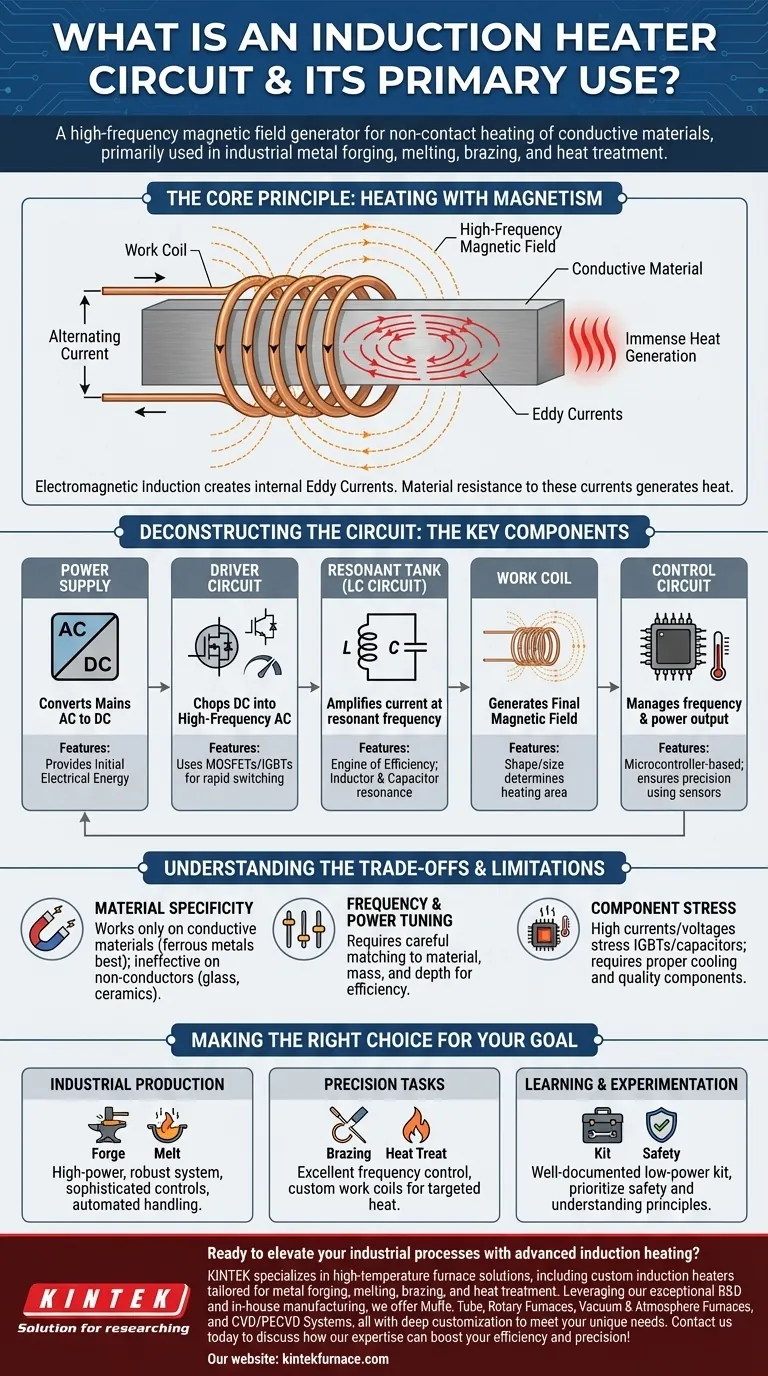
At its core, an induction heater circuit is a device that generates a powerful, high-frequency magnetic field to heat electrically conductive materials without any physical contact. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, creating internal currents within the target material itself. This method is primarily used in industrial settings for processes like metal forging, melting, brazing, and precise heat treatment.
The true innovation of an induction heater isn't just using magnetism to create heat. It is the use of a resonant tank circuit to create an extremely efficient and precisely controlled electromagnetic field, allowing for rapid, clean, and targeted heating that flame or resistance heating cannot match.
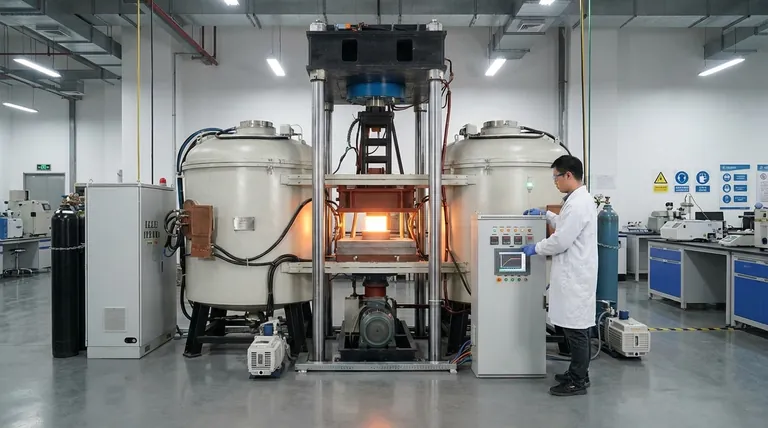

The Core Principle: Heating with Magnetism
The entire process is governed by a fundamental law of physics discovered by Michael Faraday.
Electromagnetic Induction
When you pass an alternating current through a coil of wire, it generates a fluctuating magnetic field around it. If you place a conductive object (like a piece of steel) inside this field, the field induces electrical currents within the object.
The Role of Eddy Currents
These induced currents are called eddy currents. Due to the material's natural electrical resistance, the flow of these eddy currents generates immense heat. Think of it as creating countless microscopic heating elements directly inside the material itself.
Deconstructing the Circuit: The Key Components
An induction heater is a system where each part plays a critical role. The design can vary, but most circuits share these core components.
The Power Supply
This is the starting point, providing the initial electrical energy. It converts mains AC voltage into the DC voltage required by the driver circuit.
The Driver Circuit: The High-Speed Switch
The driver's job is to take the steady DC power and "chop" it into a high-frequency alternating current. It uses powerful semiconductor switches like MOSFETs or IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) that can turn on and off thousands or even millions of time per second.
The Work Coil: The Heart of the System
This is the copper coil that generates the final magnetic field. Its shape and size are critical, as they determine the shape and intensity of the magnetic field and, consequently, where the heating occurs on the workpiece.
The Resonant Tank (LC Circuit): The Engine of Efficiency
This is the most crucial part of the circuit. The work coil (which is an inductor, L) is paired with a bank of capacitors (C). Together, they form an LC circuit, also known as a resonant tank.
This tank has a natural resonant frequency. By driving the circuit at this specific frequency, the energy oscillates between the coil's magnetic field and the capacitors' electric field with very little loss. This resonance dramatically amplifies the current in the work coil, creating an exceptionally strong magnetic field and maximizing heating efficiency.
The Control Circuit: The Brains of the Operation
A control circuit, often using a microcontroller, manages the entire process. It adjusts the driver circuit's frequency and power output to maintain the desired temperature, often using feedback from sensors like thermocouples. This allows for incredibly precise and repeatable heating cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Material Specificity
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrically conductive. It is highly effective on ferrous metals like iron and steel but less so on materials like aluminum and copper, and it does not work at all on non-conductors like glass or ceramics.
Frequency and Power Tuning
The system is not "plug-and-play." The operating frequency and power level must be carefully matched to the type of material, the mass of the object being heated, and the desired heating depth. An improperly tuned circuit will be inefficient and may not heat the object effectively.
Component Stress
The high currents and voltages present in a resonant tank place significant stress on the driver components (IGBTs/MOSFETs) and capacitors. Proper cooling and the use of high-quality components are essential for reliability and to prevent catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this technology, you must align the circuit's design with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is industrial production (forging, melting): You need a high-power, robust system with sophisticated temperature controls and automated handling.
- If your primary focus is precision tasks (brazing, heat treating): You need a system with excellent frequency control and custom-designed work coils to deliver heat to very specific areas.
- If your primary focus is learning and experimentation: Start with a well-documented, low-power kit and prioritize understanding the principles of the resonant LC circuit and driver safety.
By mastering these principles, you can harness the power of electromagnetism for clean, rapid, and precise heating.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Converts AC to DC | Provides initial electrical energy |
| Driver Circuit | Chops DC into high-frequency AC | Uses MOSFETs/IGBTs for rapid switching |
| Work Coil | Generates magnetic field | Copper coil, determines heating area |
| Resonant Tank (LC Circuit) | Amplifies current for efficiency | Uses inductor and capacitor for resonance |
| Control Circuit | Manages frequency and power | Microcontroller-based, ensures precision |
Ready to elevate your industrial processes with advanced induction heating? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom induction heaters tailored for metal forging, melting, brazing, and heat treatment. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can boost your efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability



















