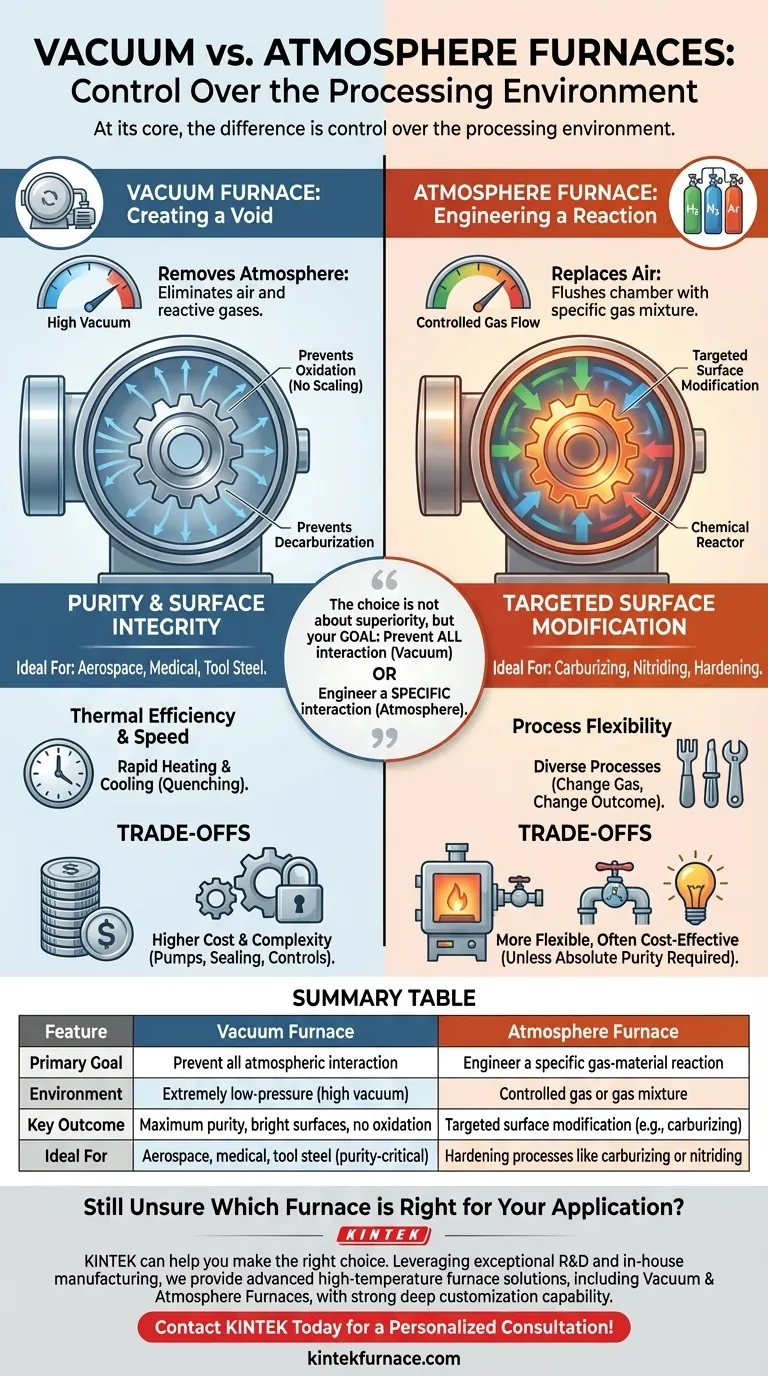
At its core, the difference is control over the processing environment. A vacuum furnace works by removing the atmosphere to create an extremely low-pressure, non-reactive space. In contrast, an atmosphere furnace works by replacing the ambient air with a specific, carefully controlled gas or mixture of gases to achieve a desired chemical interaction with the material.
The choice between a vacuum and an atmosphere furnace is not about which is superior, but about defining your goal. You must decide if you need to prevent all atmospheric interaction (vacuum) or engineer a specific atmospheric interaction (atmosphere).

How Each Furnace Controls the Environment
The primary distinction lies in their approach to managing the gases surrounding the part during heating. Each method serves a distinct metallurgical purpose.
The Vacuum Furnace: Creating a Void
A vacuum furnace uses a system of pumps to remove virtually all air and other gases from a sealed chamber before and during the heating cycle.
The goal is to create a near-perfect vacuum. This eliminates reactive elements like oxygen and water vapor that can contaminate or damage sensitive materials at high temperatures.
The Atmosphere Furnace: Engineering a Reaction
An atmosphere furnace flushes its chamber with a specific gas or a precise blend of gases, creating a controlled, artificial atmosphere.
Commonly used gases include inert gases like argon or nitrogen to prevent reactions, or reactive gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, or carbon-rich gases to intentionally cause surface reactions like carburizing or nitriding.
Key Process Outcomes and Applications
The environment directly dictates the final properties of the material, making the choice of furnace critical for success.
Purity and Surface Integrity (Vacuum's Strength)
By removing the atmosphere, a vacuum furnace prevents negative surface reactions. This makes it the ideal choice for processes where purity is paramount.
Key outcomes include the prevention of oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (loss of carbon from steel). This results in bright, clean parts that often require no post-process cleaning, common in aerospace, medical, and tool steel applications.
Targeted Surface Modification (Atmosphere's Purpose)
An atmosphere furnace is used when the gas itself is an active ingredient in the heat treatment process.
For example, in carburizing, a carbon-rich atmosphere is used to diffuse carbon into the surface of steel to harden it. The furnace is a chemical reactor, not just a heater.
Thermal Efficiency and Speed
Vacuum environments have very low thermal mass, allowing for extremely rapid heating and cooling (quenching). This high degree of control over thermal cycles is crucial for achieving specific microstructures and material properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While both are powerful tools, they come with different operational costs, complexities, and limitations.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are typically more expensive to purchase and operate. The high-vacuum pumps, robust chamber sealing, and sophisticated controls required to maintain a deep vacuum add significant complexity and cost.
Atmosphere furnaces, especially those using simple inert gas flows, can be a more cost-effective solution when absolute purity is not required.
Process Flexibility
An atmosphere furnace can offer broader flexibility for processes that require gas-surface interaction. A single furnace can be used for carburizing, nitriding, or neutral hardening simply by changing the gas mixture.
The "Low Vacuum" Overlap
Some advanced atmosphere furnaces can pull a low vacuum (e.g., around 1 Torr) to purge the chamber before introducing the process gas. It is critical to understand this is not the same as the high vacuum in a dedicated vacuum furnace, which operates at pressures many orders of magnitude lower to ensure purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision must be driven by the end goal for your material.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and a bright, clean surface: A vacuum furnace is the correct choice to prevent all unwanted atmospheric reactions.
- If your primary focus is to induce a specific surface chemical reaction like carburizing or nitriding: An atmosphere furnace is necessary to supply the required reactive gases.
- If your primary focus is general oxidation prevention on a budget: An atmosphere furnace using an inert gas like argon or nitrogen is often a sufficient and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, you are choosing the precise environment that will deliver the specific material properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Furnace | Atmosphere Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent all atmospheric interaction | Engineer a specific gas-material reaction |
| Environment | Extremely low-pressure (high vacuum) | Controlled gas or gas mixture |
| Key Outcome | Maximum purity, bright surfaces, no oxidation | Targeted surface modification (e.g., carburizing) |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, medical, tool steel (purity-critical) | Hardening processes like carburizing or nitriding |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Application?
Choosing between a vacuum and atmosphere furnace is critical to achieving your desired material properties. KINTEK can help you make the right choice.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution for your specific process needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















