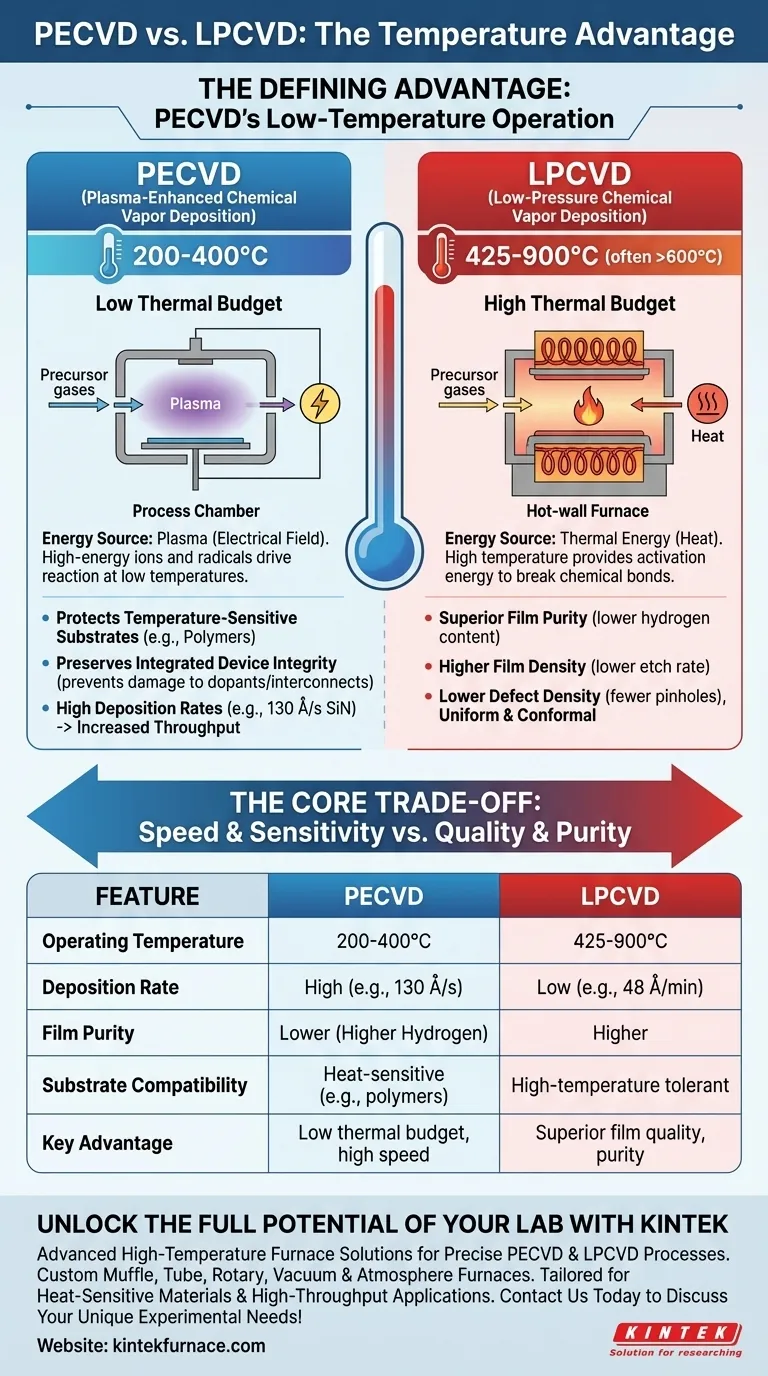
The defining advantage of Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) over Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) is its dramatically lower operating temperature. PECVD processes typically run between 200-400°C, whereas LPCVD requires significantly higher temperatures, generally in the range of 425-900°C. This fundamental difference makes PECVD essential for manufacturing modern electronic devices and working with heat-sensitive materials.
The choice between PECVD and LPCVD is not merely about temperature; it's a strategic decision based on a core trade-off. PECVD uses plasma to achieve high deposition rates at low temperatures, while LPCVD uses high thermal energy to produce films of superior purity and uniformity, albeit more slowly.

The Source of the Temperature Difference
To understand the advantages of PECVD's lower temperature, we must first understand why the two methods operate so differently. The key lies in how each process supplies the energy needed for the chemical reaction.
The Role of Thermal Energy in LPCVD
LPCVD relies exclusively on thermal energy to drive deposition. Precursor gases are introduced into a hot-wall furnace, and the high temperature provides the activation energy required to break chemical bonds and initiate the reaction that forms a thin film on the substrate.
This reliance on heat is why LPCVD requires temperatures often exceeding 600°C. The entire system, including the substrate, must be heated to this level to make the chemistry work.
The Role of Plasma in PECVD
PECVD bypasses the need for high thermal energy by using plasma. An electrical field is applied to the precursor gases, stripping electrons and creating a highly reactive environment of ions and radicals.
These energized particles have more than enough energy to react and deposit onto a substrate without requiring the substrate itself to be extremely hot. This allows the deposition to occur at a fraction of the temperature needed for LPCVD.
Strategic Advantages of a Low Thermal Budget
The ability to deposit films at low temperatures is not just a minor improvement; it is a critical enabler for many advanced applications. This "low thermal budget" provides several key advantages.
Protecting Temperature-Sensitive Substrates
The most obvious benefit is the ability to coat materials that would degrade, melt, or be destroyed at LPCVD temperatures. This makes PECVD the only viable choice for depositing films on substrates like polymers or certain metals.
Preserving Integrated Device Integrity
In modern semiconductor manufacturing, wafers undergo many processing steps. By the time a deposition is needed, the device may already have sensitive, precisely engineered components.
Exposing these partially fabricated devices to the high temperatures of LPCVD could ruin them by, for example, altering dopant profiles or damaging metallic interconnects. PECVD's low temperature preserves the integrity of previously fabricated structures on the wafer.
Increasing Throughput and Deposition Rate
Because PECVD uses plasma to drive the reaction, it can achieve much higher deposition rates than thermally-driven LPCVD. This dramatically increases manufacturing throughput.
For example, PECVD can deposit silicon nitride at rates of 130 Å/second at 400°C, while a high-temperature LPCVD process at 800°C might only achieve 48 Å/minute.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature vs. Film Quality
The lower temperature and higher speed of PECVD come at a cost, typically related to the quality of the deposited film. It is crucial to understand these trade-offs to make an informed decision.
Film Purity and Hydrogen Content
The plasma process in PECVD often results in a higher concentration of hydrogen being incorporated into the film. This can affect the film's electrical properties, density, and stability over time. LPCVD films, by contrast, are generally purer due to the high-temperature process driving off such impurities.
Film Density and Etch Rate
PECVD films tend to be less dense than their LPCVD counterparts. This lower density results in a higher etch rate, meaning the film is removed more quickly by chemical etchants. While sometimes desirable, it can be a significant drawback if the film is intended to be a robust, protective barrier.
Pinholes and Film Defects
Especially for thinner layers (under ~4000 Å), PECVD films are more prone to containing pinholes and other defects. The high-temperature, slower-growth environment of LPCVD generally produces a more uniform, conformal, and defect-free film, which is critical for demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between PECVD and LPCVD depends entirely on the priorities of your specific project. By weighing the benefits of low temperature against the need for high film quality, you can select the optimal method.
- If your primary focus is processing speed or temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is the clear choice, enabling high throughput and the ability to coat materials that cannot withstand high heat.
- If your primary focus is ultimate film quality, purity, and conformality: LPCVD is often the superior option, provided your substrate can tolerate the high thermal budget.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off between plasma-driven speed and thermally-driven quality is the key to selecting the right deposition process for your goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PECVD | LPCVD |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | 200-400°C | 425-900°C |
| Deposition Rate | High (e.g., 130 Å/s) | Low (e.g., 48 Å/min) |
| Film Purity | Lower (higher hydrogen) | Higher |
| Substrate Compatibility | Heat-sensitive (e.g., polymers) | High-temperature tolerant |
| Key Advantage | Low thermal budget, high speed | Superior film quality, purity |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Whether you need precise PECVD or LPCVD processes, our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—backed by deep customization—deliver unmatched performance for heat-sensitive materials and high-throughput applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution to meet your unique experimental needs and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications
- What are the drawbacks of CVD compared to PECVD? Key Limitations for Your Lab
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency



















