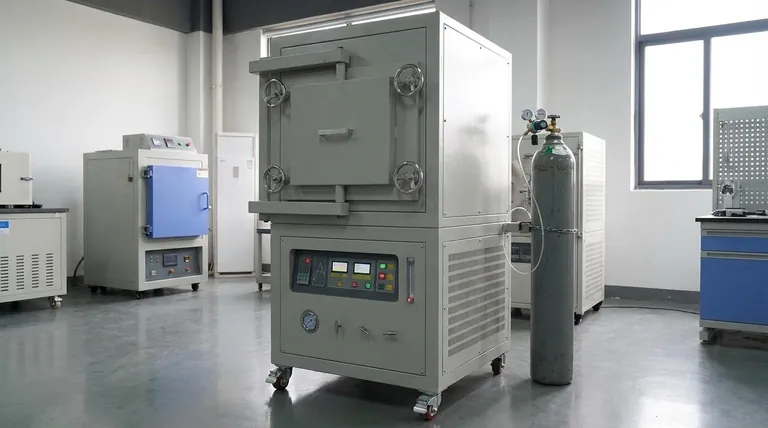
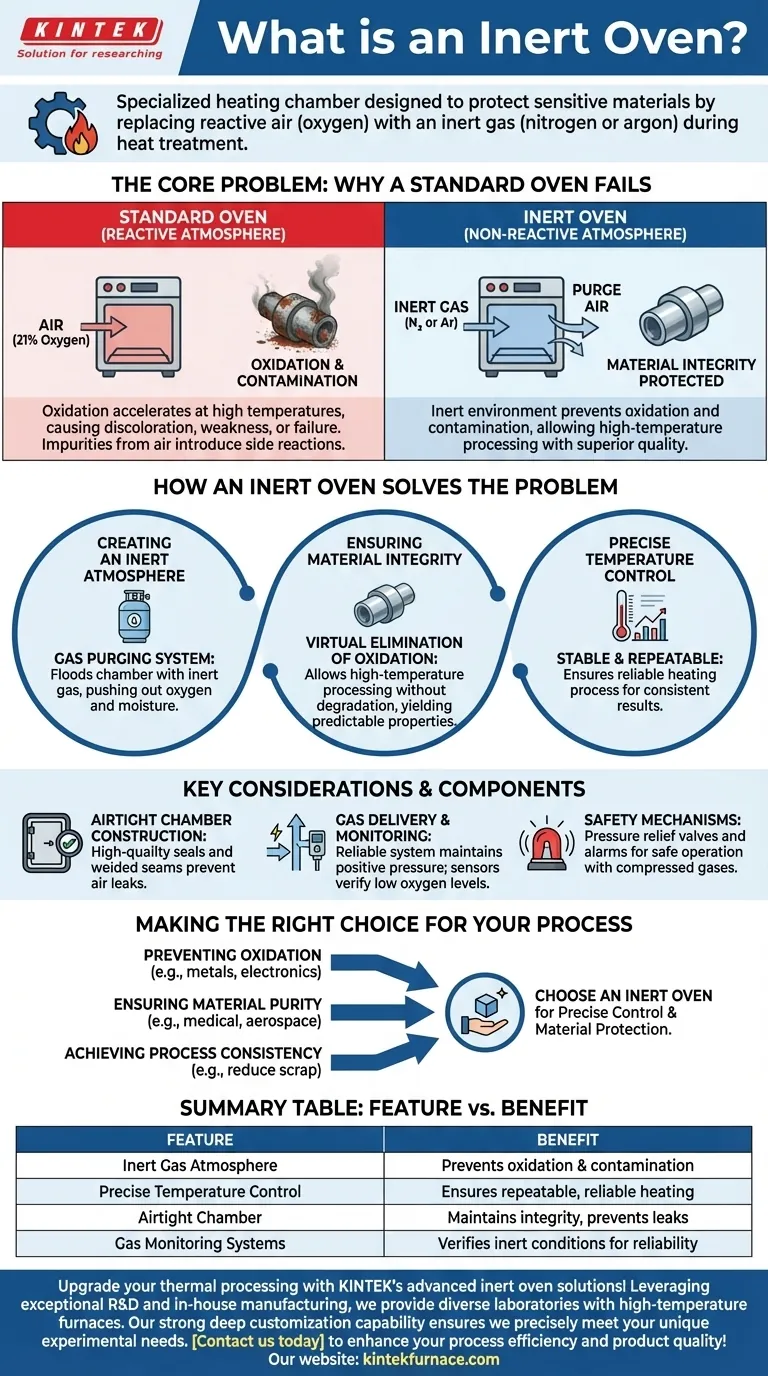
At its core, an inert oven is a specialized heating chamber designed to protect sensitive materials from reacting with the air during heat treatment. It achieves this by replacing the normal, reactive atmosphere (containing oxygen) with a non-reactive or "inert" gas, such as nitrogen or argon, preventing processes like oxidation and ensuring the material's integrity.
The true purpose of an inert oven is not just to heat an object, but to control the chemical environment while it is being heated. This control is what prevents unwanted degradation and enables high-precision manufacturing and research.

The Core Problem: Why a Standard Oven Fails
Heating materials in a conventional oven means exposing them to ambient air, which is roughly 21% oxygen. At elevated temperatures, this oxygen becomes highly reactive and can cause significant problems.
The Challenge of Oxidation
Oxidation is a chemical reaction that occurs when a material is exposed to oxygen. A common example at room temperature is the rusting of iron.
At high temperatures, this process accelerates dramatically. For many metals, electronics, and advanced polymers, heating in the presence of oxygen can cause discoloration, structural weakness, or complete failure of the component.
Contamination and Unwanted Reactions
Beyond oxygen, other elements in the air can act as contaminants. These can introduce impurities into a material's surface or trigger unintended side reactions.
This is especially critical in fields like semiconductor manufacturing or medical device fabrication, where even microscopic impurities can render a product useless.
How an Inert Oven Solves the Problem
An inert oven directly addresses the issues of oxidation and contamination by fundamentally changing the environment in which heating occurs.
Creating an Inert Atmosphere
The primary function of an inert oven is its gas purging system. Before the heating cycle begins, the system floods the chamber with an inert gas, typically nitrogen or argon.
This process purges the chamber, physically pushing out the oxygen and moisture until the internal atmosphere is almost entirely non-reactive.
Ensuring Material Integrity
By heating the material in this controlled, oxygen-free environment, the risk of oxidation is virtually eliminated.
This allows materials to be processed at high temperatures without degradation. The result is a final product with superior quality, predictable properties, and the intended performance characteristics.
The Role of Precise Temperature Control
Alongside atmospheric control, inert ovens feature highly precise temperature control. The combination of a stable temperature and a non-reactive environment ensures that the heating process is both repeatable and reliable.
Key Considerations and Components
The effectiveness of an inert oven depends on its design and how it maintains the integrity of the inert atmosphere.
Airtight Chamber Construction
To prevent reactive air from leaking back in, an inert oven must have an exceptionally well-sealed chamber. This involves high-quality gaskets, reinforced doors, and welded seams that can withstand pressure changes during operation.
Gas Delivery and Monitoring Systems
A reliable gas delivery system is essential for purging the chamber and maintaining a slight positive pressure during the cycle. Many advanced ovens also include gas monitoring systems, such as oxygen sensors, to verify that the environment remains truly inert.
Safety Mechanisms
Handling compressed gases introduces safety considerations. Inert ovens are equipped with features like pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization and alarms to alert operators to any system-level issues.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use an inert oven is driven entirely by the sensitivity of your material to the ambient atmosphere during heating.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation: An inert oven is non-negotiable for heat-treating most metals, bonding electronic components, or curing certain polymers.
- If your primary focus is ensuring material purity: In medical, aerospace, or semiconductor applications, the controlled atmosphere prevents surface contamination that standard ovens cannot.
- If your primary focus is achieving process consistency: Removing the variable of atmospheric reaction leads to more repeatable outcomes, reducing scrap rates and improving overall product quality.
Ultimately, investing in an inert oven is about gaining precise control over your thermal process to protect your material's integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Inert Gas Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and contamination by replacing oxygen with non-reactive gases like nitrogen or argon |
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures repeatable and reliable heating processes for consistent results |
| Airtight Chamber | Maintains integrity of inert environment, preventing leaks and ensuring safety |
| Gas Monitoring Systems | Verifies oxygen levels to confirm inert conditions, enhancing process reliability |
Upgrade your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced inert oven solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, protecting sensitive materials from oxidation and contamination. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance



















