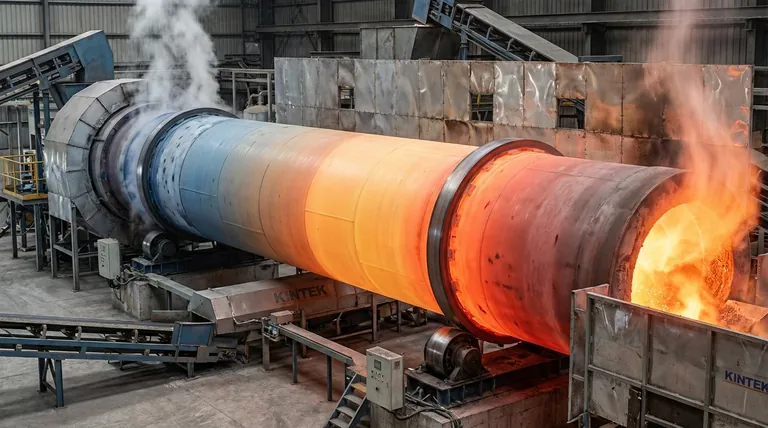
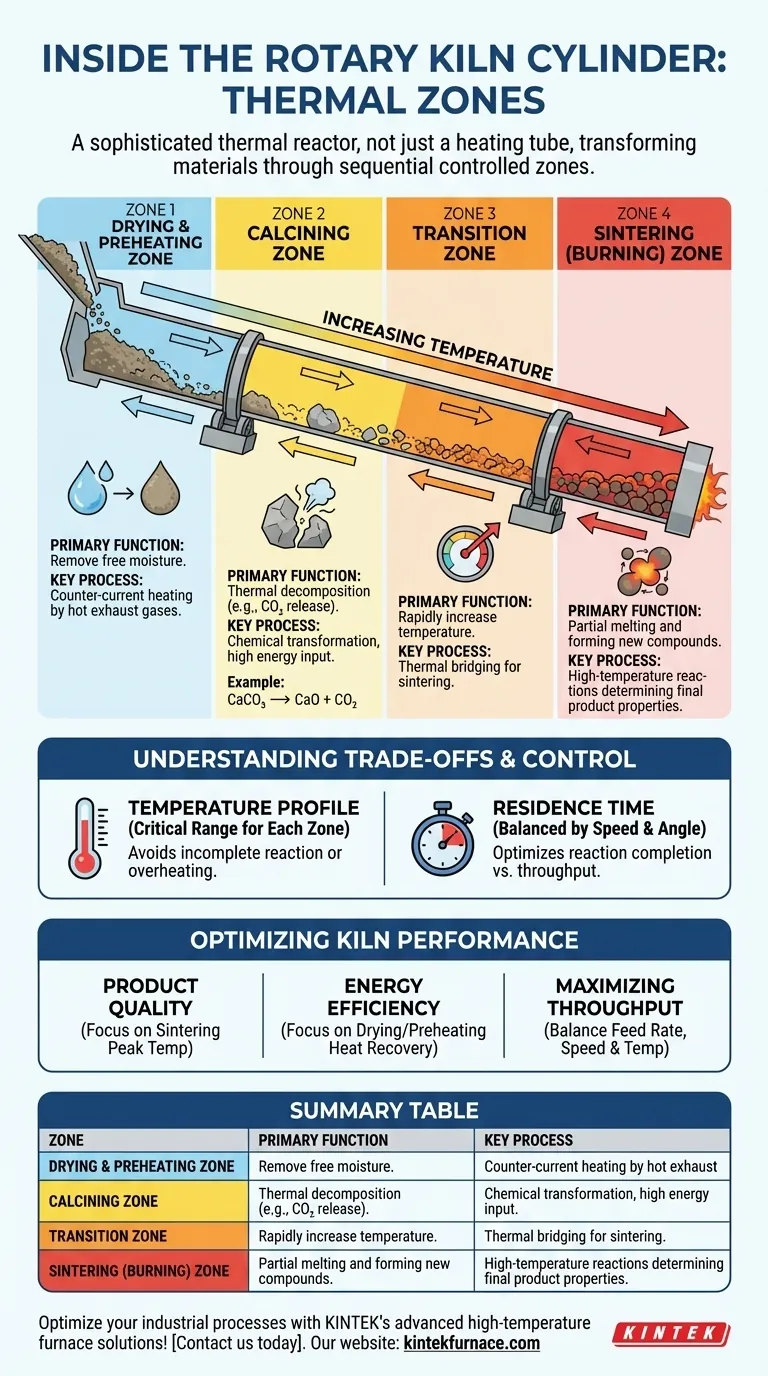
At its core, a rotary kiln is engineered with distinct thermal sections to systematically transform raw materials. The primary zones, arranged sequentially along the length of the cylinder, are the drying and preheating zone, the calcining zone, the transition zone, and the sintering (or burning) zone. Each stage performs a specific physical or chemical task required to create the final product.
A rotary kiln is not simply a hot, rotating tube. It is a sophisticated thermal reactor where materials travel through a series of carefully controlled temperature zones, each designed to induce a specific and necessary change. Understanding this sequence is the key to controlling the entire process.

The Journey Through the Kiln: A Zone-by-Zone Analysis
As material enters the elevated end of the inclined kiln, it begins a slow journey, tumbling toward the heat source at the lower end. This journey is a carefully orchestrated process divided into distinct functional zones.
Zone 1: The Drying and Preheating Zone
This is the first section the raw material encounters. Its primary purpose is to remove any free moisture from the feed.
As the material tumbles forward, it is heated by the hot exhaust gases traveling in the opposite direction from the burning zone. This counter-current flow efficiently raises the material's temperature, preparing it for the chemical reactions to come.
Zone 2: The Calcining Zone
Once preheated, the material enters the calcining zone, where the first major chemical transformation occurs. The term calcination refers to thermally decomposing a material, often by driving off a component like carbon dioxide (CO₂).
For example, in cement production, this is where limestone (CaCO₃) is converted into lime (CaO) by releasing CO₂. This is an energy-intensive step that requires a significant and sustained heat input.
Zone 3: The Transition Zone
The transition zone acts as a thermal bridge. While some minor reactions may continue, its main function is to rapidly increase the material's temperature from calcination levels to the much higher temperatures required for sintering.
Proper control of this zone is critical to ensure the material is sufficiently prepared for the final, high-temperature phase without being overheated prematurely.
Zone 4: The Sintering Zone
Also known as the burning zone, this is the hottest part of the kiln. Here, the material reaches its peak temperature, causing it to partially melt and form new mineral compounds through a process called sintering or clinkering.
The final properties of the product, such as strength in cement clinker, are determined by the chemical reactions that occur in this zone. The material then exits the kiln into a cooler to solidify its newly formed structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Control
Simply knowing the zones is not enough; operational success depends on managing the interplay between them. The kiln is a dynamic system where a change in one zone impacts all the others.
The Critical Role of Temperature Profile
Each zone has an ideal temperature range that must be maintained. Kilns are equipped with separately settable temperature controls to manage the heat input along its length.
An incorrect temperature profile can lead to an incomplete reaction, wasted energy, or a damaged final product. For instance, insufficient heat in the calcining zone results in an incomplete conversion, while excessive heat in the sintering zone can create a non-reactive, overly-fused material.
Balancing Residence Time
Residence time—the amount of time material spends inside the kiln—is just as important as temperature. It is controlled by the kiln's rotational speed and its angle of inclination.
Slowing the rotation increases residence time, allowing reactions more time to complete, but it also reduces throughput. Finding the optimal balance between temperature and residence time is a core challenge in kiln operation.
Optimizing Kiln Performance for Your Goal
Your operational strategy will depend on whether your priority is quality, efficiency, or throughput. Understanding the function of each zone allows you to make targeted adjustments.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Ensure a stable and correct temperature profile, paying closest attention to the peak temperatures in the sintering zone.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Optimize the drying and preheating zone to maximize heat recovery from the exhaust gas, ensuring material enters the calcining zone as hot as possible.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: Carefully balance increases in feed rate with adjustments to rotational speed and temperature to ensure complete calcination without overloading the system.
Mastering the rotary kiln process begins with viewing it as a sequence of interconnected thermal stages, not a single heating chamber.
Summary Table:
| Zone | Primary Function | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Drying and Preheating | Remove moisture and preheat material | Counter-current heating |
| Calcining | Thermally decompose materials (e.g., CO₂ release) | Chemical transformation |
| Transition | Rapidly increase temperature for sintering | Thermal bridging |
| Sintering | Form new compounds through partial melting | High-temperature reactions |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored rotary kilns and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems



















