like atmosphere and typical cycle times.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Confusing these terms is a common and costly mistake. The gap between these temperature ratings is not arbitrary; it represents an essential engineering safety margin.
Why Classification Temperature Is a Poor Guide
The classification temperature of the insulation will always be substantially higher than the furnace's application temperature. For example, a furnace with a 1200°C application temperature might use insulation with a 1400°C classification temperature.
Operating a furnace near its insulation's classification temperature would cause rapid and permanent damage. The insulation would shrink, crack, and lose its insulating properties, leading to catastrophic heat loss and potential structural failure.
The Element-to-Application Gap
The difference between the element temperature and the application temperature reveals how hard the elements must work. A very large gap might indicate poor insulation or an inefficient design.
Conversely, an element temperature that is too close to the application temperature can shorten the element's lifespan, as it may be operating near its own maximum limit.
The Danger of Misinterpretation
Basing your process on the classification temperature is the most common pitfall. This will invariably lead to the destruction of the furnace's insulation lining and is a misapplication of the specification. Always design your process around the manufacturer's stated application temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this understanding to guide your decisions, whether you are buying, operating, or maintaining high-temperature equipment.
- If your primary focus is purchasing new equipment: Focus on the application temperature. This is the only number that guarantees the furnace can meet your process requirements for continuous, long-term operation.
- If your primary focus is maintenance or repair: Use the classification temperature to select the correct replacement insulation, ensuring it provides an adequate safety margin above your required application temperature.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Monitor the relationship between element temperature and application temperature. A sudden change can indicate insulation degradation or other system inefficiencies.
By understanding these distinct ratings, you move from simply using equipment to truly engineering a reliable and safe high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Type | Definition | Key Role |
|---|---|---|
| Application Temperature | Maximum continuous operating temperature of the entire system | Defines the furnace's safe, sustainable operating limit |
| Classification Temperature | Standardized material rating for insulation based on shrinkage | Used for material selection and quality control, not operation |
| Element Temperature | Surface temperature of the heating elements | Indicates heat source intensity and system efficiency |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's precision solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met for enhanced safety and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















