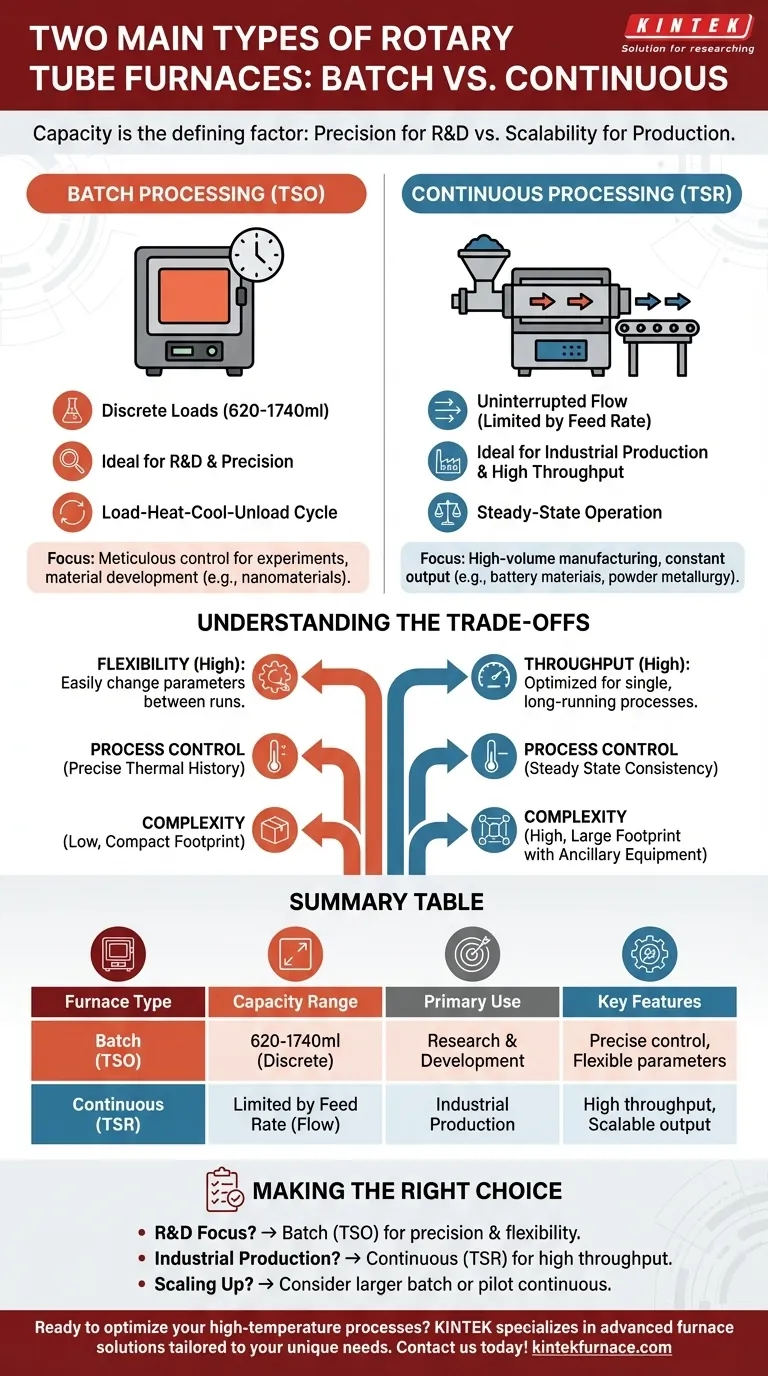
When selecting a rotary tube furnace, capacity is the defining factor that splits them into two primary categories: batch processing furnaces (TSO) and continuous processing furnaces (TSR). Batch furnaces are designed to process a single, discrete load of material at a time, with typical capacities from 620 to 1740 ml. In contrast, continuous furnaces are built for uninterrupted, high-volume production, where material is constantly fed in and processed, with capacity limited only by the feed rate and hopper size.
The choice between a batch and continuous furnace is a strategic decision between the precision required for research and development (batch) versus the high-throughput efficiency needed for industrial production (continuous).

The Two Fundamental Operating Models
The core difference between these furnace types lies not just in their size, but in their fundamental method of operation. This distinction dictates which applications each is best suited for.
Batch Processing Furnaces (TSO): Precision for a Defined Volume
A batch processing furnace operates on a load-heat-cool-unload cycle. A specific, measured quantity of material is loaded into the furnace tube, which is then sealed and processed under controlled conditions.
These furnaces are the standard for laboratory and research settings. Their defined volume allows for meticulous control over experiments, making them ideal for developing new materials or studying reaction mechanisms.
Common applications include the synthesis of advanced materials like nanomaterials, high-temperature material studies, and the sintering of small, precise quantities of metal powders.
Continuous Processing Furnaces (TSR): Scalability for Production
A continuous processing furnace is designed for a constant, flowing stream of material. A feed hopper steadily supplies material into one end of the rotating tube, the material is processed as it travels along the length of the tube, and the finished product is discharged at the opposite end.
This model is built for industrial-scale manufacturing where high throughput is the primary goal. The capacity is not defined by a single batch size but by the rate of processing (e.g., kilograms per hour).
They are critical in industries like battery material manufacturing (for positive and negative electrodes), powder metallurgy, and the production of specialized chemical compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding the inherent trade-offs between flexibility, throughput, and system complexity. Your process goals will directly determine which model is the correct tool for the job.
Flexibility vs. Throughput
Batch furnaces offer maximum flexibility. You can easily change process parameters, atmospheres, and even materials between each run, making them perfect for experimentation.
Continuous furnaces prioritize throughput. They are optimized to run a single, established process for extended periods to achieve maximum output and efficiency. Changing the process is a more involved undertaking.
Process Control and Uniformity
Both furnace types provide excellent temperature uniformity due to the constant tumbling of material. However, the nature of control differs.
In a batch furnace, you have absolute control over the thermal history of one specific sample. In a continuous furnace, control is focused on maintaining a steady state by balancing feed rate, rotation speed, and temperature profile to ensure consistency across the entire output.
System Complexity and Footprint
Batch systems are generally simpler, more compact, and require less ancillary equipment. They are a self-contained unit for processing a single load.
Continuous systems are inherently more complex. They require integrated hoppers, precision feeders, and material collection systems, resulting in a significantly larger operational footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace type is a critical decision that impacts everything from research outcomes to production efficiency.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A batch processing (TSO) furnace provides the precision and flexibility needed to test new materials and processes on a manageable scale.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: A continuous processing (TSR) furnace is designed for the high throughput and consistent output required for efficient manufacturing.
- If your goal is scaling up from the lab to pilot production: Consider a larger batch furnace or a small-scale continuous furnace to validate your process before committing to full industrial capacity.
Understanding this fundamental difference in operating philosophy is the key to aligning your equipment with your ultimate objective.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Capacity Range | Primary Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Processing (TSO) | 620 to 1740 ml | Research & Development | Discrete loads, precise control, flexible parameters |
| Continuous Processing (TSR) | Limited by feed rate | Industrial Production | High throughput, steady-state operation, scalable output |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Whether you're in R&D requiring precision batch furnaces or industrial production needing high-throughput continuous systems, our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your exact experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory efficiency and productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















