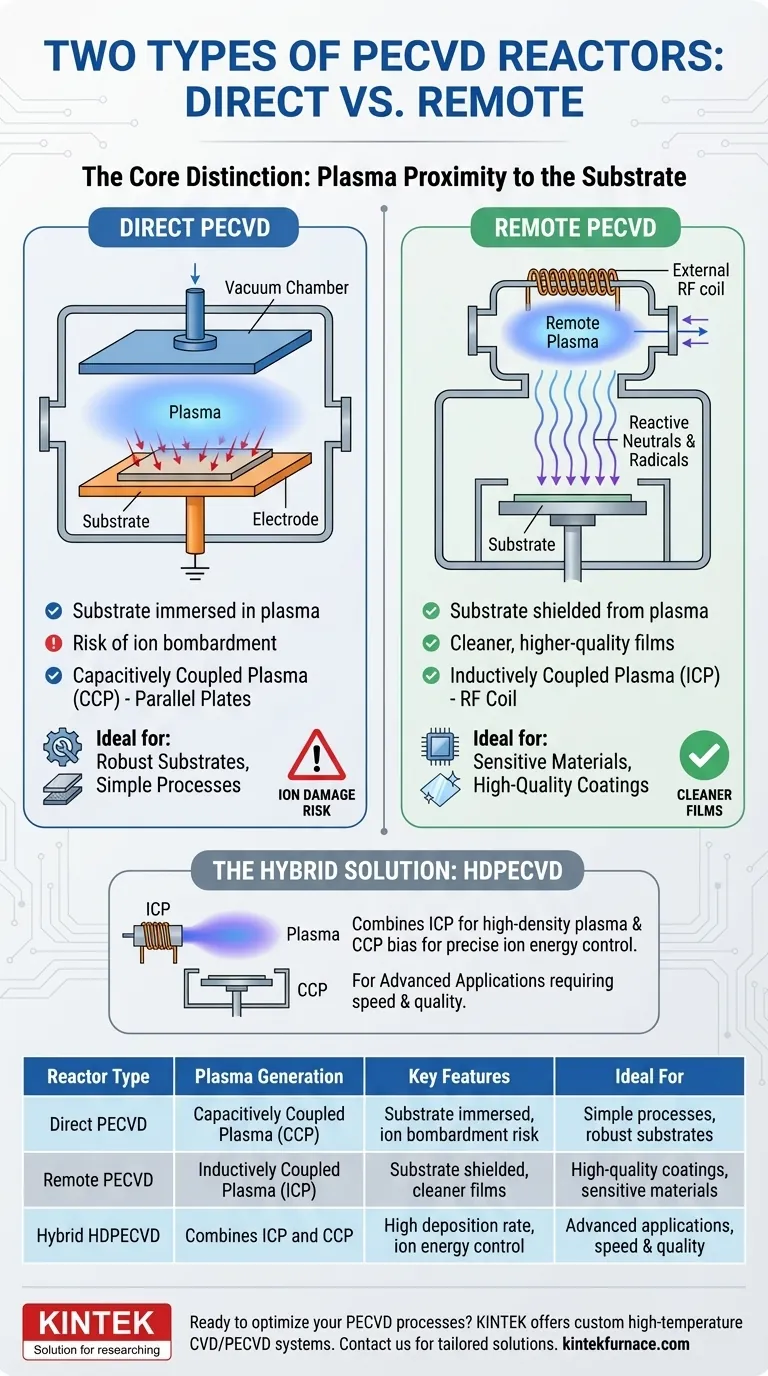
In plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), the two primary reactor configurations are direct and remote. The essential difference lies in the placement of the substrate relative to the plasma source. In a direct system, the substrate is immersed directly within the plasma, whereas in a remote system, the plasma is generated separately and only the reactive chemical species flow over the substrate.
The choice between direct and remote PECVD is a fundamental trade-off between process simplicity and final film quality. Direct reactors risk substrate damage from ion bombardment, while remote reactors protect the substrate to produce cleaner, higher-quality coatings.
The Core Distinction: Plasma Proximity
The most critical factor distinguishing these two reactor types is whether the substrate is in direct contact with the high-energy plasma environment.
Direct PECVD: Substrate Inside the Plasma
In a direct PECVD system, the substrate is placed on one of the electrodes used to generate the plasma itself. This configuration is often a capacitively coupled plasma (CCP) setup.
The substrate is an active part of the electrical circuit. This direct exposure means it is subject to bombardment by high-energy ions from the plasma.
Remote PECVD: Substrate Shielded from Plasma
In a remote PECVD system, the plasma is intentionally generated in a separate chamber or an area away from the substrate. This is often achieved using inductively coupled plasma (ICP).
The high-density plasma is created upstream, and only the desired reactive neutrals and radicals are transported to the substrate. This significantly reduces or eliminates damage from direct ion bombardment.
How Each Reactor Generates Plasma
The method of plasma generation is intrinsically linked to whether the reactor is direct or remote.
Capacitively Coupled Plasma (CCP) in Direct Reactors
Direct PECVD typically uses a parallel-plate design where the substrate rests on the powered or grounded electrode. An RF (radio frequency) signal is applied across the plates, igniting a plasma in the gas between them.
This design is relatively simple and effective but inherently exposes the substrate to the full plasma environment.
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) in Remote Reactors
Remote PECVD often uses an RF-powered coil wrapped around a dielectric tube. The oscillating magnetic field from the coil induces an electric current in the gas, creating a very dense plasma.
Because this happens away from the substrate, it allows for a high concentration of reactive species to be created without the damaging ions reaching the wafer surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reactor type involves balancing film quality requirements against process complexity and potential side effects.
Risk of Substrate Damage
The primary drawback of direct PECVD is the potential for ion bombardment. This can damage sensitive substrates, create defects in the crystal lattice, and alter the electronic properties of the material being coated.
Film Quality and Purity
Remote PECVD excels at producing cleaner, higher-quality films. By shielding the substrate from the plasma, it minimizes the incorporation of unwanted ions and reduces defect density, which is critical for high-performance optical and electronic devices.
The Hybrid Solution: HDPECVD
Modern systems often use a hybrid approach called High-Density PECVD (HDPECVD). This method combines the benefits of both configurations.
It uses an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source to generate a dense, remote plasma while simultaneously applying a separate capacitively coupled (CCP) bias to the substrate holder. This allows for a high deposition rate while giving engineers independent control over the ion energy bombarding the surface.
Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Application
Your specific goal determines the ideal reactor configuration.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and depositing on robust substrates: A direct, capacitively coupled reactor is often the most straightforward and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, damage-free films on sensitive materials: A remote, inductively coupled reactor is necessary to protect the substrate from direct ion bombardment.
- If your primary focus is achieving high deposition rates with precise control over film properties: A hybrid HDPECVD system offers the most advanced capabilities by combining the benefits of both methods.
Understanding this core distinction between direct and remote plasma generation empowers you to select the precise deposition strategy for your material and device goals.

Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Plasma Generation | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct PECVD | Capacitively Coupled Plasma (CCP) | Substrate immersed in plasma, risk of ion bombardment | Simple processes, robust substrates |
| Remote PECVD | Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) | Substrate shielded from plasma, cleaner films | High-quality coatings, sensitive materials |
| Hybrid HDPECVD | Combines ICP and CCP | High deposition rate, precise ion energy control | Advanced applications requiring both speed and quality |
Ready to optimize your PECVD processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems with deep customization. Whether you need direct, remote, or hybrid reactors for sensitive materials or high-throughput applications, our expert R&D and in-house manufacturing ensure tailored solutions. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and elevate your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition



















