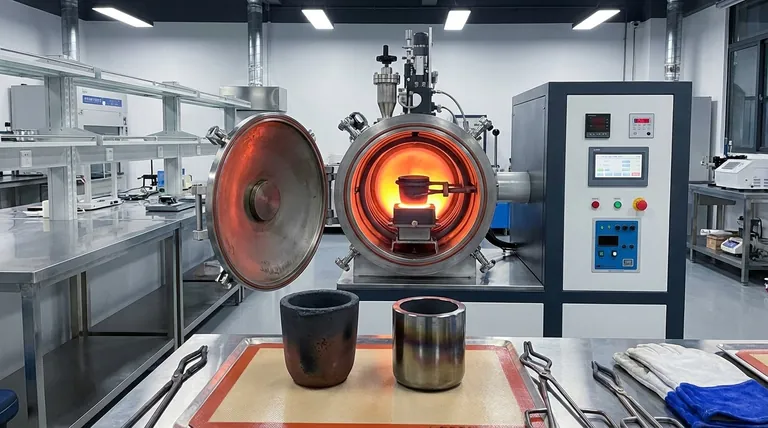
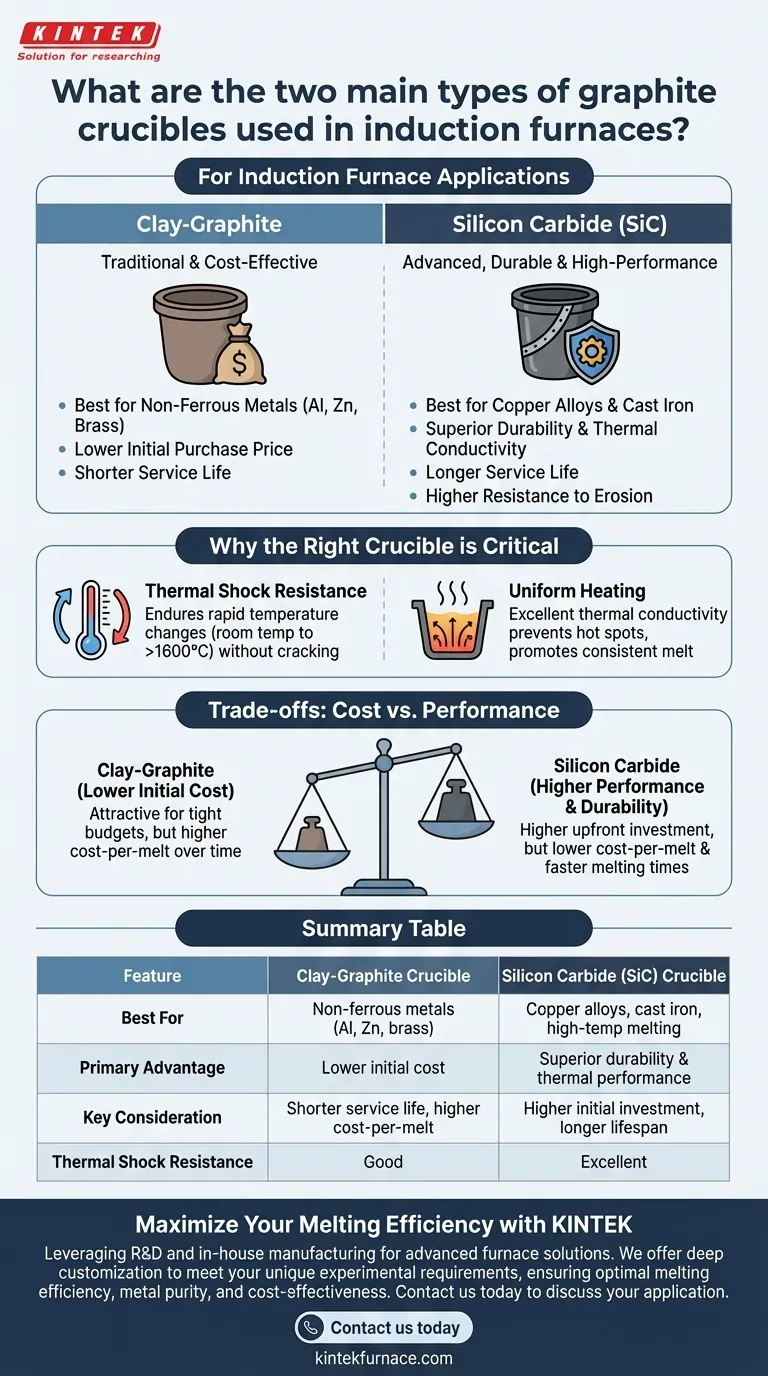
For induction furnace applications, the two principal types of graphite crucibles are clay-graphite and silicon carbide-graphite. Clay-graphite crucibles are a traditional, cost-effective choice made by binding graphite flakes with clay, while silicon carbide-graphite crucibles are a more advanced composite material known for superior durability and performance at high temperatures. The selection between them hinges on the specific metal being melted, the required operating temperature, and the desired service life.
Your choice of crucible is not just a material selection; it is a critical operational decision that directly impacts melting efficiency, metal purity, and overall cost per melt. Understanding the fundamental trade-off between the initial cost of a clay-graphite crucible and the long-term performance of a silicon carbide one is key.

Why the Right Crucible is Critical
An induction furnace crucible is more than just a container. It must withstand extreme thermal shock, resist chemical erosion from molten metal, and efficiently conduct heat to ensure a uniform melt.
The Role of Thermal Shock Resistance
The crucible is subjected to rapid and extreme temperature changes. A material with high thermal shock resistance can endure this cycling from room temperature to over 1600°C (2900°F) and back without cracking, ensuring operational safety and longevity.
The Importance of Uniform Heating
Graphite-based materials possess excellent thermal conductivity. This property ensures that the heat generated by the induction field is distributed evenly throughout the metal charge, preventing hot spots and promoting a consistent, high-quality melt.
A Detailed Look at the Two Primary Types
While both types use graphite for its thermal properties, their composition dictates their ideal use cases.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
These are the traditional standard, formed by mixing natural flake graphite with binders like clay and silica, then firing them to create a ceramic bond.
They are best suited for melting non-ferrous metals at lower temperatures, such as aluminum, brass, and zinc alloys. Their primary advantage is a lower initial purchase price.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
These advanced crucibles are made from a composite of silicon carbide and graphite. The manufacturing process creates an exceptionally dense and durable material.
SiC crucibles offer superior strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and higher resistance to erosion. This makes them suitable for a wider range of metals, including copper alloys and cast iron, and ensures a significantly longer service life than their clay-graphite counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
Choosing a crucible requires balancing the upfront investment against long-term operational value.
The Cost Factor
Clay-graphite crucibles have a lower initial cost, making them an attractive option for operations with tight budgets or infrequent melting schedules. However, their shorter lifespan can lead to a higher cost-per-melt over time.
The Performance and Durability Factor
Silicon carbide crucibles command a higher price but deliver a much longer service life, often lasting many times more cycles than clay-graphite models under similar conditions. Their superior thermal efficiency can also lead to faster melting times and lower energy consumption.
The Material Compatibility Factor
The chemical nature of the alloy being melted is paramount. Highly reactive metals can leach elements from the crucible, leading to contamination. The robust, dense structure of a SiC crucible generally offers better resistance to this chemical attack than a standard clay-graphite version.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by your specific operational goals and constraints.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals at lower temperatures on a limited budget: A clay-graphite crucible is often the most cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature melting, maximizing furnace uptime, or achieving the lowest cost-per-melt: A silicon carbide crucible's durability and performance will provide a better return on investment.
Ultimately, selecting the correct crucible is a strategic choice that enhances the efficiency, safety, and quality of your melting operations.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Clay-Graphite Crucible | Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Non-ferrous metals (Al, Zn, brass) | Copper alloys, cast iron, high-temp melting |
| Primary Advantage | Lower initial cost | Superior durability & thermal performance |
| Key Consideration | Shorter service life, higher cost-per-melt | Higher initial investment, longer lifespan |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good | Excellent |
Maximize Your Melting Efficiency with the Right Crucible
Choosing between a cost-effective clay-graphite crucible and a high-performance silicon carbide model is critical for your operation's productivity and bottom line. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions.
Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability. We can help you select or custom-engineer the perfect crucible solution to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring optimal melting efficiency, metal purity, and cost-effectiveness.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get expert advice on the ideal crucible for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















