Beyond the cooktop, induction technology is poised to become a cornerstone of next-generation manufacturing and energy systems. Its future applications are driven by its unique ability to deliver precise, rapid, and highly efficient heat to a vast range of conductive materials, including advanced composites and critical metals like titanium and silicon. This makes it a key enabling technology for creating engineered materials and components essential for the green energy transition and advanced industrial processes.
The true potential of induction lies not just in improving existing heating methods, but in unlocking entirely new manufacturing capabilities. Its future is defined by its capacity to apply controlled, clean energy precisely where it's needed, making previously difficult or impossible processes viable and efficient.

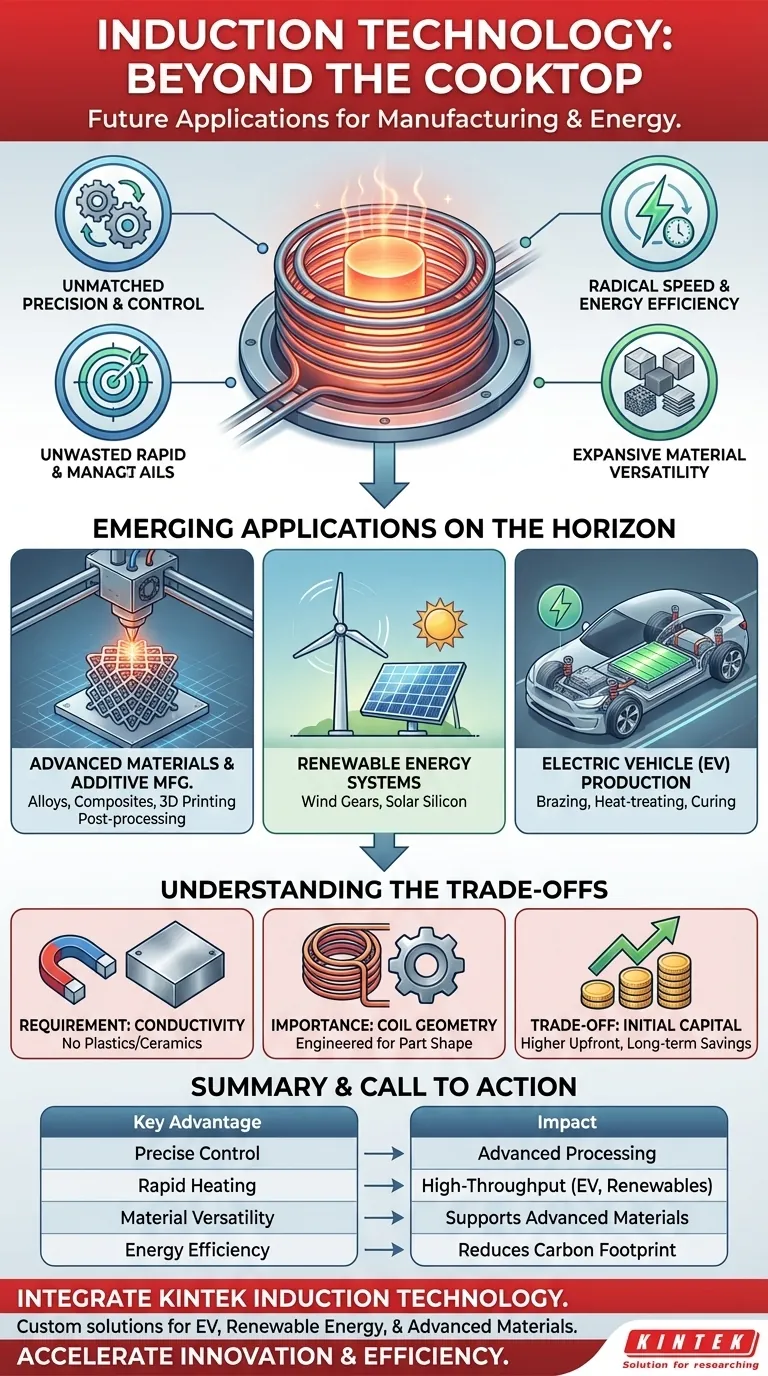
The Core Principles Driving Future Adoption
To understand where induction is going, we must first understand why it is so effective. The technology's promise isn't based on a single benefit, but on the powerful combination of three core characteristics.
Unmatched Precision and Control
Induction heating works by generating an electromagnetic field that induces an electrical current directly within the target material. This means the heat is generated inside the part itself, not applied from an external source.
This allows for an incredible level of control. You can heat a very specific area of a complex part to a precise temperature, leaving the surrounding material unaffected. This is critical for creating advanced components where material properties must be tightly managed.
Radical Speed and Energy Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly within the workpiece, the process is exceptionally fast and efficient. There is no need to heat up a large oven or wait for energy to transfer via convection or radiation.
This dramatically reduces cycle times and slashes energy consumption compared to traditional furnaces. In an era focused on sustainability and lean manufacturing, this efficiency is a powerful driver of adoption.
Expansive Material Versatility
Induction is not limited to just steel. It can process virtually any electrically conductive material.
This includes copper, aluminum, titanium, silicon, precious metals, and even advanced metal-matrix composites. This versatility means that as new materials are engineered for demanding applications, induction stands ready as a compatible and effective processing tool.
Emerging Applications on the Horizon
The unique advantages of induction are paving the way for its use in some of the most innovative sectors of the economy.
Advanced Materials and Additive Manufacturing
The creation of new alloys and composites often requires complex, multi-stage heating and cooling cycles. Induction's precise control makes it ideal for developing these next-generation materials.
In metal 3D printing (additive manufacturing), induction can be used to pre-heat substrates or post-process printed parts, relieving internal stresses and improving the final component's metallurgical quality.
Renewable Energy Systems
The transition to green energy relies on high-performance components, many of which are perfect candidates for induction processing.
This includes hardening the massive gears inside wind turbines for longevity and manufacturing high-purity silicon for more efficient solar panels. The speed and efficiency of induction reduce the embodied energy in these critical components.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Production
Automakers are increasingly turning to induction to build lighter, safer, and more efficient electric vehicles.
Its speed is ideal for the high-throughput world of automotive manufacturing. Applications include brazing connections for battery packs, heat-treating electric motor components for strength, and curing the adhesives used in lightweight aluminum or composite body structures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction technology is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to applying it correctly.
The Requirement of Conductivity
The most fundamental limitation is that induction only works on materials that conduct electricity. It cannot be used to directly heat plastics, ceramics, or other insulators unless a conductive susceptor is used as an intermediary.
The Importance of Coil Geometry
The induction coil, which creates the magnetic field, must be carefully designed and shaped for the specific part being heated. A coil designed for a flat plate will not work for a complex gear.
This means that new applications require upfront engineering investment to develop and optimize the coil and process parameters, making it less flexible than a simple oven for low-volume, high-mix production.
Initial Capital Investment
The initial cost of induction heating systems, including the power supply and custom coils, can be higher than that of conventional gas or resistance-based furnaces.
However, this initial investment is often quickly offset by significant long-term savings in energy consumption, reduced cycle times, and improved product quality.
Evaluating Induction for Your Application
To determine if induction is the right choice, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is process speed and throughput: Induction's rapid, targeted heating can dramatically shorten cycle times compared to batch processing in conventional ovens.
- If your primary focus is material integrity and quality: The precise control offered by induction minimizes heat-affected zones, reduces part distortion, and enables the creation of superior metallurgical properties.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and sustainability: Induction's direct heating method is fundamentally more efficient, leading to lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint for your manufacturing process.
By understanding its core principles, you can identify where induction heating moves from a simple process improvement to a truly enabling technology for your most ambitious projects.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Impact on Future Applications |
|---|---|
| Precise Control | Enables advanced material processing and complex component manufacturing. |
| Rapid Heating | Drives high-throughput production in EV and renewable energy sectors. |
| Material Versatility | Supports processing of advanced composites, silicon, and critical metals. |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces carbon footprint in green energy and industrial applications. |
Ready to integrate induction technology into your next-generation projects?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and advanced industries with high-performance induction heating solutions. Our product line, including custom induction systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique material processing requirements—whether for EV components, renewable energy systems, or advanced material development.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored induction solutions can accelerate your innovation and enhance your manufacturing efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- What role does Vacuum Hot Press technology play in the automotive industry? Boost EV Batteries, Safety, and Efficiency



















