Vacuum sintering furnaces are a cornerstone technology for industries that require components with exceptional purity, strength, and performance. They are most commonly used in aerospace, medical device manufacturing, automotive, electronics, and advanced materials sectors like powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing. This process is chosen when atmospheric gases like oxygen would contaminate or weaken the final product during high-temperature consolidation.
The critical insight is that the choice to use a vacuum sintering furnace is driven by material requirements, not by industry alone. Any field that needs to create dense, pure, and strong parts from powdered materials—especially those reactive to air—will inevitably rely on this technology to prevent contamination and achieve superior final properties.

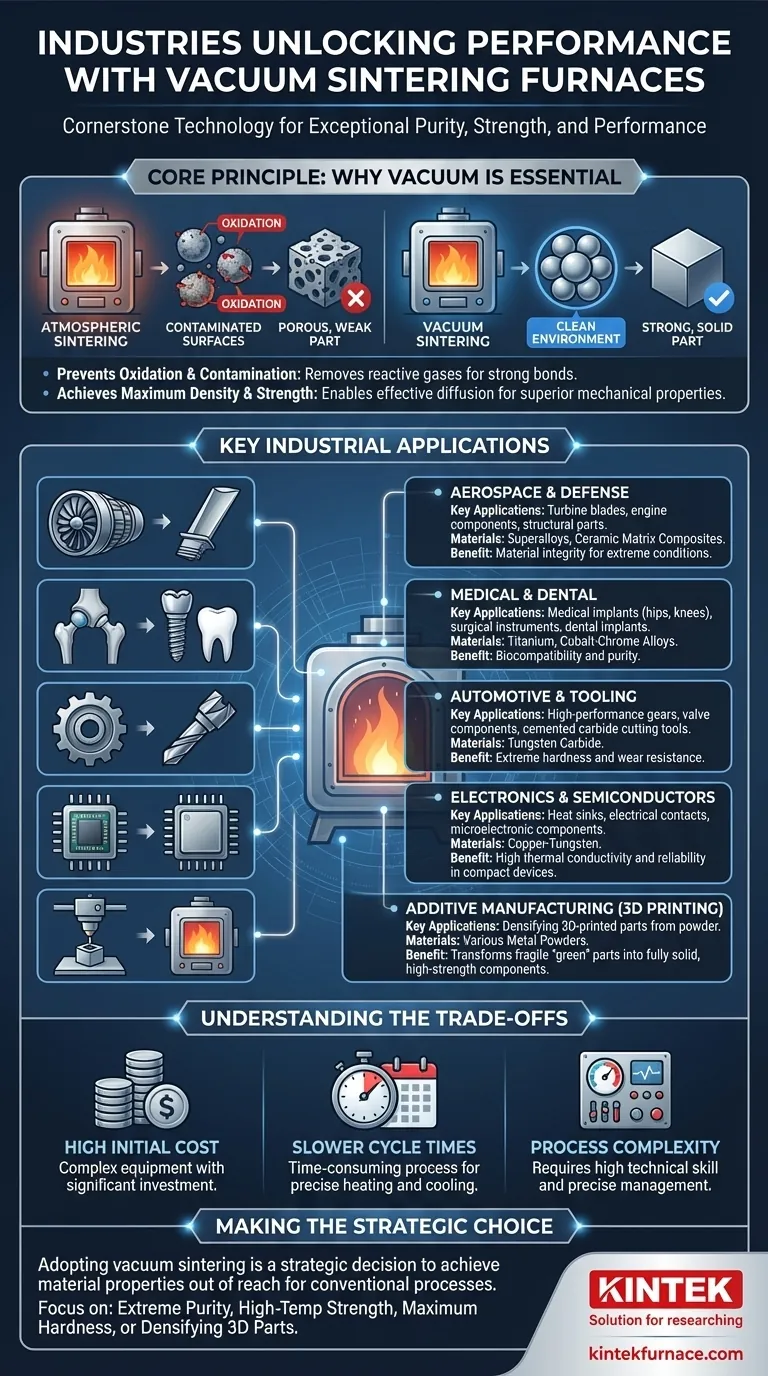
The Core Principle: Why Vacuum is Essential
Sintering is the process of bonding powdered material into a solid mass using heat below the material's melting point. Performing this inside a vacuum unlocks unique capabilities.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At the high temperatures required for sintering, most metals and many ceramics will rapidly react with oxygen and nitrogen in the air.
This reaction forms oxides and nitrides on the surface of the powder particles. These contaminant layers act as a barrier, preventing the particles from properly bonding, which results in a weak and porous final part.
A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases, creating a clean environment that allows for direct, strong metallurgical bonds to form between particles.
Achieving Maximum Density and Strength
By eliminating surface contamination, vacuum sintering allows for more effective diffusion and bonding between particles.
This leads to components with higher final density, often approaching 100% of the theoretical maximum. Higher density directly correlates to superior mechanical properties, including increased strength, hardness, and durability.
Enabling Advanced and Reactive Materials
Many high-performance materials are impossible to process in a normal atmosphere.
Materials like titanium, refractory metals (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum), and certain advanced ceramics are highly reactive. Vacuum sintering is not just an improvement for them; it is often the only viable manufacturing method.
Key Industrial Applications Breakdown
The need for pure, dense, and strong components drives the adoption of vacuum sintering across several high-tech fields.
Aerospace and Defense
This sector requires components that are both lightweight and can withstand extreme temperatures and stress.
Vacuum sintering is used to produce parts like high-pressure turbine blades, engine components, and other structural parts from superalloys or ceramic matrix composites. The process ensures the material integrity needed for mission-critical applications.
Medical and Dental
Purity and biocompatibility are non-negotiable for any material placed inside the human body.
Vacuum sintering is essential for manufacturing medical implants like artificial hips and knees, dental implants, and surgical instruments from materials such as titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys. The clean environment guarantees the final product is free from contaminants that could cause an adverse reaction.
Automotive and Tooling
The goal here is extreme hardness and wear resistance for parts that endure constant friction and stress.
The process is used to create high-performance gears, valve components, and especially cemented carbide (tungsten carbide) cutting tools. The near-perfect density achieved in a vacuum provides the exceptional hardness and longevity required for these applications.
Electronics and Semiconductors
In electronics, managing heat and electrical conductivity in smaller and smaller packages is a primary challenge.
Vacuum sintering is used to produce heat sinks, electrical contacts, and other microelectronic components from materials like copper-tungsten. The process ensures high thermal conductivity and reliability in compact, high-power devices.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing is a modern frontier for vacuum sintering. After a metal part is 3D printed layer-by-layer from powder, it often exists in a fragile "green" state.
The printed part is then placed in a vacuum sintering furnace to consolidate the powder, remove binder materials, and densify it into a fully solid, high-strength final component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum sintering is a specialized process with specific constraints that make it unsuitable for all applications.
High Initial Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines that are significantly more expensive to purchase, install, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces. This high capital investment means the process is typically reserved for high-value components.
Slower Cycle Times
Achieving a deep vacuum, precisely ramping up the temperature, holding it, and then cooling down in a controlled manner is a time-consuming process. These longer cycle times can limit throughput compared to simpler heat treatment methods.
Process Complexity
Operating a vacuum sintering furnace requires a high degree of technical skill. Operators must manage precise temperature profiles and vacuum levels to achieve consistent results, making the process more demanding than conventional manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use vacuum sintering hinges on whether the material properties you need are achievable through other means.
- If your primary focus is extreme purity and biocompatibility: Vacuum sintering is essential for manufacturing medical-grade titanium and cobalt-chrome parts.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength and performance: This process is the standard for producing aerospace superalloy and advanced ceramic components.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Vacuum sintering is critical for creating top-tier cemented carbide tools and high-stress automotive parts.
- If your primary focus is densifying complex 3D-printed metal parts: This is the key post-processing step to turn a printed object into a functional, high-strength component.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum sintering is a strategic decision to achieve material properties that are simply out of reach for conventional atmospheric processes.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Materials Used |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, engine components | Superalloys, ceramics |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments | Titanium, cobalt-chrome |
| Automotive | Gears, cutting tools | Cemented carbides |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, contacts | Copper-tungsten |
| Additive Manufacturing | Densifying 3D-printed parts | Various metal powders |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum sintering furnaces can help you achieve superior density, strength, and performance in your components!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement



















