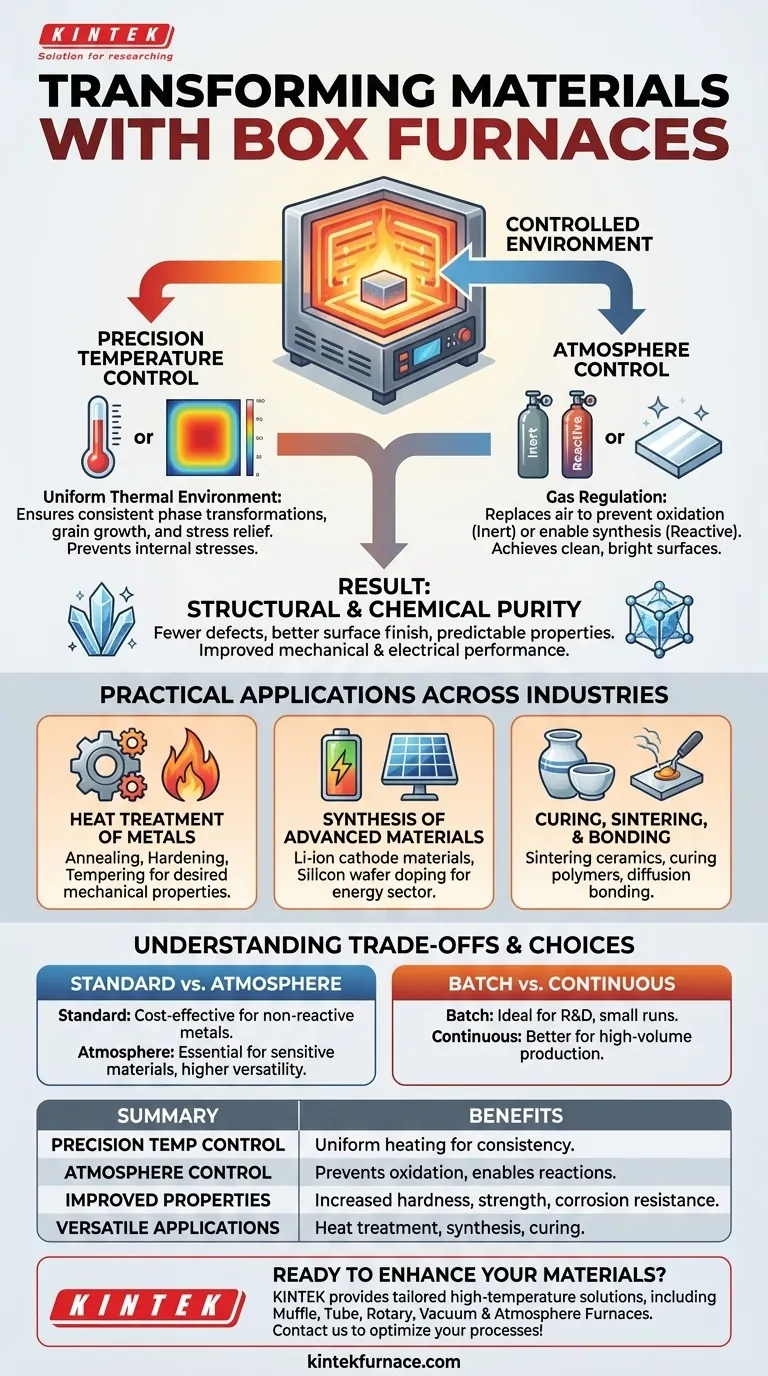
At their core, box furnaces provide the controlled environment necessary to fundamentally alter and improve a material's properties. By precisely managing heat, they enable processes that increase hardness, enhance strength, and improve corrosion resistance. The most advanced models also control the atmospheric chemistry, preventing oxidation and enabling the synthesis of new, high-performance materials.
The primary benefit of a box furnace is not merely heating, but achieving precise environmental control. This control over temperature and atmosphere is what allows you to dictate the final chemical and structural properties of your material with high repeatability.
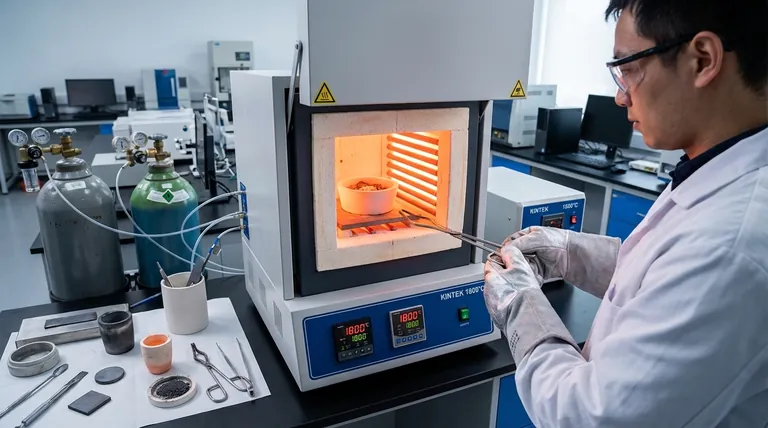

How Box Furnaces Achieve Material Transformation
A box furnace's value comes from its ability to create a highly stable and uniform processing environment. This control is exerted through two primary mechanisms: temperature and atmosphere.
The Foundation: Precision Temperature Control
All heat treatment relies on accurate temperature. A box furnace excels at providing a uniform thermal environment, ensuring the entire part or material batch experiences the same temperature profile.
This uniformity is critical for consistent phase transformations, grain growth, and stress relief. Inconsistent heating leads to internal stresses and variable properties, which a quality box furnace is designed to prevent.
The Differentiator: Atmosphere Control
Many material processes are highly sensitive to the surrounding air, especially oxygen. Atmosphere box furnaces add a layer of control by allowing you to replace the air with a specific gas.
Using inert gases like argon or nitrogen prevents oxidation, resulting in a clean, bright surface finish and preserving the material's integrity. Using reactive gases (e.g., hydrogen for a reducing atmosphere) can actively participate in chemical reactions, which is essential for synthesizing specific compounds or surface treatments.
Result: Structural and Chemical Purity
The combination of uniform heat and a controlled atmosphere minimizes the formation of unwanted phases, such as oxides or carbides. This results in a material with fewer defects, a better surface finish, and a more predictable chemical structure, directly leading to improved mechanical and electrical performance.
Practical Applications Across Industries
The ability to precisely tailor material properties makes box furnaces indispensable in both traditional and advanced manufacturing.
Heat Treatment of Metals
This is the classic application. Processes like annealing (softening), hardening (strengthening), and tempering (improving toughness) all rely on the precise temperature cycles that a box furnace provides to achieve desired mechanical properties.
Synthesis of Advanced Materials
Box furnaces are critical tools in research and development for creating new materials. In the new energy sector, they are used for the high-temperature synthesis of lithium-ion battery cathode materials and for the doping and annealing of silicon wafers to improve solar cell efficiency.
Curing, Sintering, and Bonding
Beyond metals, box furnaces are used to sinter ceramics, cure coatings and polymers, and perform diffusion bonding. In each case, the uniform temperature and controlled atmosphere ensure a consistent and reliable outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a box furnace is a specific tool with its own set of considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Standard vs. Atmosphere Furnaces
A simple furnace that heats in ambient air is significantly less expensive and complex than one with atmosphere control. However, it cannot be used for materials that are sensitive to oxidation. The added cost of an atmosphere furnace buys you process versatility and higher-quality results for reactive materials.
Batch Processing Limitations
By design, a box furnace is a batch-processing tool. You load a batch, run the cycle, cool it down, and unload it. This is ideal for R&D, one-off jobs, or small production runs, but it can be a bottleneck for high-volume manufacturing, where continuous conveyor furnaces are more efficient.
The Importance of the "Recipe"
The furnace only provides the environment; it does not guarantee results. The final material properties are dictated by the process parameters—the temperature ramps, soak times, and gas composition. A sophisticated furnace cannot save a flawed process recipe.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment of non-reactive metals: A standard box furnace with precise temperature control is a cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials or synthesis: An atmosphere-controlled box furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and enable specific chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A box furnace is best suited for process development, while a conveyor or continuous furnace should be evaluated for the production line.
Ultimately, a box furnace is a tool that empowers you to precisely engineer the final properties of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control | Ensures uniform heating for consistent phase transformations and stress relief. |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation and enables chemical reactions with inert or reactive gases. |
| Improved Material Properties | Increases hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance while reducing defects. |
| Versatile Applications | Used in heat treatment, material synthesis, and curing across various industries. |
Ready to enhance your material properties with advanced box furnaces? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental needs are met precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment process of chalcopyrite ore?
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?



















